Bell has announced it will boost broadband speeds for selected residents of Ontario and Quebec as high as 100/20Mbps service through a fiber service upgrade it will begin this year.
Bell has announced it will boost broadband speeds for selected residents of Ontario and Quebec as high as 100/20Mbps service through a fiber service upgrade it will begin this year.
While Canada’s largest phone company is providing a “fiber to the neighborhood” service that still relies in part on traditional copper phone wiring in other parts of Ontario, Bell promises to install true fiber to the home connections starting in Quebec City, and in new housing developments elsewhere in both provinces.
Quebec City was chosen because most of the city’s telecommunications wiring is installed above ground on traditional telephone poles. Upgrading above-ground service costs considerably less than coping with buried cables. It will take the company three years to complete the upgrade.
Bell claims the upgrades are part of a natural evolution of telecommunications service in Canada.
“Investment in broadband networks and services is a core strategic imperative at Bell,” said chief executive George Cope in a statement. “We’re actively building the communications platforms that support the growth of competitive new internet, video and other digital services now and into the future.”
Competition may be the key factor in Bell’s decision to upgrade service, particularly in Quebec. Incumbent cable provider Videotron has effectively called out Bell for its slower broadband DSL service, which offers “up to” 7Mbps DSL service. Videotron already provides speed tiers up to 50Mbps for just under $80 a month, and is capable of expanding service to 100Mbps in the future.
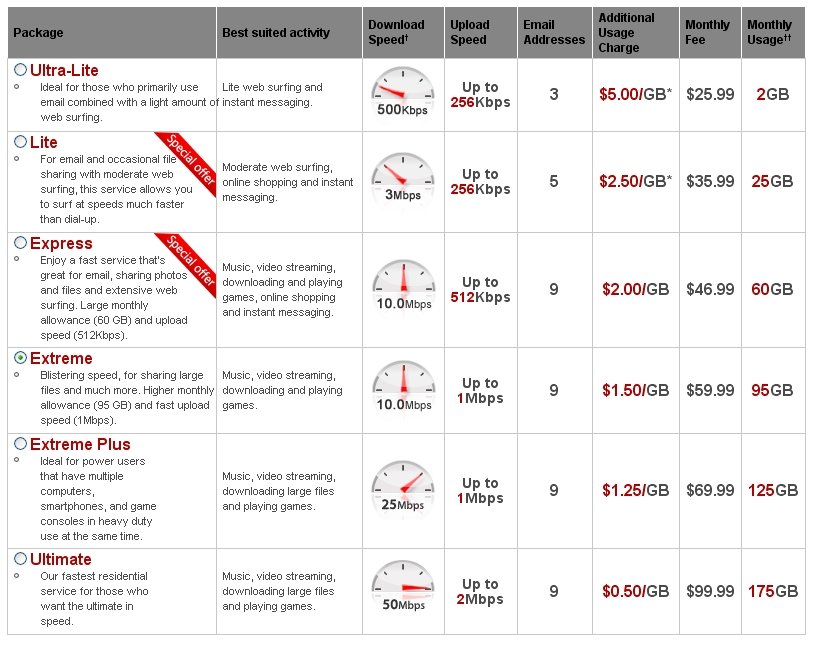
In Ontario, Bell faces competition from Rogers Cable, which itself has boosted speeds after a DOCSIS 3 upgrade. The cable operator offers residents in the Greater Toronto Area 50Mbps for $100 per month.
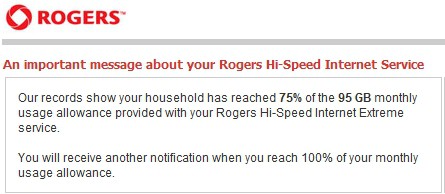
But two things that will come along for the ride are Bell’s notoriously low usage allowances and throttled speeds when using bandwidth-intensive applications like file swapping software.
The company did not release what usage limits are anticipated for their fiber optic offerings, but consumers acquainted with Bell service are skeptical the upgrade will be worth the price.
“Who cares what Bell’s speeds are when you cannot use the service at promised speeds,” writes Stop the Cap! reader Noelle. “Besides, if Bell’s usual stingy limits remain in place, if you did maximize your connection, you could blow through their usage limit in an hour or so. As usual, we get to pay for what most others get for free as part of their subscription price.”
Some other online reactions:
“Sure we’ll all have faster speeds, but Bell will make us pay through our teeth for it. Faster speeds mean less time to reach the bit-cap limit = more profit for Bell. Also everyone with an independent ISP will continue to use whatever crumbs of service Bell wishes to dole out as part of it’s non-monopoly obligations. Having a hyper-fast internet with Bell is like having a Ferrari and having to drive the speed limit everywhere. I know it can do 200mph, but Ma Bell limits me to 50. Its like throwing your money away.”
“Bell’s theoretical DSL download speed of 7Mbps is a joke. Most people barely break 1Mbps, and after they’re done throttling you to death, you’d beg for that speed if you could get it. I dumped the Bell nightmare years ago.”
“I can’t wait to find out what my bill will be after they charge me another arm and a leg to pay for all these upgrades. Who cares about speed upgrades when their usage-based limits mean you cannot use them. Instead of upgrading speed, how about upgrading your network capacity and do away with the usage limits and throttled broadband speeds?”


 Subscribe
Subscribe