CEO Glenn Britt tells investors the company successfully pushed through modem fee as hidden “price increase”; Warns programmers unfettered rate hikes will result in networks being dropped, Disses Google Fiber as publicity stunt, and suggests more broadband rate hikes are in our future.
 Time Warner Cable has announced its intention to broaden its consumption billing scheme offering $5 discounts to customers willing to keep their monthly usage under 5GB per month to every cable system it owns, with the exception of Oceanic Cable in Hawaii.
Time Warner Cable has announced its intention to broaden its consumption billing scheme offering $5 discounts to customers willing to keep their monthly usage under 5GB per month to every cable system it owns, with the exception of Oceanic Cable in Hawaii.
CEO Glenn Britt, speaking Monday to a UBS conference in New York, told investors that despite the fact the Internet Essentials program which caps monthly usage has attracted little interest from customers, the company was still going to take the program nationwide for symbolic reasons.
“At the moment what we have been trying to do is to get this idea into the marketplace,” Britt said. “It probably won’t surprise you that not very many people have taken the lower offer. That is fine. It hasn’t had much impact on [average revenue per customer]. But I think the idea is to have this consumption idea out there in addition to the unlimited.”
Britt’s attitude about consumption billing has evolved since its 2009 public relations disaster that forced the company to pull back on a plan to introduce consumption-based billing tiers for its Internet product. Protests erupted in test markets in New York, North Carolina, and Texas, several organized by Stop the Cap!, leading to proposed legislation to ban usage caps from one Rochester-area congressman and intervention from Sen. Charles Schumer (D-N.Y.) who helped convince Britt to shelve the plan.
“I actually don’t like the idea of caps,” Britt has said consistently. “That is a negative connotation.”
Britt’s views have evolved over the years to argue that an unlimited service tier should always be available from Time Warner Cable for customers who want it. But encouraging customers to use more broadband under some type of consumption pricing offers a new source for revenue for the company and its shareholders.
“What we think is we should always offer unlimited service but that we should offer a choice of a lower price with a consumption dimension for people who don’t need unlimited, so that’s quite different than what other [broadband providers] have talked about.”
Time Warner Cable is in the middle between operators advocating monetizing broadband usage with compulsory usage limits and overlimit fees and those, like Cablevision, that oppose usage limits of any kind. But Britt is intent on getting customers to begin thinking about associating usage with cost, and stop believing in the traditional “all-you-can-eat” unlimited broadband model that has been around since the 1990s.
Britt characterized the company’s increasing emphasis on broadband as part of an evolution of the cable industry beyond the video services that defined it for decades. With its video business increasingly pressured by increased programming costs the company can no longer pass entirely onto its customers, broadband and phone service now deliver more gross profit margin than its video package.
Time Warner Cable Broadband Has a 95% Gross Profit Margin?
“The gross margin on broadband has got to be the highest gross margin of any product offered by any industry in the United States — like 95%,” noted one Wall Street audience member that quizzed Britt about future threats Time Warner’s broadband business could face with a margin like that.
 “I think actually this gross margin thing is something that is a perception that maybe our company caused in our effort to be transparent,” Britt tried to explain.
“I think actually this gross margin thing is something that is a perception that maybe our company caused in our effort to be transparent,” Britt tried to explain.
Britt argued the 95% figure was misleading because the company’s accounting methods allocate all of their costs to the specific services the company offers.
“In the case of the video business because it’s all the programming costs, that’s a big number,” Britt explained, noting video profits are tempered by programming costs. “In the case of broadband it’s just the direct bandwidth costs from third parties. It’s a small number so it looks like the margin is really high.”
With a few accounting changes, the company’s gross profits could be split more evenly across the video, broadband, and telephone services. But Britt explained the expense of switching to cost accounting made it not worth the effort. But the exposure of the enormous profits and very low cost of delivering broadband service may have inadvertently created a political problem for the cable industry as consumer groups suggest the vast profits earned on broadband come at the same time the industry is hiking prices and in some cases limiting service.
Britt tried to temper enthusiasm.
“If you look at the complete picture — broadband is a great business but it is not quite as profitable as just that gross margin number might make you think,” Britt said.
The Gradual Evolution of Time Warner Cable Towards Broadband, With Rate Increases to Follow
Britt said the company continued to gradually switch off analog video channels to free up capacity for additional broadband bandwidth.
“I think if you look at our physical plants we still devote a disproportionate amount of capacity to analog video so we’re still running broadband on a relatively small part of the capacity, but as [demand] grows we will keep adding more to broadband and we’re gradually reclaiming the analog video channels,” Britt explained. “We have not seen the need to flash cut/get rid of the analog and go all-digital, but we’re doing it over time.”
Britt called cable broadband a growth industry, with new entrants getting online for the first time.
“Broadband is a great business. It is still not fully penetrated,” Britt said. “There are homes that don’t have broadband that aren’t even online yet. And the homes that have it keep using it more and more all the time. I think somewhere recently I saw a study that said the average use is now 50GB a month.”
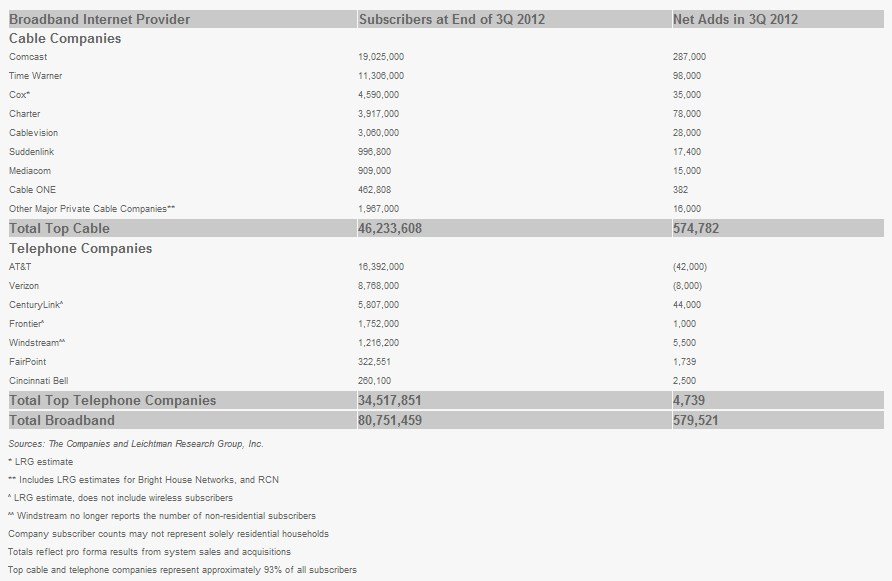
Cable operators continue to win the vast majority of new broadband customers, according to this chart from Leichtman Research Group, Inc.
With consumer demand for broadband at an all-time high, Britt said as usage and dependence on broadband continues to grow, the company will have more and more ability to raise prices. Britt noted the company implemented a modem rental fee in November he characterized as “essentially a price increase,” and called its implementation successful.
Britt acknowledged only about 3% of customers have elected to buy their own cable modems to date, and Britt said he believed most people will continue to rely on Time Warner’s rented modem, bringing lucrative new revenue to the company indefinitely.
The company’s gradual move to an all-IP network is an acknowledgment of the success of broadband, but also allows the company to become more nimble with its video offerings and services.
“We are talking about using IP standards and IP technology to enhance our video offering,” Britt said. “What we are trying to do is recognize that all consumer electronics are increasingly moving to IP standards. Writing software to IP standards allows you to create software that can be much more easily updated and iterated than traditional forms of software. We’re embracing that wholeheartedly.”
The company is currently testing a cloud-based program guide and set top box interface in 190,000 homes in upstate New York with positive results, according to Britt.
“We are going to have the second version of that next year and roll it our more broadly,” Britt said. “We have not been as noisy about that as some others. Again, the beauty of this is that it resides centrally, not on everyone’s set top box, and you can change the software little bits and pieces once a week or every two weeks. You don’t have to have these giant software releases.”
Other initiatives:
- Getting streaming video on every device capable of displaying it in a customer’s home;
- Introducing local broadcast station video on the company’s streaming product. “We now have the ability to encode 1,000 broadcast signals from around the country,” said Britt. “Here in New York City, the broadcasters are in the package now;”
- Will shortly introduce video-on-demand streaming through its device apps;
- Its Wi-Fi network in Los Angeles is on track to offer 10,000 hotspots. The company’s next expansion priority is more Wi-Fi for New York City.
Britt Downplays the Competition: ‘AT&T U-verse is bandwidth constrained, FiOS is mostly finished expanding, and Google Fiber is a publicity stunt.’
Britt recognized AT&T planned to restart expansion of its fiber to the neighborhood U-verse service, which actually competes with Time Warner Cable in more communities than Verizon’s FiOS fiber optic network.
 “U-verse overlaps about 25 percent of our footprint today,” Britt said. “Presumably it will add a little more when they’re done with this. I would remind you that U-verse is more bandwidth constrained than our plant. We have a route to faster speeds, so we’re confident with our ability to compete with that.”
“U-verse overlaps about 25 percent of our footprint today,” Britt said. “Presumably it will add a little more when they’re done with this. I would remind you that U-verse is more bandwidth constrained than our plant. We have a route to faster speeds, so we’re confident with our ability to compete with that.”
Britt said Time Warner Cable has gained experience predicting what happens when new competition arrives in town, and continued to downplay its impact on cable’s dominant market position.
“There is a phenomenon in consumer behavior that when a new competitor comes to town a certain number of people move just because they want to try the new thing,” Britt said. “After you are there for awhile that part ends and you are just into a normal marketing game. I think leaving aside the AT&T announcement, that is true generally of the two phone companies who have built what they said they would build initially.”
The one city where competition has turned into building-to-building combat is New York City, where Verizon FiOS continues to only gradually expand into new buildings. When FiOS becomes available, marketing begins to get customers to consider switching, kicking Time Warner’s customer retention efforts into high gear.
The cable operator has traditionally offered aggressive retention and new customer deals to attract and hold cable customers, and in some cases it has thrown in high value prepaid credit card rebate offers. Currently, Time Warner Cable pitches new and returning customers its triple play package for $89-99 in New York, often giving existing customers the same deal when they complain.
In Kansas City, Time Warner Cable now faces competition from both AT&T U-verse and Google Fiber, but Britt claims the company is not as worried as some might think.
“I guess I would remind everybody [Google] in the past announced they were doing things like this,” Britt said. “I think they were going to build Wi-Fi over San Francisco and they built a couple of blocks. Obviously I’m not inside their company — I can’t exactly know their motivation, but certainly if it is like the past, their motivation is to demonstrate what technology can do and try to prod the government and other players to go bigger, faster, whatever.”
Britt doubts Google will take the project much farther than Kansas City, and even if it does, the cable industry will have decades to prepare.
“I would remind you it took the cable industry which built the second wire into the home — the phone being the first — four decades or more to build across the country and many billions of dollars,” said Britt. “Even if Google builds, we’re not going to wake up and see Google instantly building out the whole country.”
Britt took a swipe at Google’s white-collar business focus and wondered exactly who needs the service Google has started to offer.
“This is not like their other businesses; it is very physical, it is blue collar workers, it is process, it is a very different thing,” Britt said. “I think what they’re doing is trying to demonstrate the wonders of 1Gbps. The problem with that is even if you build the last mile access plant to do that, there is neither the applications that require that nor a broader Internet backbone and servers delivering at that speed. It ends up being more about publicity and bragging. There has been a whole series of articles in the paper about ‘I’m a little startup business and boy it is really great I can get this’ and my reaction is we already have plant there that can deliver whatever it is they are talking about in those articles, which is usually not stuff that requires that high speed. So we’ll see.”
But Britt acknowledged the company will have a challenge competing with at least one Google Fiber service.
“They are giving one level of broadband away for free with an upfront installation,” Britt noted. “It’s hard to compete with free, although it is hard to make money at free also.”
The Cord-Cutting “Myth”: It’s the economy, stupid.
 Britt continued to downplay and dismiss the popular media meme that cord-cutting is taking a toll on cable television subscriptions. Britt argued with television sets left on in most homes an average of eight hours a day, and pay television services reaching 90 percent of those homes, parting with cable TV is not that easy for a product with that level of consumer acceptance.
Britt continued to downplay and dismiss the popular media meme that cord-cutting is taking a toll on cable television subscriptions. Britt argued with television sets left on in most homes an average of eight hours a day, and pay television services reaching 90 percent of those homes, parting with cable TV is not that easy for a product with that level of consumer acceptance.
“Is there some cord cutting typically among young people — maybe they were cable-nevers? Yes, but it appears to be fairly minor at the moment,” Britt said. “I think the bigger issue for the industry is a combination of price and the economy.”
“These packages keep getting more and more expensive. Programming gets more and more expensive,” Britt added. “I hope the economy gets better but at the moment there are still an awful lot of people who have been unemployed a long time and this stuff is starting to cost too much and I never miss the chance to get on my bully pulpit about it. If we, as a broader industry, want to keep this going, we need to figure out some way to have packages and prices that are lower for people who just cant afford it. That is a bigger factor right now than cord-cutting.”
Britt was lukewarm about his company’s own efforts to deliver a discounted cable television package which pares down the basic package to a few dozen channels with some notable gaps, especially for sports fans.
“We have a package called TV Essentials and whether it is the ideal configuration of programming and price — it is probably not — it is what we’re able to do,” Britt said. “It does have some uptake but not enormous. I think we need as an industry to work on that. We all know the big package works for the content companies and the little packages don’t. At some point this whole thing has to be responsive to the people who ultimately pay the bills and that is the consumer.”
Throwing Down the Gauntlet: ‘We’re going to start dropping little-watched channels at contract renewal time if prices don’t come down.’
“I think the trend has been pretty constant over the last several years: Since 2008, our programming costs per customer have gone up about 30 percent while the Consumer Price Index is up about 10%, so clearly those two things are out of whack,” Britt said. “Our video pricing has gone up about 15% so we are able to close that gap a little bit but not completely. I don’t have any magic bullet about this except clearly these trends can’t continue forever.”
Britt warned programmers have become too comfortable with the status quo for cable packages and pricing that some have gotten lazy about the quality of their programming, dependent on the subscriber fees they earn whether customers watch their channels or not.
 “Content companies will all gloat and chortle about how wonderful the structure is and they can charge whatever they want,” Britt complained. “We’ve accumulated networks that hardly anybody watches. If you speak to the people who run those networks or own them they almost feel it’s a birthright — I have this network that has distribution to 70-80 million homes, and I’m getting paid every month for ads — maybe this year I wasn’t able to get a big audience but you know next year I am going to work harder and I am going to spend more money on programming and it’s going to be good.”
“Content companies will all gloat and chortle about how wonderful the structure is and they can charge whatever they want,” Britt complained. “We’ve accumulated networks that hardly anybody watches. If you speak to the people who run those networks or own them they almost feel it’s a birthright — I have this network that has distribution to 70-80 million homes, and I’m getting paid every month for ads — maybe this year I wasn’t able to get a big audience but you know next year I am going to work harder and I am going to spend more money on programming and it’s going to be good.”
Britt noted some of the channels Time Warner added have transformed into entirely different channels the company would have never signed up for had they known.
“Sometimes people even change the entire content of the network and our company has been pretty aggressive in not letting that happen since we’re selling a whole package that appeals to different people,” Britt said. “It’s not a birthright, it’s not a carte blanche.”
“I think what we’re saying because the consumer is telling us they can’t afford these prices anymore, where we can we’re going to have to start cutting things off,” Britt warned. “So if you have a network that gets hash mark ratings and no real sign it’s going to get any better, and your contract is up, we’re going to have a different kind of conversation than we might have had five, six or ten years ago.”
Britt said some networks will be dropped altogether, others will be invited to remain, but only on an added-cost tier for subscribers willing to pay more.
“We can’t keep carrying these giant packages of things with the services that don’t carry their own weight,” Britt said.
But Britt understands the perspective of the entertainment companies as well, having formerly been with Time Warner, Inc., the entertainment-oriented company that owns several cable networks.
“A-la carte just doesn’t work for those companies,” Britt noted. “If you think about the existing package, it’s a wonderful mechanism to mitigate risk in a business that I would argue is one of the riskiest businesses on the planet.”
Britt compared a-la-carte economics with that of a typical Broadway theater show, where a small group of individuals risk substantial sums of money on the success of a production that either makes it or it doesn’t, and most don’t. The only revenue stream is from consumers willing to pay ticket prices for admission.
Today’s cable package offers niche and general interest channels in the same package, with assured subscription revenue regardless of ratings, combined with ad revenue which can be meager or substantial depending on the ratings. With guaranteed revenue, cable channels invest in programming production or acquisition — purchases that would not be likely if reliant on an uncertain a-la-carte business model.
Therefore, in Britt’s view, a-la-carte per channel or per program changes the dynamics of the cable business away from a stable one that obtains programming on the basis of predicted revenue to one closer to a Broadway production, where risks of failure are very high, especially for niche programming.
Britt believes in today’s bundled cable package, but not in its current size or monthly price.
“I think aside from that there is a lot of value in the package if you think about cost avoidance,” Britt said. “In reality we as distributors do the marketing, the billing, the customer relationship and although somebody from a network might rail at us for not being great marketers, the reality is if each network had to separately market and bill itself and deal with consumers separately, you would introduce a whole lot of cost in the system that is not there today. This actually works quite well for consumers today and it’s a relatively good value. I think the problem is the trajectory of it and if you are in the content business you are trying to seek eyeballs so you are competing with each other and the only way people seem to know how to do that is to spend even more for programming and that is what sort of killed you with consumer behavior.”
Time Warner Cable CEO Glenn Britt took questions for an hour from Wall Street investors and analysts at the UBS Conference in New York. (December 3, 2012) (55 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.


 Subscribe
Subscribe