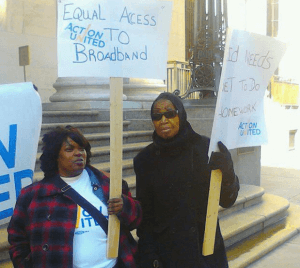
A Philadelphia community group is accusing Comcast of keeping its low-income budget Internet program a secret and denying needy families access for the flimsiest excuses.
A Philadelphia community group is accusing Comcast of keeping its low-income budget Internet program a secret and denying needy families access for the flimsiest excuses.
Action United, which fights for low and moderate income Pennsylvanians, dropped off complaints with federal officials in Philadelphia from residents who are upset because they never heard of the discounted Internet access program or were disqualified from applying.
Comcast’s Internet Essentials offers families who qualify for the federal student lunch program access to 1.5Mbps broadband for around $9.95 a month. But an informal survey by the group found scores of residents who never heard of the program and would have applied if they had known it existed.
 The group, which says it has 44,000 members in Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Harrisburg and Allentown, says it could find only two families among its members that actually qualified to sign up for the service. Some were disqualified because they didn’t participate in the school lunch program, others because they already have Internet service or had a long-forgotten past due bill.
The group, which says it has 44,000 members in Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Harrisburg and Allentown, says it could find only two families among its members that actually qualified to sign up for the service. Some were disqualified because they didn’t participate in the school lunch program, others because they already have Internet service or had a long-forgotten past due bill.
“I feel as though the Internet service will help my son to progress in math, reading, spelling,” Dawn from North Philadelphia told CBS Philadelphia. But she says Comcast refused to sign her up.
“They told me I had a back bill from 10 years ago, so I was not qualified,” Dawn said.
As Stop the Cap! reported in September, Comcast’s program is effectively designed to reap positive publicity for the cable company while discouraging customers from applying and actually obtaining the service.
Action United says area schools, an obvious place to promote low cost Internet for students, knew nothing about the program.
Comcast counters it sent mailings about Internet Essentials to 4,000 school districts, which covers 30,000 schools.
The group originally planned to protest Wednesday in front of Comcast’s corporate headquarters in Philadelphia to draw attention to the problem. Earlier today, Action United announced it had reached an agreement to meet with Comcast executives to discuss the program and help cut some of the red tape for families experiencing trouble applying.
Comcast’s decision to offer budget Internet service came as a result of negotiations with the federal government to approve its merger with NBC-Universal. Critics contend Internet Essentials is too restrictive and requires applicants to navigate through a cumbersome qualification process. After approval, the program only provides discounted service for a period of three years and can be terminated if a family falls past due on their account.
From the byzantine terms and conditions for enrollment in the Comcast Internet Essentials program:
The program is only available to households that (i) are located where Comcast offers Internet service; (ii) have at least one child who receives free school lunches through the National School Lunch Program (the “NSLP”) and as confirmed annually while enrolled in the program; (iii) do not have an overdue Comcast bill or unreturned equipment; and (iv) have not subscribed to any Comcast Internet service within the last ninety (90) days (sections 1(i)-(iv) collectively are defined as “Eligibility Criteria”). This program is not available to households that have children who receive reduced price lunches under the NSLP. The program will accept new customers for three (3) full school years, unless extended at the sole election of Comcast. Comcast reserves the right to establish enrollment periods at the beginning of each academic year in which it accepts new customers that may limit the period of time each year in which you have to enroll in the program.
2. In order to confirm your eligibility for the program, Comcast will need to verify that your children receive free school lunches through the NSLP in the initial enrollment year and each subsequent year you are enrolled in the program. In order to confirm eligibility, participants in the program will be required to provide copies of official documents establishing that a child in the household is currently receive free school lunches through the NSLP. Each year you will be required to reconfirm your household’s current eligibility by providing Comcast or its authorized agent with up-to-date documentation. If you fail to provide documentation proving your eligibility in the program, you will be deemed no longer eligible to participate in the program.
3. You will no longer be eligible to participate in the program if (i) you no longer have at least one child living in your household who receives free school lunches under the NSLP; (ii) you fail to maintain your Comcast account in good standing; (iii) Comcast ceases to provide the Covered Service to your location; or (iv) your account opened under the program is closed. A change in address may result in your account being closed, even if you continue to receive Comcast services at a different address. Program participation also may be terminated if the Covered Service is upgraded, altered or changed by you for any reason. If you are no longer eligible for the program, but continue to receive the Covered Service from Comcast, regular rates, and any other applicable terms and conditions will apply to the Covered Service.


 Subscribe
Subscribe