Verizon Wireless customers are seeing declining wireless internet speeds and the greater potential for congestion because Verizon Wireless is experiencing the impact of some overburdened cell sites in some of its largest markets.
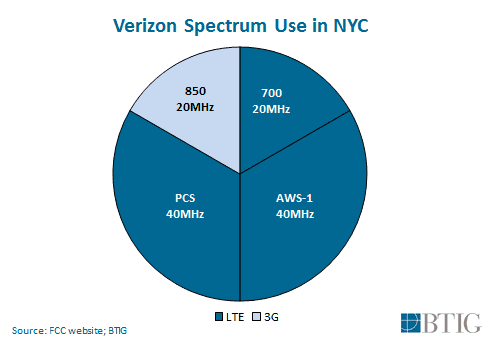
Walter Piecyk from BTIG Research reports over the last few weeks, Verizon has begun using the last 10MHz of PCS spectrum left in its inventory in New York City, nine months earlier than expected.
Verizon’s reserve spectrum in PCS Band 2 near 1900MHz is not as ideal as lower frequency spectrum better able to manage inside buildings in a city as densely packed as New York, but if that is all the company has left for immediate use, that is what it will use. The newly activated frequencies, first uncovered by Milan Milanovic, are not yet operational across all of Verizon’s extensive cell network in the Big Apple. Verizon’s need to activate its last remaining PCS frequencies suggests former chief financial officer Fran Shammo may have been overly optimistic when he claimed Verizon was only using 40% of its spectrum inventory. That may be true in smaller cities, but is no longer the case in large metropolitan areas.
 “This latest action also means that the only spectrum Verizon has left to convert to LTE in NYC is the 25MHz of 800MHz spectrum that the FCC gave it for free in 1984,” wrote Piecyk. “Unfortunately, that 800MHz spectrum is being used to support CDMA voice traffic and legacy 3G data for enterprise/IoT applications. Meanwhile, Dish sits on 125MHz of vacant spectrum in NYC.”
“This latest action also means that the only spectrum Verizon has left to convert to LTE in NYC is the 25MHz of 800MHz spectrum that the FCC gave it for free in 1984,” wrote Piecyk. “Unfortunately, that 800MHz spectrum is being used to support CDMA voice traffic and legacy 3G data for enterprise/IoT applications. Meanwhile, Dish sits on 125MHz of vacant spectrum in NYC.”
BTIG Research has been carefully tracking Verizon’s deployment of its spectrum for years. In New York, LTE expansion has depended heavily on spectrum acquisitions and enabling LTE+, which bonds frequencies together to increase speed and capacity.
BTIG Research Tracks Verizon Wireless’ LTE Deployment in NYC
- 20 MHz: December 2010 – launched LTE on the 20MHz of 700MHz spectrum it bought in the 2008 700MHz auction for $0.46/MHz/POP for the Northeast regional license and $0.77/MHz/POP nationwide.
- 40 MHz: December of 2013 – XLTE-branded rollout of AWS spectrum, which mainly included the spectrum it bought from Cable in 2011 for $0.69/MHz/POP, but also the spectrum it acquired in the 2006 AWS-1 auction, where it spent $1.33/MHz/POP for the Northeast regional license and $0.73/MHz/POP overall.
- 20 MHz: December of 2014 – LTE conversion begins on PCS spectrum. Verizon purchased 10MHz from Northcoast as part of a larger transaction valued at $1.58/MHz/POP in 2003, 10MHz covering NYC from NextWave for $4.63/MHz/POP in 2004, and 20MHz from NextWave in 2005 as part of a larger transaction valued at $2.85/MHz/POP. (Link)
- 10 MHz: Q1 of 2016 – This enabled Verizon to deliver 15MHz x 15MHz connections on Band 2, thereby improving speeds. When this happened we predicted the remaining PCS spectrum would be used in early 2018. (Link)
- 10 MHz: Q3 of 2017 – Once again, this was spotted by Milanovic (Link), who notes that it has not been deployed on all sites. This effectively expands the Band 2 deployment to a 20MHz x 20MHz deployment.
The company has also attempted to increase capacity with network densification, which adds more cell sites to divide up the traffic load. But activating a new cell site can take years, especially if Verizon encounters zoning and permitting problems or public opposition. Small cells can ease congestion in particularly dense traffic areas, but are not enough alone to deal with increasing network traffic.
 Verizon’s own business practices have also complicated things for the wireless company. Ditching two-year contracts and subsidized phones in favor of customers acquiring devices at retail prices financed through wireless carriers like Verizon have led to a slowdown in subscriber upgrades as consumers hold on to their devices for longer.
Verizon’s own business practices have also complicated things for the wireless company. Ditching two-year contracts and subsidized phones in favor of customers acquiring devices at retail prices financed through wireless carriers like Verizon have led to a slowdown in subscriber upgrades as consumers hold on to their devices for longer.
Most phones acquired in the last year or two now support Voice over LTE (VoLTE), which means phone calls travel over Verizon’s LTE network, not the legacy CDMA network Verizon has used for well over a decade. Verizon has to dedicate a significant amount of prime spectrum in the 850MHz band for its CDMA network. Although Verizon claims it has migrated “more than 50%” of its voice traffic to the newer, more efficient VoLTE standard, that is below analysts’ expectations.
Piecyk thinks it may be possible Verizon has been slow to convert because of the record low phone upgrade rate of its customers. As a result, it cannot repurpose its CDMA spectrum for LTE use. Discussions with Verizon engineers suggest the company may eventually cut back CDMA spectrum, but will likely still keep 5 x 5MHz reserved for CDMA voice calling for at least the next four years to support its customers with older devices.
As part of its network densification effort, Verizon is once again relying on fiber optic buildouts, some of which it may take on itself in areas where it does not provide landline service. Verizon will be placing cables with 1,700 strands of fiber, so it is obviously thinking about future network demands.
Before it can deploy additional upgrades or acquire more spectrum, customers can anticipate more “network management” techniques, suspects Piecyk, especially now that unlimited data plans are for sale again. Verizon already limits its “unlimited” plan to 22GB of usage per month, before wireless data speeds are throttled. OpenSignal believes Verizon’s recent speed drops are a result of its unlimited plans putting more pressure on its network.
“We suspect management will now follow T-Mobile’s lead and suppress video quality like BingeOn to help with the rise in network traffic,” Piecyk wrote. “They might also discuss control of overall peak data speeds. However, if no mobile applications require more than 10Mbps service, would it make any sense to suppress the speeds on your customers’ phone? What’s the benefit other than offering a convenient excuse on why your speed tests are slower than the competition?”


 Subscribe
Subscribe