Thune
When Sen. John “Net Neutrality is unjustified” Thune (R-S.D.) and Rep. Fred “Net Neutrality is a solution in search of a problem” Upton (R-Mich.) last week magically became Internet activists ready to solve the Net Neutrality issue with an “unambiguous” bill to “protect Americans” from greedy ISPs, you will pardon me if I am just a tad suspicious.
The two Republicans who champion “less government regulation is better” and “let the marketplace decide for itself”-principles are proposing new legislation that will regulate the conduct of Internet Service Providers, claiming it will tie their hands and prevent the launch of Internet fast lanes and ban traffic degradation.
The two legislators are traveling in a fast lane of their own — hurrying to schedule hearings, mark up a bill, and speed it to the floor for consideration by the end of this month. That’s a marked departure for the U.S. Congress-as-usual, the one that can’t manage to pass virtually anything, much less in a hurry. So where is the fire?
It is at the Federal Communications Commission in Washington, scheduled to vote on its own new Net Neutrality proposal by the end of February. Thune and Upton are hoping to launch a pre-emptive strike against the anticipated strong Open Internet protections the FCC will probably enact on a party line vote. The FCC is likely to pursue a reclassification of broadband away from the lobbyist-lovin’, largely deregulated “information service” it is today towards a “telecommunications service” under Title II of the Communications Act. That represents Comcast’s worst nightmare.
 Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.
Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.
The proposed Republican alternative suggests a “third way” compromise only Comcast and AT&T could love. While ostensibly banning intentional interference with Internet traffic, the two legislators include a Grand Canyon-sized loophole in the form of one word you could fly an Airbus A380 through: reasonable
SEC. 13. INTERNET OPENNESS.
(a) OBLIGATIONS OF BROADBAND INTERNET ACCESS SERVICE PROVIDERS.—A person engaged in the provision of broadband Internet access service, insofar as such person is so engaged (1) may not block lawful content, applications, or services, subject to reasonable network management; may not prohibit the use of non-harmful devices, subject to reasonable network management; may not throttle lawful traffic by selectively slowing, speeding, degrading, or enhancing Internet traffic based on source, destination, or content, subject to reasonable network management; may not engage in paid prioritization; and shall publicly disclose accurate and relevant information in plain language regarding the network management practices, performance, and commercial terms of its broadband Internet access services sufficient for consumers to make informed choices regarding use of such services and for content, application, service, and device providers to develop, market, and maintain Internet offerings, except that a provider is not required to publicly disclose competitively sensitive information or information that could compromise network security or undermine the efficacy of reasonable network management practices.
No ISP has ever declared its own traffic management policies unreasonable, so whatever they do, in their minds, is “reasonable” by definition.

Upton
The proposed bill would keep Net Neutrality far away from the critical Title II foundation it needs — essential armor that will help withstand inevitable court challenges by providers outraged by the government’s attempt to interfere with their free speech rights (at the expense of their customers’ freedom from content-killing traffic slowdowns).
The concept of “network management” is Play-Doh in Comcast and AT&T’s hands. It could mean balancing traffic by adding more capacity as needed or implementing a “fair access policy” that rations inadequate capacity. Both could easily be called “reasonable” by them. Customers paying for 25Mbps and getting 6Mbps during the evenings may think otherwise.
But no worries, the Republicans’ plan requires ISPs to disclose exactly how they are undercutting the broadband service you paid good money to receive. They claim that will give you an “informed choice,” except for many Americans, there is no choice.
The FCC’s plan is much more likely to stop to the tricks, traps, and traffic manipulation in whatever form arises now or in the future. It uses well-established precedent that is unlikely to be thrown out by the courts, delivers real oversight desperately needed in the monopoly/duopoly broadband marketplace, and will actually protect consumers.
The Republican alternative primarily protects AT&T, Comcast, and their chances of getting more campaign contributions from their friends in the cable and phone business. In short, it isn’t worth your time, and you should tell your member of Congress it isn’t worth theirs either.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 The proposed bill also carefully protects existing providers from pressure to upgrade their networks.
The proposed bill also carefully protects existing providers from pressure to upgrade their networks. The group urged the Missouri legislature to reject the bill.
The group urged the Missouri legislature to reject the bill.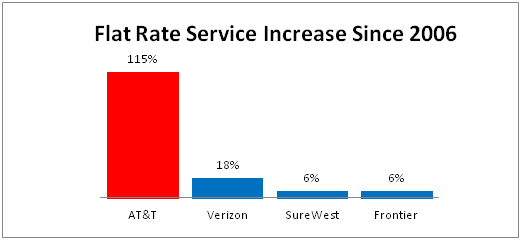
 AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra.
AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra. Looking for civil rights groups to support your multi-billion dollar telecom merger and keep minority groups off your back?
Looking for civil rights groups to support your multi-billion dollar telecom merger and keep minority groups off your back? While the money keeps rolling in, Sharpton has
While the money keeps rolling in, Sharpton has 

 Unfortunately for consumers, even the chairman of the FCC concedes the broadband marketplace isn’t exactly teeming with the kind of competition Section 706 envisioned to keep the marketplace in check. In fact, Wheeler suggested most Americans live with a broadband duopoly, and often a monopoly when buying Internet access at speeds of 25Mbps or greater. Further industry consolidation is already underway, which
Unfortunately for consumers, even the chairman of the FCC concedes the broadband marketplace isn’t exactly teeming with the kind of competition Section 706 envisioned to keep the marketplace in check. In fact, Wheeler suggested most Americans live with a broadband duopoly, and often a monopoly when buying Internet access at speeds of 25Mbps or greater. Further industry consolidation is already underway, which 


