President Trump met with Softbank’s Masayoshi Son in December, 2016.
Japan’s Softbank has a deal tailor-made for President Donald Trump’s desire to inspire companies to invest more in the United States and hire more workers, and all the president has to do is get Washington regulators concerned with mergers, acquisitions, and competition out of Softbank’s way.
Softbank’s Masayoshi Son has delivered a lot of speeches and made a lot of promises since acquiring Sprint in 2013 for $21.6 billion, originally promising to rebuild the struggling wireless company into a potential competitive juggernaut, capable of beating Verizon and AT&T and even take on cable operators. Now he’s offering to invest another $50 billion in the U.S., and create 50,000 new jobs, assuming the business climate is right.
Before accepting such a deal, one should take a closer look at how Sprint is doing three years under Softbank’s ownership. Few would argue with the fact Sprint has languished and fallen to last place among the four national carriers, now behind T-Mobile. Despite Son’s commitment to Donald Trump to invest and hire, Sprint has severely cut investment by more than 60% between 2014 and 2016 and has laid off more than 4,000 employees, most in the United States. Customers continue to complain about the perpetual ‘massive upgrade’ undertaking the company embarked on years ago that never seems to be finished and hasn’t helped service quality as much as customers expected.
In January 2016, BusinessWeek reported SoftBank has “plowed more than $22 billion into Sprint, and yet all of Sprint is now valued at $11.8 billion. The company’s $2.2 billion in cash is about the same as its 2016 debt obligations.”
 Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
“You’ve watched a once-great institution deteriorate to the point that it is now a badly, badly compromised asset,” said Craig Moffett, an analyst at MoffettNathanson. “They’ve been living from hand-to-mouth for years, constantly making short-term decisions in order to live to fight another day.”
It calls into question Softbank’s vision to use technology “to reduce loneliness and ease the sadness of people as much as possible.” There are a lot of sad Sprint customers, churning away into the arms of competitors like T-Mobile faster than Sprint can sign new customers up.
Son’s dream depended on his business plan that reduced the number of U.S. competitors to three by merging Sprint and T-Mobile together, something federal regulators under the Obama Administration failed to accept despite Son’s argument the combined resources of the two companies would theoretically make a super-sized Sprint more competitive with AT&T and Verizon.
In contrast to Son’s plan to consolidate the wireless industry to improve Sprint’s financial health, T-Mobile instead decided to boost investments in network upgrades and improved coverage to attract new customers. Ironically, some of the money to pay for those upgrades came from AT&T after it paid a reverse breakup fee of $3 billion in cash and $1–3 billion in wireless spectrum after its merger proposal with T-Mobile collapsed.
While Son promises he will invest billions in the United States, he is already spending much less on Sprint. In 2017, Verizon planned to spend $9.12 per subscriber (adjusted spending per monthly phone-equivalent subscriber), AT&T will spend $9.67 and T-Mobile will spend $9.04. Sprint will lag behind with $6.78 per subscriber in network investments. Moffett predicted of the $22 billion Verizon has committed for capital spending this year, about $11.3 billion will go toward wireless. By contrast, Sprint will spend $2.97 billion, excluding costs of leased phones. T-Mobile is spending just over $5 billion.
In the last two years, customers have delivered a new paradigm to wireless companies: bigger isn’t necessarily better. The only bright spot among all four national carriers in 2016 was the scrappy T-Mobile, once destined for a fire sale by owner Deutsche Telekom. But under the “Uncarrier” leadership of CEO John Legere, T-Mobile USA is worth pure gold in Deutsche Telekom’s global wireless portfolio. The turnaround came not from trying to consolidate the industry but rather giving customers what they have asked for — more data, unlimited data, better deals, and better service. T-Mobile’s network investments paid off, giving the company very competitive 4G LTE speeds and comparable urban and suburban coverage to its larger competitors. Legere has been so successful, the German owners of T-Mobile no longer seem to be interested in selling T-Mobile USA.
Softbank’s record of achievement with Sprint in the last two years has been much less of a success story.
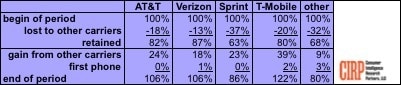
Customer Gains and Losses by Carrier – 2016-Q4 Phone Activators
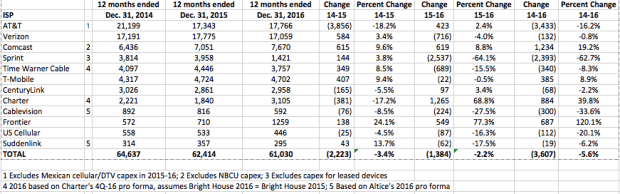
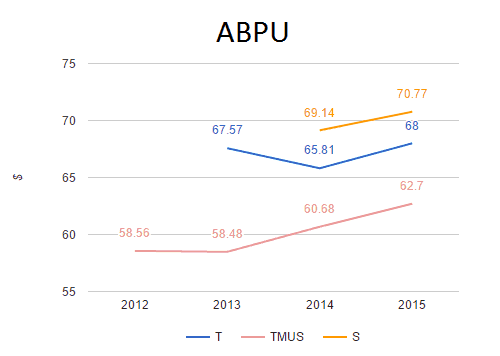
Investments by Sprint in its wireless network have plummeted 62.7% under the leadership of Softbank from 2014-2016. (Chart: Hal Singer)
In 2015, Sprint’s capex was $3.958 billion. Last year, it was $1.421 billion — less than half the previous year. Mr. Son seems reticent about maintaining the kind of investment necessary to grow Sprint’s network over the long term to keep up with customer demand, instead willing to compete short term on price and promotions. Sprint’s past reputation for poor customer service, a slow data network, dropped calls, and coverage dead zones makes attracting former customers back to Sprint a hard sell, especially considering T-Mobile exists as a credible alternative to Sprint for those seeking cheaper service plans.
 Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.
Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.
Convincing President Trump to loosen merger standards to allow Softbank a stronger position in the U.S. market in return for vague and illusory investment and job creation promises is ridiculous considering Mr. Son’s performance with Sprint has not been as rosy as his rhetoric. No president should agree to a de facto bailout deal for Softbank that reduces competition and guarantees higher prices. Mr. Son should instead direct some of the $50 billion he apparently has stashed in waiting to improve Sprint’s network to more effectively compete. If he cannot or will not, the entire country should not pay for his investment mistake by watching more wireless competition get eliminated in yet another merger.
 Son originally planned to combine Charter and Sprint into a new public company. Something similar would likely happen if SoftBank attempts a direct takeover of Charter Communications. Son’s investment in Sprint has not paid off. The wireless carrier has lost billions since SoftBank took control of Sprint in 2013.
Son originally planned to combine Charter and Sprint into a new public company. Something similar would likely happen if SoftBank attempts a direct takeover of Charter Communications. Son’s investment in Sprint has not paid off. The wireless carrier has lost billions since SoftBank took control of Sprint in 2013.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

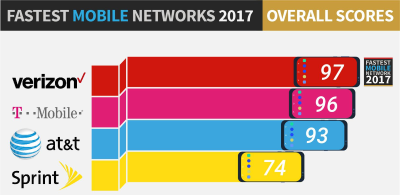




 Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.

 Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.
Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war. Smartphone manufacturers are dealing with sluggish sales for the newest and greatest phone models because American consumers are increasingly resistant to paying for top of the line devices.
Smartphone manufacturers are dealing with sluggish sales for the newest and greatest phone models because American consumers are increasingly resistant to paying for top of the line devices.