Comcast may be undercutting its own fiber broadband aspirations by introducing a cheaper way for customers to get gigabit broadband service over their existing Comcast cable connection.
Customers in seven new areas, including most of Colorado, Oregon, southwest Washington State, and the cities of Houston, Kansas City, San Francisco and Seattle now have access to Comcast’s DOCSIS 3.1-powered gigabit downloads. (Upload speeds are limited to a much less impressive 35Mbps.)
Comcast announced the new communities as part of their gradual rollout of DOCSIS 3.1 — the standard that powers cable broadband — across their national footprint. These communities join Utah, Detroit, Tennessee, Chicago, Atlanta, and Miami where Comcast has already introduced the new speeds.
It is Comcast’s latest foray into gigabit speed broadband, and it is decidedly focused on the cities outside of the northeast (except Boston) where Comcast has not faced significant competition from Google Fiber or AT&T Fiber, both delivering gigabit speed internet access. Verizon FiOS, predominately in the northeast, only recently introduced gigabit speed options for its residential customers. Comcast continues to be among the most aggressive cable operators willing to boost broadband speeds for its customers, in direct contrast to Charter Communications, the second largest cable operator in the country that is predominately focused on selling 60-100Mbps internet packages to its customers.

Comcast sells multiple broadband speed tiers to its customers.
Comcast’s efforts may undercut its own fiber-on-demand project, which wires fiber to the home service for some Comcast customers seeking up to 2Gbps service. That plan comes with a steep installation fee and term commitment, making it a harder sell for customers. Comcast’s DOCSIS-powered gigabit will retail for $159.95 a month, but Comcast is offering pricing promotions ranging from $70-109.99 a month with a one-year term commitment in several cities. The more competition, the lower the price.
In Kansas City, where Google Fiber premiered and AT&T is wiring its own gigabit fiber, Comcast charges $70 a month, price-locked for two years with a one-year contract. Customers who don’t want a contract will pay dearly for that option — $160 a month, which is more than double the promotional price.
In Houston, where AT&T has not exactly blanketed the city with gigabit fiber service and Comcast has been the dominant cable operator for decades, gigabit speed will cost you $109.99 — almost $40 more a month because of the relative lack of competition. Customers who bundle other Comcast services will get a price break however. Upgrading to gigabit service will cost those customers an additional $50 to $70 a month, depending on their current package.
 “Additional prices and promotions may be tested in the future,” the company said in a news release.
“Additional prices and promotions may be tested in the future,” the company said in a news release.
Comcast does not expect many customers will want to make the jump to gigabit speeds and a higher broadband bill. Rich Jennings, senior vice president of Comcast’s Western/Mountain region, told the Colorado Springs Gazette that gigabit service was a “niche product for people who want that kind of speed.”
Comcast does suspect a number of signups will be from broadband-only customers who don’t subscribe to cable television.
Mike Spaulding, Comcast’s vice president of engineering, thinks the service will appeal most to those who rely entirely on a broadband connection for entertainment and communications.
“There’s not a lot of need for gigabit service for one customer to do one thing,” Spaulding told the Denver Post. “But what it does is enable an even better experience as more devices in the home are streaming, whether it’s video or gaming or whatever they are doing in the home. Most of our customers subscribe to the 100Mbps package today. Less than 10 percent of our customers are in the 200-250Mbps. We’ll see where one gig takes us.”
One place a gig may take customers is perilously close to Comcast’s notorious 1TB usage cap, which is currently enforced in Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, New Mexico, Western Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, Texas, South Carolina, Utah, Southwest Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin, even for this premium-priced internet tier. Customers exceeding it will automatically pay a $10 overlimit fee for each 50GB of excess usage, up to a maximum of $200 a month. An unlimited ‘insurance plan’ is also available for $50 a month, which removes the 1TB cap.
Customers will have to use a new modem if they upgrade to gigabit service, either renting one from Comcast for around $10 a month or buying a compatible DOCSIS 3.1 modem. Two of the most recommended: the Arris Surfboard SB8200 ($189) or the Netgear CM1000 ($171.99) (prices subject to change).
 YouTube TV, an online streaming alternative to cable television, now reaches 50% of U.S. residents after the company introduced local TV service in 14 new markets.
YouTube TV, an online streaming alternative to cable television, now reaches 50% of U.S. residents after the company introduced local TV service in 14 new markets.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 A Los Angeles man has reached the boiling point after two years of telemarketing calls from Charter Communications that turn out to be the result of a wrong number.
A Los Angeles man has reached the boiling point after two years of telemarketing calls from Charter Communications that turn out to be the result of a wrong number. 2013: “I have never been more harassed by spam telemarketing/calling in my life than from Charter Communications and they already have my business! It’s
2013: “I have never been more harassed by spam telemarketing/calling in my life than from Charter Communications and they already have my business! It’s  Video programmers that want to avoid the problem of usage allowances that can deter internet video streaming have a new way to make an end run around Net Neutrality, distributing their content “cap-free” through “virtual cable channels” that are distributed over broadband, but appear like traditional cable TV channels on a set-top box.
