 CenturyLink CEO Glenn Post does not think much about AT&T’s plans to shift its most rural landline customers to wireless in its efforts to decommission traditional landline service.
CenturyLink CEO Glenn Post does not think much about AT&T’s plans to shift its most rural landline customers to wireless in its efforts to decommission traditional landline service.
“From a regulatory standpoint, that could be a tough go,” Post explained to Wall Street investors on a conference call last week. “There may be some areas that will have better service with wireless in some ways. As far as a competitive threat, we don’t see that being a real issue for us because just the bandwidth requirements and the limited wireless access or capability in a lot of areas.”
CenturyLink, one of four large independent phone companies and owner of former Baby Bell Qwest, is doubling down on its wired infrastructure to reach customers. The company recently announced Phoenix would be the latest city to get its fiber-to-the-neighborhood service Prism TV — the first legacy Qwest market to get IPTV service from CenturyLink. The service soft-launches in Phoenix this month, with a second city in the region or Pacific Northwest slated to get Prism sometime next year.
The company has spent much of 2012 investing in broadband, managed hosting and cloud computing for business customers, and fiber expansion to reach more than 15,000 cell towers across CenturyLink’s national service area, depicted in green on the accompanying map.
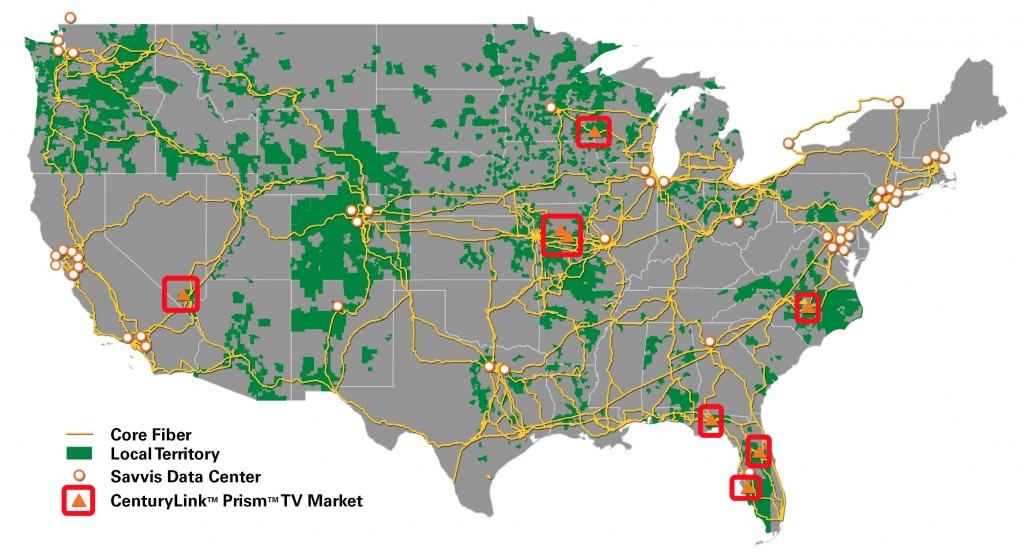 But CenturyLink executives stress their investments are “strategic” — made in areas that are most likely to deliver quick returns for the company.
But CenturyLink executives stress their investments are “strategic” — made in areas that are most likely to deliver quick returns for the company.
While CenturyLink spends money to secure video franchising agreements in metro Denver and Colorado Springs for Prism TV service, it is moving at “a snail’s pace” to deliver broadband service in northeastern North Carolina’s Northampton County. County officials there anticipate CenturyLink will take years to deploy basic DSL service to communities outside and around Conway and Gaston.
The broadband problem in income-challenged parts of North Carolina illustrate the conundrum for county officials, who have to advocate for broadband improvement while combating misleading broadband maps that suggest access is not a problem in the state.
Donna Sullivan with the Department of Commerce notes that broadband maps in states like North Carolina have a census block granularity which does not always reveal the true picture of broadband availability.
“That means if one household in that census block can receive broadband services, the entire census block is considered covered—even though there very well may be households who cannot receive broadband to that location,” she told the Roanoke-Chowan News-Herald.
Northampton County, N.C.
CenturyLink is in no hurry to expand broadband to the 1,921 households in the county of 22,000 who cannot buy broadband service at any price.
Derek Kelly, a CenturyLink spokesman, said the company is working to expand broadband services in the region, but noted the costs to lay down a fiber network to help reach the unserved is “one of the largest costs.”
That cost is much less of a problem if the customer at the end of the line happens to be a wireless company like Verizon or AT&T.
Company officials admit they are spending enormous sums “investing in fiber builds to as many [cell] towers in our service area as economically feasible.” In the third quarter alone, more than 1,000 cell towers received fiber upgrades for a total of 3,300 so far this year. The company hopes to reach 4,000-4,500 cell towers by New Year’s Eve.
The reason why CenturyLink chases wireless business while allowing rural and income-challenged service areas to go without broadband is a simple matter of economics. Cell phone companies sign lucrative, multi-year contracts for fiber connectivity to cell towers to support forthcoming 4G service. In contrast, CenturyLink was surprised to find an astounding 94 percent of families with children in Northampton are qualified for the company’s special Lifeline Program which delivers slow speed, discounted broadband service for families on public assistance.

Post
For CenturyLink’s more urban and prosperous service areas, the news for broadband service improvements is better.
As CenturyLink continues to extend its middle mile fiber network, broadband speeds are gradually improving.
Over 70 percent of CenturyLink customers can receive at least 6Mbps DSL service, more than 57% can receive at least 10Mbps and 29% can access the Internet at 20Mbps speeds or better, according to Post.
But the more urban and prosperous a service area is, the greater the chance a cable competitor has successfully poached many of CenturyLink’s DSL customers with the promise of better speed.
Post said he recognizes the company must do better to remain competitive.
“We’re shooting for 20-25Mbps for a very large percentage of our areas,” Post said. “But with [pair] bonding, we can virtually double the broadband capacity and speeds in our markets. We’re already doing bonding in a number of markets today. So where we have 20Mbps, we could have 40Mbps.”
CenturyLink’s fiber to the neighborhood network, essential where it plans to roll out Prism TV, can also support faster broadband speeds if a customer wants broadband alone and does not care about television service.

Nationwide, the company added 10,000 Prism TV subscribers in the third quarter and has a total customer base of around 104,000 subscribers. But that represents a penetration rate of just over 10%, hardly noticed by still-dominant cable operators.
CenturyLink executives were asked to comment on AT&T’s strategic plan to transform their landline network announced last week in New York. Post found little in common between CenturyLink and AT&T’s vision for the future and does not think the company has to respond to AT&T’s attempt to redefine rural America as wireless territory.
“We don’t see that as a major investment for us or a major risk at this point.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe









