Cricket, the regional wireless carrier that claims to offer “unlimited” data plans that really are not, has jacked up prices on its wireless broadband plans and reduced wireless data usage allowances.
Cricket, the regional wireless carrier that claims to offer “unlimited” data plans that really are not, has jacked up prices on its wireless broadband plans and reduced wireless data usage allowances.
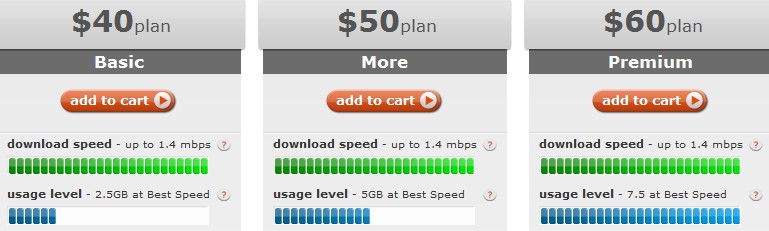
Cricket used to charge $40 a month for 5GB of monthly usage, $60 for 10GB. No more.
Now the company wants you to pay more for less:
Thankfully, existing Cricket customers are grandfathered into their existing $40 for 5GB plan, so they do not face the price hike and allowance cut.
Cricket’s claimed speeds up to 1.4Mbps are fiction — in our own tests we found service never exceeding 650kbps, and often averages 500kbps or less in the Rochester, N.Y. area. When Cricket cell sites become congested, as they have in the southeastern part of the city, speeds can drop to 56kbps or less, making the service completely unusable. While web page browsing and audio streaming are acceptable using Cricket, video streaming is not. YouTube and other video multimedia was too painful to watch.
Cricket’s best advantage in the wireless broadband market was its pricing. Customers accepted dramatically reduced coverage areas (don’t expect Cricket to work outside of the city, nearby suburbs, and adjacent major highways), slower speeds, and a “Fair Access Policy” that throttles your connection to dial-up speeds (or less) once you exceed your monthly allowance, all in return for service priced $20 less than most of the competition. The modem is usually free or deeply discounted, and there is no contract requirement.
But at Cricket’s new pricing, consumers should take a look at Clearwire’s new 4G service, Comcast High Speed 2Go, or Road Runner Mobile instead. Clear’s 4G-only plan offers unlimited access for $40.00 a month without a “Fair Access Policy” throttling your service to dial-up speeds, and much faster service than Cricket can provide. The only downsides are the up front cost of the modem and being sure 4G is available in your area.
Clear, Comcast High Speed 2Go and Road Runner Mobile offer 4G service plans with a fallback option to 3G coverage for about $55 a month. Clear and Comcast do not limit 4G usage, but do limit 3G access to 5GB per month before overlimit fees apply. Road Runner Mobile offers unlimited access to both 3G and 4G service.
Cricket likes to claim it “respeKts your wallet.” Raising prices and reducing usage allowances isn’t exactly a sign of respect.


 Subscribe
Subscribe