 Two years after energy conservation groups revealed many television set-top boxes use almost as much electricity as a typical refrigerator, a voluntary agreement has been reached to cut the energy use of the devices 10-45 percent by 2017.
Two years after energy conservation groups revealed many television set-top boxes use almost as much electricity as a typical refrigerator, a voluntary agreement has been reached to cut the energy use of the devices 10-45 percent by 2017.
The Department of Energy, the Natural Resources Defense Council, the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, the Appliance Standards Awareness Project, the Consumer Electronics Association, and the National Cable & Telecommunications Association agreed to new energy efficiency standards for cable boxes expected to save more than $1 billion in electricity annually, once the new equipment is widely deployed in American homes. That represents enough energy to power 700,000 homes and cut five million tons of CO2 emissions each year.
“These energy efficiency standards reflect a collaborative approach among the Energy Department, the pay-TV industry and energy efficiency groups – building on more than three decades of common-sense efficiency standards that are saving American families and businesses hundreds of billions of dollars,” said Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz. “The set-top box efficiency standards will save families money by saving energy, while delivering high quality appliances for consumers that keep pace with technological innovation.”
DVR boxes are the biggest culprits. American DVRs typically use up to 50W regardless of whether someone is watching the TV or not. Most contain hard drives that are either powered on continuously or are shifted into an idle state that does more to protect the life of the drive than cut a consumer’s energy bill. A combination of a DVR and an extra HD set-top box together consume more electricity than an ENERGY STAR-qualified refrigerator-freezer, even when using the remote control to switch the boxes off.
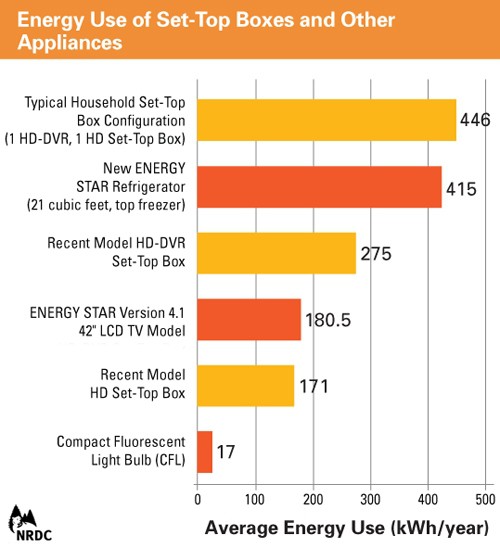
Manufacturers were never pressed to produce more energy-efficient equipment by the cable and satellite television industry. Current generation boxes often require lengthy start-up cycles to configure channel lineups, load channel listings, receive authorization data and update software. As a result, any overnight power-down would inconvenience customers the following morning — waiting up to five or more minutes to begin watching television as equipment was switched back on. As a compromise, many cable operators instruct their DVR boxes to power down internal hard drives when not recording or playing back programming, minimizing subscriber inconvenience, but also the possible power savings.
In Europe, many set-top boxes are configured with three levels of power consumption — 22.5W while in use, 13.2W while in standby, and 0.65W when in “Deep Sleep” mode. More data is stored in non-volatile memory within the box, meaning channel data, program listings, and authorization information need not be re-downloaded each time the box is powered on, resulting in much faster recovery from power-saving modes.
The new agreement, which runs through 2017, covers all types of set-top boxes from pay-TV providers, including cable, satellite and telephone companies. The agreement also requires the pay-TV industry to publicly report model-specific set-top box energy use and requires an annual audit of service providers by an independent auditor to make sure boxes are performing at the efficiency levels specified in the agreement. The Energy Department also retains its authority to test set-top boxes under the ENERGY STAR verification program, which provides another verification tool to measure the efficiency of set-top boxes.
Comcast, DirecTV, DISH Network, Time Warner Cable, AT&T, Verizon, Cox Communications, Charter Communications, Cablevision, Bright House Networks and CenturyLink will begin deploying new energy-efficient equipment during service calls. Some customers may be able to eventually swap equipment earlier, depending on the company.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WCCO Minneapolis Check Your Cable Box 6-27-11.mp4[/flv]
WCCO in Minneapolis reported in 2011 cable operators like Comcast may make subscribers wait 30 minutes or more for set-top box features to become fully available for use after plugging the box in. (1:50)


 Subscribe
Subscribe A Wall Street research firm is asking questions about the “mixed messages” AT&T is sending consumers over its broadband offerings.
A Wall Street research firm is asking questions about the “mixed messages” AT&T is sending consumers over its broadband offerings. AT&T says it intends to boost part of its Project VIP footprint to 75Mbps or 100Mbps with VDSL2 vectoring, but the extent of this is unknown. It has also deployed a small amount of GPON FTTH in greenfield markets, typically designed to support 80–100Mbps to each household. Also as part of Project VIP, it plans to reach 1 million businesses with symmetric 1Gbps FTTH.
AT&T says it intends to boost part of its Project VIP footprint to 75Mbps or 100Mbps with VDSL2 vectoring, but the extent of this is unknown. It has also deployed a small amount of GPON FTTH in greenfield markets, typically designed to support 80–100Mbps to each household. Also as part of Project VIP, it plans to reach 1 million businesses with symmetric 1Gbps FTTH. AT&T today announced it was selling off its residential wireline network in Connecticut to Stamford-based Frontier Communications for $2 billion in a deal that includes an expanded license for U-verse TV that could eventually be available to Frontier customers nationwide.
AT&T today announced it was selling off its residential wireline network in Connecticut to Stamford-based Frontier Communications for $2 billion in a deal that includes an expanded license for U-verse TV that could eventually be available to Frontier customers nationwide. Frontier’s acquisition will give the company hands-on experience with AT&T’s U-verse network in Connecticut and offer a path to bring improved service to Frontier customers elsewhere. Company officials also acknowledged a key reason for the transaction was boosting Frontier’s lagging dividend, a critical part of its share price. By taking on nearly 1,000,000 new customers, Frontier will boost its cash flow, returning some of that new revenue in a higher dividend payout to shareholders. But the company will take on an extra $2 billion in debt to manage higher dividend payouts.
Frontier’s acquisition will give the company hands-on experience with AT&T’s U-verse network in Connecticut and offer a path to bring improved service to Frontier customers elsewhere. Company officials also acknowledged a key reason for the transaction was boosting Frontier’s lagging dividend, a critical part of its share price. By taking on nearly 1,000,000 new customers, Frontier will boost its cash flow, returning some of that new revenue in a higher dividend payout to shareholders. But the company will take on an extra $2 billion in debt to manage higher dividend payouts. SNET began operations in 1878 as the District Telephone Company of New Haven and pre-dated the Bell System. The company founded the first exchange and printed the world’s first telephone directory. It remained independent of Bell System ownership until 1998, when SBC Communications (formerly Southwestern Bell) acquired the company. In late 2005, SBC purchased AT&T and AT&T Connecticut was born.
SNET began operations in 1878 as the District Telephone Company of New Haven and pre-dated the Bell System. The company founded the first exchange and printed the world’s first telephone directory. It remained independent of Bell System ownership until 1998, when SBC Communications (formerly Southwestern Bell) acquired the company. In late 2005, SBC purchased AT&T and AT&T Connecticut was born.

 AT&T has informed Google it will not allow the search engine company to use its utility poles to build a fiber optic network that will compete with AT&T’s own GigaPower fiber service, which launched in Austin this week.
AT&T has informed Google it will not allow the search engine company to use its utility poles to build a fiber optic network that will compete with AT&T’s own GigaPower fiber service, which launched in Austin this week.
