 Connecticut’s telecommunications regulator has effectively banned public broadband in the state, ruling that municipalities cannot use their reserved space on utility poles if it means competing with the state’s dominant telecom companies — Comcast, Altice, and Frontier Communications.
Connecticut’s telecommunications regulator has effectively banned public broadband in the state, ruling that municipalities cannot use their reserved space on utility poles if it means competing with the state’s dominant telecom companies — Comcast, Altice, and Frontier Communications.
The ruling by Connecticut’s Public Utilities Regulatory Authority (PURA) is a death-blow for municipalities seeking to build gigabit fiber networks to offer residents the broadband speeds and services that incumbent phone and cable companies either refuse to provide or offer at unaffordable prices.
Among the petitioners appealing to PURA to protect them from competition is Frontier Communications, which owns a large number of utility poles across the state acquired from AT&T. The company was unhappy that municipalities were planning to use reserved space on state utility poles to construct fiber to the home networks that are generally superior to what Frontier offers consumers and businesses in the state. Other providers, like Frontier, said little about the early 1900s Connecticut statute that guarantees municipalities “right of use space” on poles until it became clear some communities were planning to threaten their monopoly/duopoly profits.
The law was originally written to deal with the dynamic telecommunications marketplace that was common in the U.S. during the late 1800s and early 1900s. Utility pole owners were confronted with a myriad of companies selling telegraph and telephone service — all seeking a place on increasingly crowded poles. Local governments could have been crowded out, were it not for the “Act Concerning the Use of Telegraph and Telephone Poles,” approved on July 19, 1905. It was one sentence long:
Every town, city, or borough shall have the right to occupy and use for municipal purposes, without payment therefor, the top gain of every pole now or hereafter erected by any telephone or telegraph company within the limits of any such town, city, or borough.
 The law stood as written until 2013, when the legislature clarified exactly who could benefit from the use of “municipal gain.” Where the original law effectively protected reserved pole space for “municipal” use, the language was broadened in 2013 to read “for any purpose.”
The law stood as written until 2013, when the legislature clarified exactly who could benefit from the use of “municipal gain.” Where the original law effectively protected reserved pole space for “municipal” use, the language was broadened in 2013 to read “for any purpose.”
Observers said the law was modified because of ongoing disputes with pole owners relating to planned municipal broadband projects. Frontier, in particular, has sought restrictive pole attachment agreements with communities trying to build out their broadband networks. In addition to accusations of foot-dragging over issues like “make ready” — when existing pole users move wiring closer together to make room for new providers, Frontier has tried to impose restrictive language on communities that would permanently restrict their ability to offer service. The most common restriction is to compel towns to agree to use their pole space exclusively “for government use,” which would restrict third-party providers hired to manage a community’s municipal broadband service.
PURA’s decision surprised many, because it completely ignored the 2013 language changes and relied instead on its perception of a conflict between state and federal laws. PURA ruled “municipal gain” establishes “preferential access” for towns and communities, and could be in conflict with the federal Communications Act, which mandates “non-discriminatory access” to utility poles, and prohibits local governments from blocking companies from providing telecommunications services.
“Providing municipal entities free access to the communications gain for the purpose of offering competitive telecommunications services … appears to be inconsistent with these principals and other aspects of federal law,” the decision reads.
