Who needs FiOS when you can get 5G wireless service with a data plan?
Fran Shammo has a message for Verizon customers and investors: fiber optic broadband is so… yesterday. Your millennial kids aren’t interested in gigabit speed, unlimited use Internet in the home. They want to watch most of their content on a smartphone and spend more on usage-capped wireless plans.
Shammo is Verizon’s money man – the chief financial officer and prognosticator of the great Internet future.
Like his boss, CEO Lowell McAdam, Frammo has his feet firmly planted in the direction of Verizon Wireless, the phone company’s top moneymaker. If one ever wondered why Verizon Communications has let FiOS expansion wither on the vine, Mr. McAdam and Mr. Shammo would be the two to speak with.
This week, Shammo doubled down on his pro-wireless rhetoric while attending the Bank of America Merrill Lynch 2016 Media, Communications & Entertainment Conference — one of many regular gathering spots for Wall Street analysts and investors. He left little doubt about the direction Verizon was headed in.

Shammo
“As we look at the world if you will, and we look at our ecosystem, […] the world is moving to a broadband wireless world,” Shammo told the audience. “Now, I am really – when I say world, I am really talking the U.S., right. So, but I do think the world is moving to a wireless world.”
In Shammo’s view, the vast majority of people want to consume content, including entertainment, over a 4G LTE (or future 5G) wireless network on a portable device tied to a data plan. Shammo predicted wireless usage will surpass DSL, cable broadband, and even FiOS consumption in 3-5 years. If he’s right, that means a mountain of money for Verizon and its investors, as consumers will easily have to spend over $100 a month just on a data plan sufficient to cope with Shammo’s predicted usage curve. In fact, your future Verizon Wireless bill will likely rival what you pay for cable television, broadband, and phone service together.
Millennials don’t want fiber, they want wireless data plans
Shammo argued millennials are driving the transition to wireless, claiming they already watch most of their entertainment over smartphones and tablets, not home broadband or linear TV. His view is the rest of us are soon to follow. Shammo claims those under 30 are turning down cable television and disconnecting their home broadband service because they prefer wireless. Others wonder if it is more a matter of being able to afford both. A 2013 survey by Pew data found 84% of households making more than $54,000 have broadband. That number drops to 54% when annual household incomes are lower than $30,000 per year. But those income-challenged millennials don’t always forego Internet access — some rely on their wireless smartphone to access online content instead.