Video programmers that want to avoid the problem of usage allowances that can deter internet video streaming have a new way to make an end run around Net Neutrality, distributing their content “cap-free” through “virtual cable channels” that are distributed over broadband, but appear like traditional cable TV channels on a set-top box.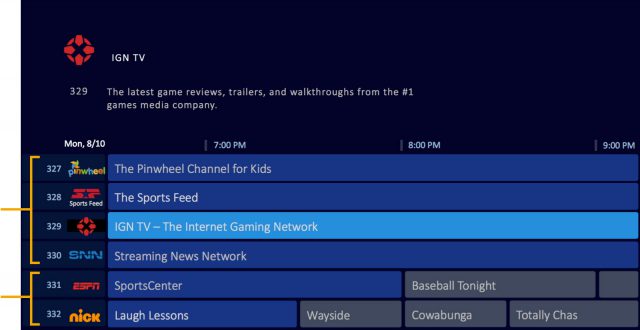
 Yet Wurl’s networks consume just as much bandwidth as traditional online video. But because Wurl is partnering with cable operators, that content is not subject to the usage caps Netflix, Hulu, or Amazon Video customers have to contend with.
Yet Wurl’s networks consume just as much bandwidth as traditional online video. But because Wurl is partnering with cable operators, that content is not subject to the usage caps Netflix, Hulu, or Amazon Video customers have to contend with. Time Warner Cable subscribers in Otsego County, N.Y. have been able to watch WBNG-TV, the CBS affiliate in Binghamton, since there has been a cable company called Time Warner Cable. But as of yesterday, that is no longer the case. In Baxter County, Ark., Suddenlink customers suddenly lost KARK (NBC) and KTHV (CBS), two stations from Little Rock, after the cable company decided it would henceforth only carry KYTV (NBC) and KOLR (CBS) instead. Part of the problem for subscribers is those two stations are located in Springfield, Missouri, a different state.
Time Warner Cable subscribers in Otsego County, N.Y. have been able to watch WBNG-TV, the CBS affiliate in Binghamton, since there has been a cable company called Time Warner Cable. But as of yesterday, that is no longer the case. In Baxter County, Ark., Suddenlink customers suddenly lost KARK (NBC) and KTHV (CBS), two stations from Little Rock, after the cable company decided it would henceforth only carry KYTV (NBC) and KOLR (CBS) instead. Part of the problem for subscribers is those two stations are located in Springfield, Missouri, a different state.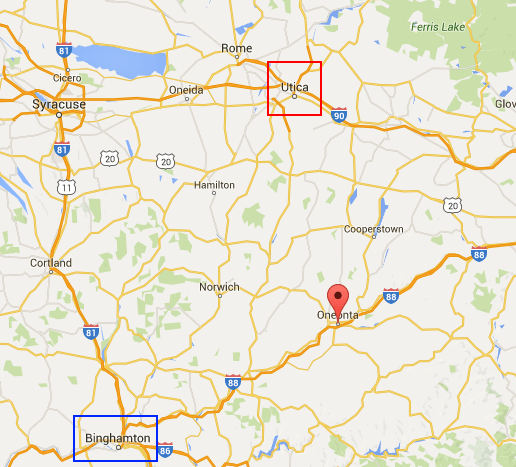
 Another cable company with cost-cutting fever is Altice-owned Suddenlink, which stopped carrying the two Little Rock-based broadcast stations in northern Arkansas on June 7, leaving KATV (ABC) as the only central Arkansas-based news outlet on the cable provider’s Mountain Home-area system.
Another cable company with cost-cutting fever is Altice-owned Suddenlink, which stopped carrying the two Little Rock-based broadcast stations in northern Arkansas on June 7, leaving KATV (ABC) as the only central Arkansas-based news outlet on the cable provider’s Mountain Home-area system.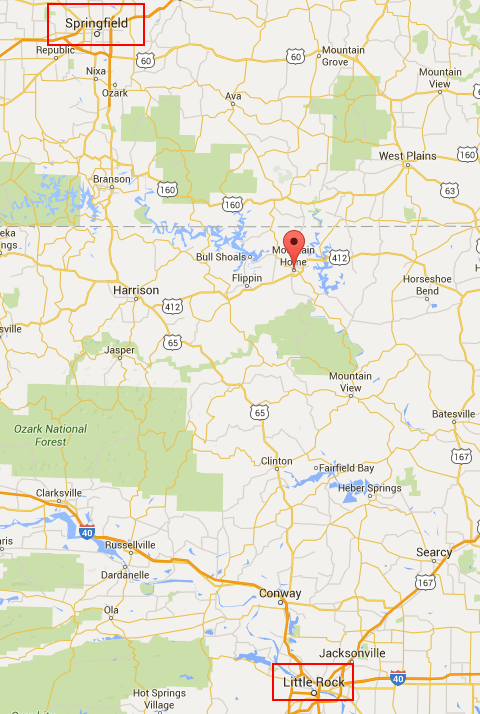 Suddenlink has standing orders from Altice to look for savings wherever possible, but none of those savings are returned to subscribers. The loss of the stations has not reduced anyone’s cable bill and Suddenlink recently moved TBS and INSP — a Christian cable network — to a more costly Expanded Basic tier. In place of the two networks dropped from the Basic package are home shopping networks that actually make Suddenlink money – Evine Live and Jewelry TV.
Suddenlink has standing orders from Altice to look for savings wherever possible, but none of those savings are returned to subscribers. The loss of the stations has not reduced anyone’s cable bill and Suddenlink recently moved TBS and INSP — a Christian cable network — to a more costly Expanded Basic tier. In place of the two networks dropped from the Basic package are home shopping networks that actually make Suddenlink money – Evine Live and Jewelry TV.