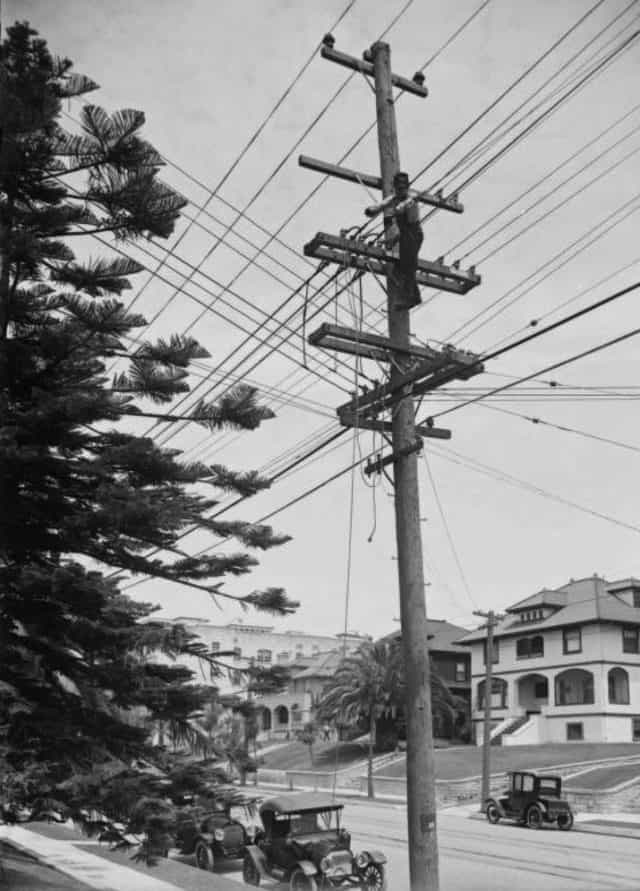

In the early 20th century, vibrant competition meant a lot of utility poles were crowded with wires.
Except communities are not seeking to block providers looking to offer broadband service. These communities are seeking to become a provider. Pole attachment controversies typically relate to unreasonable limits on access to poles and allegations of price gouging pole attachment fees, not “preferential access.”
The end effect of PURA’s ruling: communities can use their pole space for government or institutional purposes only, such as building closed fiber networks available only in public buildings like libraries, schools, town halls, and police and fire departments. It also means any community seeking to build a fiber broadband network serving homes and businesses will either have to pay market rates for pole space, give up on the project, or place all the project’s wiring exclusively underground — a potentially costly alternative to aerial cable and one likely to cost taxpayers millions.
“We are very disappointed in the decision,” Consumer Counsel Elin Katz told Hartford Business. Katz is a strong supporter of municipal broadband. “It ignores the plain language of the statute, and by deciding that [municipal gain] cannot be used by our cities and towns to provide broadband to those affected by the digital divide, denies our municipalities a tool provided by the legislature for just that purpose.”
Frontier and the state’s cable and wireless companies, however, are delighted PURA has come to their rescue, calling its decision “fully consistent with the law.”
“Frontier Communications continues to support efforts to expand broadband access in Connecticut,” said spokesman Andy Malinowski. “PURA reached the correct result. This decision helps ensure the continuation of robust broadband competition in our state.”
The New England Cable & Telecommunications Association (NECTA), the cable industry’s regional lobbying group in the region, was also happy to see an end to unchecked municipal broadband growth and the competition it will bring.
“Our members, who pay millions of dollars annually to rent space on utility poles, offer competitive broadband services with speeds ranging up to 1 gigabit-per-second for residential Connecticut customers, in addition to offering speeds up to 10 gigabits for business customers,” noted NECTA CEO Paul Cianelli.
Other supporters of PURA’s decision include the wireless industry lobbying group CTIA and the Communications Workers of America — unionized employees at Frontier Communications who fear their jobs may be at risk if a municipal provider gives Connecticut customers an additional option for broadband service.
PURA’s decision leaves little room for municipal broadband expansion efforts that have been underway in the state for a decade. Most projects that cannot afford to pay for space on utility poles or the cost to switch to underground cable burial will probably not survive unless a court overturns the regulator’s decision or the state legislature clarifies state law in a way that makes PURA’s current interpretation untenable.
A number of groups are considering suing PURA to overturn its decision, noting the regulator completely ignored the very clear and understandable 2013 language that allows municipalities to use their allotted space on utility poles “for any purpose.” That purpose includes giving the state’s telecom duopoly some competition.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Some Spectrum customers are getting nasty surprises in their latest cable bills.
Some Spectrum customers are getting nasty surprises in their latest cable bills.