The days of wine and roses from wireless data profits may be at risk, according to some Wall Street analysts, after Verizon Wireless on Monday brought back an unlimited data plan it vowed was dead for good in 2011.
 The “Cadillac” wireless network reintroduced unlimited data, phone, and texting this week at prices that vary according to the number of lines on your account:
The “Cadillac” wireless network reintroduced unlimited data, phone, and texting this week at prices that vary according to the number of lines on your account:
- $80 a month for one line
- $70 a line for two lines
- $54 a line for three lines
- $45 a line for four lines
Verizon Wireless last enrolled customers in its old unlimited data plan in 2011, and a dwindling number of customers remain grandfathered on that plan, which began increasing in price last year and has since been restricted to no more than 200GB of “unlimited” usage in a month.
Verizon’s new unlimited data plan is a response to pressure from increasing competition, especially from T-Mobile and Sprint. All of Verizon’s national competitors have unlimited data plans with varying restrictions, and Verizon’s lack of one is likely to have cost it new customer signups last year. The company only managed to add 2.3 million postpaid customers in 2016, down from 4.5 million signed up in 2015.

CEO McAdam swore unlimited data was dead at Verizon
Causing the most irritation is T-Mobile, which near-constantly nips at Verizon’s heels with innovative and disruptive plans designed to challenge Verizon’s business model. BTIG Research analyst Walter Piecyk noted Verizon’s claims it does not need to respond to T-Mobile’s marketing harassment just don’t ring true any longer.
“Verizon has a long history of rebuffing T-Mobile’s competitive moves as non-economic or unlikely to have an impact on the industry for more than a quarter or two, only to later replicate the offer,” Piecyk said. “That was true for phone payment plans, ETF payments for switchers, overage etc. We can now add unlimited to that list. How long will it be until Verizon offers pricing that includes taxes? Despite those delayed competitive responses, T-Mobile has maintained industry leading growth while Verizon’s has declined.”
Piecyk believes Verizon Wireless rushed their unlimited data plan into the marketplace and its introduction seemed not well planned.
“We asked Verizon what has changed to explain such an abrupt reversal, but have yet to receive a response,” Piecyk said. “They had recently been running an advertisement promoting the 5GB rate plan that argued why customers do not need unlimited. The rate plan remains, but it is not clear if the advertisement will. The launch of unlimited seemed rushed, coming a week after the exposure they could have secured with a Super Bowl advertisement. The ad run last night during the Grammy’s did not appear to have taken much to produce.”
Verizon Wireless executives have argued for years customers don’t need unlimited data plans and Verizon would no longer offer one:
- “With unlimited, it’s the physics that breaks it. If you allow unlimited usage, you just run out of gas.“ — Lowell McAdam, Verizon CEO (September, 2013)
- “At this point, we are not going to entertain unlimited. Promotions come and go. We can’t react to everything in the marketplace.” — Fran Shammo, former Verizon CFO (January, 2016)
- “I’ve been pretty public saying the unlimited model does not work in an LTE environment. Unlimited is a very short-term game in the LTE market. Eventually unlimited is going to go away because you have to generate cash to reinvest.” — Fran Shammo, former Verizon CFO (March, 2016)
- Unlimited data plans were “not something we feel the need to do.” — Matthew Ellis, Verizon CFO (January, 2017)

Shammo: Unlimited doesn’t work on LTE networks.
The impact of not having an unlimited data plan appears to have convinced Verizon to change its mind, and that comes as no surprise to Roger Entner of Recon Analytics.
“In three to five years, unlimited plans will come back,” Entner predicted in 2011. He claimed back then wireless carriers were initially unsure how to predict data usage growth on their networks and placing limits on usage gave carriers more predictable upgrade schedules. But after several years of data, Entner said carriers can now better predict the amount of data an average subscriber will use in a month, giving them confidence to remove the caps.
Verizon Wireless’ unlimited plan includes several fine print limitations that provide additional network protection for Verizon and manage any surprise usage:
- Unlimited use is only provided on Verizon’s 4G LTE network. Limits may apply to customers using older 3G networks, which are less efficient managing traffic;
- Unlimited not available to Machine-to-Machine Services;
- Customers with unlimited data plans may find their traffic deprioritized on congested cell sites after 22GB of data consumption during a billing cycle. This speed throttle can reduce network speeds to near-dial up in some circumstances, at least until site congestion eases;
- Mobile hotspot tethering on this unlimited plan is limited to 10GB per month on Verizon’s 4G LTE network. Additional usage will be provided at 3G speeds. This is designed to discourage customers from using Verizon Wireless as a home broadband replacement;
- Verizon’s ultimate 200GB monthly limit is also presumably still in place. If you exceed it on Verizon’s legacy unlimited data plan, you were told to shift to a tiered data plan or had your account closed.

Piecyk thinks Verizon’s unlimited data plan may have been rushed out.
Although consumers clamoring for an unlimited data plan from Verizon are happy, Wall Street is not. Analysts are generally opposed to Verizon’s return to unlimited, with many suggesting it is clear evidence the days of high profits and predictable revenue growth are over. That is especially bad news for AT&T and Verizon Wireless, where investors expect predictable and aggressive returns. Verizon has already warned investors it expects revenue and profits to be flat this year.
Jeffrey Kvaal with Instinet believes Verizon’s traditionally robust network coverage is no longer an advantage as competitors catch up and unlimited data is the final nail in the coffin for wireless revenue growth. That means only one thing to Kvaal, AT&T and Verizon must pursue growth outside of the wireless industry. Verizon, in particular, is facing investor expectations it will do something bold in 2017, such as making a large acquisition like a major cable operator.
Evercore ISI’s Vijay Jayant believes unlimited data is bad news for all carriers from the perspective of investors looking for revenue growth. Jayant told investors in the short term, unlimited data may help Verizon’s revenue because the plans are expensive, but in the long run Verizon is sacrificing the revenue potential of monetizing growing data usage in return for a high-priced, flat rate option. That guarantees “customers won’t see their bills rise, even as their usage does,” Jayant said.
Some analysts point out Verizon’s unlimited data plan is expensive, limiting its potential attractiveness to customers considering jumping to another carrier. While Verizon charges between $80-180 (for one to four devices), AT&T charges between $100-180 for unlimited plan customers, who must also sign up with DirecTV to get an unlimited data plan. T-Mobile charges between $70-160 and Sprint charges between $60-160. The cheapest is T-Mobile, because its plans are all-taxes/fees inclusive. All four carriers have soft limits after which customers may be exposed to a speed throttle. AT&T can temporarily throttle users at 22GB, Sprint can throttle above 23GB and T-Mobile after 28GB.
The Wall Street Journal discusses Verizon’s unlimited data plan and its caveats. (4:55)


 Subscribe
Subscribe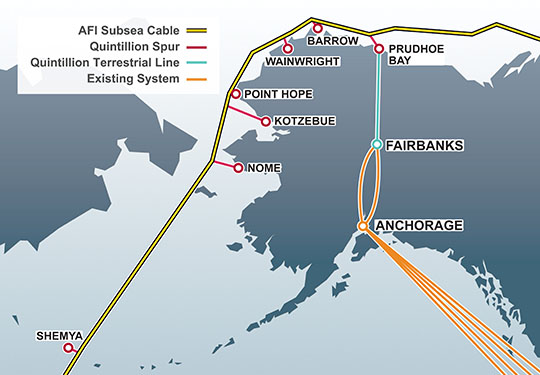
 The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point. Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.