A microcell
Verizon Wireless may be banking on the same kind of “hard choice” many made about their landline service. Pay for a landline and a mobile phone, or just keep mobile and disconnect the home phone to save money. Usage growth curves may soon force a choice about increasing your data plan or keeping broadband service at home. Shammo is betting most need Verizon Wireless more.
Verizon FiOS is really about network densification of our 4G LTE network
Shammo continued to frame its FiOS network as “east coast-centric” and almost a piece of nostalgia. The recent decision to expand FiOS in Boston is not based on a renewed belief in the future of fiber, Shammo admitted, it is being done primarily to lay the infrastructure needed to densify Verizon’s existing LTE wireless network in metro Boston to better manage increased wireless usage. Shammo’s spending priorities couldn’t be clearer.
“Obviously, we said, we would build up Boston now, because it makes sense from a LTE perspective,” Shammo said. “We can spend $300 million over the next three years to make that more palatable to expand FIOS. So we will continue to expand that broadband connection via fiber where it makes financial sense for us.”
 In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.
In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.
Shammo also believes Verizon must not just be a ‘dumb wireless’ connection. Controlling and distributing content is also critically important, and Shammo is still a big believer in Verizon’s ho-hum GO90 platform, which compared to Hulu and Netflix couldn’t draw flies.
Even Verizon CEO McAdam admitted a few weeks ago at another Wall Street conference GO90 was “a little bit overhyped.” Most of GO90’s content library is mostly short video clips targeted at millennials with short attention spans. The downside of making that your target audience is the rumor many who sampled the service early on have already forgotten about it and moved on.
Forget about congested home and on-the-go Wi-Fi and expensive fiber optics. Verizon will sell you 5G wireless (with a data plan) for everywhere.
Shammo believes the future isn’t good for Wi-Fi in the home and on-the-go. As data demands increase, he believes Wi-Fi will become slow and overcongested.
“There is a quality of service with our network that you can’t get with others,” Shammo said. “I mean, most people in this room would realize that when Wi-Fi gets clogged, quality of service goes significantly down. It’s an unmanaged network. You can’t manage that.”
Instead, Verizon will eventually deploy 5G wireless instead of FiOS in many areas without fiber optic service today. Frammo said 5G would cost Verizon a lot less than fiber, “because there is no labor to dig up your front lawn, lay in fiber, or be able to fix something.”
Shammo doesn’t believe 5G wireless will replace 4G LTE wireless, however.
“LTE will be here for a very long time and be the predominant voice, text, data platform for mobile,” Shammo said.
So instead of unlimited fiber optic broadband, Verizon plans to sell home broadband customers something closer to Wi-Fi, except with a data allowance. It’s a return to fixed wireless service.
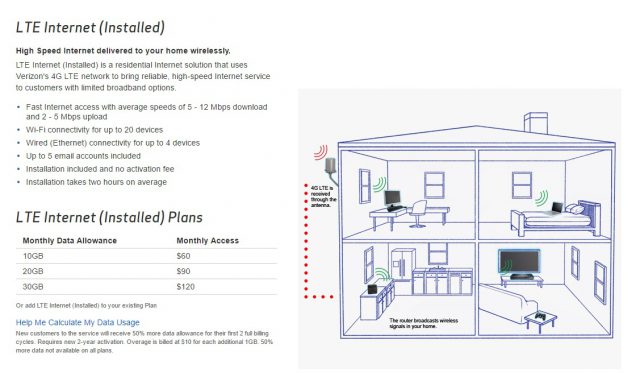
Verizon Wireless’ existing fixed wireless service is heavily usage capped and not cheap.
Just a few short years ago, Verizon was looking to fixed wireless as a replacement for rural DSL and landline service. Now Shammo sees the economics as favorable to push a similar service on all of its customers, except those already fitted for FiOS. That changes the dynamics on usage as well, because Verizon Wireless ditched unlimited service several years ago except for a dwindling number of customer grandfathered in on its old unlimited plan.
Current 4G LTE fixed wireless customers can expect 5-12Mbps speeds with data plan options of $60 for 10GB, $90 for 20GB, or $120 for 30GB. The 5G service would be substantially faster than Verizon’s current fixed LTE wireless service, but the company’s philosophy favoring data caps for wireless services makes it likely customers will pay much higher prices for service, higher than Verizon charges for FiOS itself.
 Verizon Communications announced a deal Tuesday with a leading optical fiber manufacturer to supply up to 12.4 million miles of fiber cable annually for a large buildout of Verizon’s fiber network to power its forthcoming 5G wireless service.
Verizon Communications announced a deal Tuesday with a leading optical fiber manufacturer to supply up to 12.4 million miles of fiber cable annually for a large buildout of Verizon’s fiber network to power its forthcoming 5G wireless service. “When we deployed FiOS we would run a fiber cable into a neighborhood with six or eight strands in it,” McAdam said. “Now we’re going to drop off six or eight strands to every street light in every neighborhood so that allows you to deliver a gigabit of thruput into the home and allows you to do things like intelligent transportation, electric grid management, and water system management. You hear a lot about autonomous cars and things like that today that don’t work without 5G.”
“When we deployed FiOS we would run a fiber cable into a neighborhood with six or eight strands in it,” McAdam said. “Now we’re going to drop off six or eight strands to every street light in every neighborhood so that allows you to deliver a gigabit of thruput into the home and allows you to do things like intelligent transportation, electric grid management, and water system management. You hear a lot about autonomous cars and things like that today that don’t work without 5G.”

 Subscribe
Subscribe





 In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.
In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.

