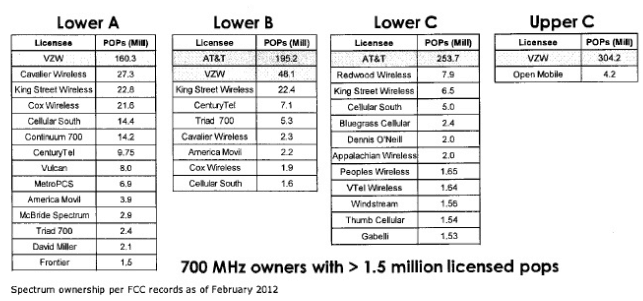
AT&T’s broadband customers are taking their business elsewhere as second quarter results show the phone company lost 649,000 DSL customers in the last three months, while only picking up 553,000 new U-verse Internet users to replace those leaving. The result was a net loss of nearly 100,000 broadband customers in a single quarter. The company also only managed to attract 155,000 new U-verse television customers away from satellite or cable operators during the quarter.
AT&T blames the losses on “seasonality” — code language for part-time residents, college students, and other fluctuations that occur as customers come and go. Total broadband connections dropped 0.2% for AT&T, with 16.43 million remaining customers.
Landline customers also continue to depart AT&T in droves. More than one million home phone customers pulled the plug on AT&T this quarter. AT&T has lost nearly 11 percent of their landline customers over the past year.
For those remaining, a combination of rate increases, cost cutting and fierce marketing of bundled packages of services are keeping revenue growing on both the residential and business side.

AT&T is getting closer to announcing a “rural landline solution,” which some analysts predict will be the company’s exit from the rural landline business.
Executives continue to hint the company is reviewing its future in the rural landline business. AT&T lobbyists have shepherded new laws in several states that would allow them to abandon rural landline customers where the company is no longer required to be “the carrier of last resort.”
AT&T U-verse is turning out to be not much of a threat to cable and satellite operators, only achieving a 17.3% penetration rate in areas where the service is available.
The real money for AT&T is being made in the wireless sector, where increasing prices, changes to service packages, and data usage-based billing are all paying off — revenue for wireless data alone is up 18.8% to $1 billion during the second quarter. AT&T earned $14.3 billion from its wireless business in just the second quarter alone.
At the same time, the company is slashing investments in parts of its network and cutting employees.
Capital expenditures in the second quarter amounted to $4.48 billion, down 15% from the $5.27 billion AT&T spent a year ago. AT&T also cut its workforce by 6.4% since June 2011, with a reported 242,380 total remaining employees.
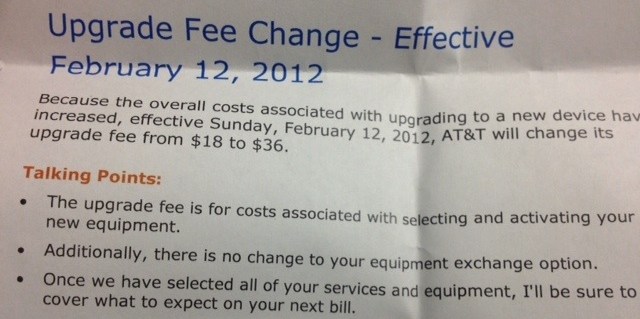
Despite the company’s talking points, AT&T’s upgrade fee is designed to slow down customers considering upgrading their smartphones.
In other highlights:
- Wall Street analysts are praising AT&T’s stricter upgrade policies and device upgrade fees. In fact, at least one analyst wants to see AT&T raise the fee to $50 for every phone upgrade. The fees discourage customers from upgrading their phones, which dramatically reduces AT&T’s costs. AT&T subsidizes phones for customers. The longer customers hold off from upgrading, the more revenue AT&T keeps for themselves and shareholders. AT&T has made it clear it will continue to “introduce discipline” in the handset market to enforce “rational pricing,” which means customers will continue to see further reductions in device subsidies and face higher prices when upgrading phones.
- Much of AT&T’s investment will be in its LTE 4G network. AT&T’s spending on wireline services including U-verse is on the decline.
- AT&T admitted its policy of monetizing data usage for profit is well underway: “[We are getting] ourselves set up for revenues that are going to be tied to usage, which will then be tied to our capital requirements and a really profitable situation.”
- AT&T is aggressively pushing customers to upgrade to smartphones so they can earn additional revenue. “Smartphone subscribers now number 43 million and make [up] 62% of our total postpaid base. But smartphones accounted for 77% of postpaid sales during the quarter, showing continuing opportunity for growth. And when you look at our total smartphone base, we’ve added 9 million high-value smartphone customers in just the last 12 months.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ATT 2Q2012 Results.flv[/flv]
AT&T spins its 2nd Quarter results for shareholders in the best possible light. Although revenues are up, the number of customers leaving AT&T for other providers may challenge future growth and earnings. (4 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe