
Malone
Cable magnate John Malone has rarely had it this good at the expense of the U.S. Treasury. Using his vast wealth to hire some of the smartest tax advisers in the country, he has personally avoided hundreds of millions in U.S. taxes and shared the benefits of his tax tips with shareholders, who collectively stiffed the tax man out of more than a billion dollars in 2013.
As the Obama Administration fights with Republicans in Congress to close the loopholes, corporate executives and fellow billionaires routinely engage in tax avoidance schemes that shift their tax burden to ordinary Americans that cover the difference in the form of service cuts or higher taxes and fees to offset the lost revenue.
In 2013, Malone jumped on the “inversion” bandwagon, shifting the corporate address of Liberty Global, Inc. from Colorado to London, largely out of reach of the Internal Revenue Service.
Bloomberg News detailed Malone’s exploits over decades of “rich get richer” deals and the consequences of loopholes unavailable to most Americans that stay in the tax code at the behest of those who directly benefit from them.
Malone is fiercely protective of his $7.5 billion net worth, structuring investments, tax shelters, and end runs around tax laws in ways that often leave him with no tax liability at all.
 Not everyone can afford to move their assets overseas or set up complicated charitable trusts to shelter income, but the enormously wealthy Malone can. He recently passed Ted Turner as America’s biggest private landowner, owning 2.2 million acres of property in the United States, including more than 5% of the state of Maine.
Not everyone can afford to move their assets overseas or set up complicated charitable trusts to shelter income, but the enormously wealthy Malone can. He recently passed Ted Turner as America’s biggest private landowner, owning 2.2 million acres of property in the United States, including more than 5% of the state of Maine.
Malone spreads his vast wealth around — owning stakes in Liberty Media, Liberty Global, and Liberty Interactive, as well as pieces of News Corp., Viacom, Time Warner, Inc., QVC, Discovery Communications, the old Court TV, DirecTV, SiriusXM satellite radio, Barnes & Noble, and Expedia.com.
Malone’s influence over the U.S. tax code comes in part from his advocacy work as an unpaid director at the Cato Institute, a Libertarian think tank that lobbies Washington hard for lower taxes and deregulation.
Malone’s personal tax code is to avoid taxes at all costs and, where possible, let someone else pick up the tab.
Malone’s baseball team, the Atlanta Braves, was instrumental as part of Liberty Media’s deal to cash out its stake in Time Warner without paying a dime in capital gains tax. Malone walked away with $1.4 billion in tax-free cash and ownership of the baseball team. Atlanta taxpayers will be responsible for more than $300 million in costs to build the Braves a brand new stadium in the Atlanta suburbs.
SiriusXM satellite radio subscribers were notified this week of the latest rate increase, due by the end of this year.
What they may not know is Malone’s Liberty Media now owns and controls the satellite radio venture. In 2009, Malone invested $530 million in the struggling operation. But he also gained the benefits of SiriusXM’s $6 billion in tax losses that Malone used to offset taxes on Liberty’s future profits. As a fringe benefit, Malone has also boosted revenue by imposing regular rate hikes on SiriusXM customers.
Like many U.S. corporations, Malone’s various Liberty ventures store massive amounts of cash in offshore bank accounts, avoiding U.S. taxes. When Liberty contemplated tapping that offshore cash, it faced a U.S. corporate tax rate of 35 percent. So Liberty joined more than a dozen other U.S. corporations relocating overseas, avoid corporate taxes back home.
 Although the corporation escapes a tax bill, shareholders usually do not, subject to tax for shares converted from the old U.S.-based company to the new overseas entity. Faced with owing capital gains taxes at a rate of 23.8 percent, the day before the inversion was announced, Malone transferred almost $600 million of his shares to the Malone-controlled, tax exempt LG 2013 Charitable Remainder Unitrust, avoiding much of the tax. Not satisfied with the fact he still would owe tax on the remaining $260 million of his personal stake in Liberty, the company hired Shearman & Sterling LLP to devise a strategy to get Malone (and shareholders) off the hook for any tax liability.
Although the corporation escapes a tax bill, shareholders usually do not, subject to tax for shares converted from the old U.S.-based company to the new overseas entity. Faced with owing capital gains taxes at a rate of 23.8 percent, the day before the inversion was announced, Malone transferred almost $600 million of his shares to the Malone-controlled, tax exempt LG 2013 Charitable Remainder Unitrust, avoiding much of the tax. Not satisfied with the fact he still would owe tax on the remaining $260 million of his personal stake in Liberty, the company hired Shearman & Sterling LLP to devise a strategy to get Malone (and shareholders) off the hook for any tax liability.
They found one, turning the government’s own efforts to plug tax loopholes against itself, manufacturing income that would not only satisfy the IRS’ recently hardened rules, but also let Malone & Co. escape any British tax liabilities in their new home.
“Malone threw a multi-billion dollar left hook at the Treasury Department,” said Samuel C. Thompson, a law professor at Pennsylvania State University. “They didn’t see it coming.”
As has been so often the case, the IRS eventually closed the loophole, but only after Malone exploited it.
Malone’s defenders point out all of his creative tax strategies are perfectly legal, and he is only taking advantage of existing U.S. tax laws. Detractors note America’s wealthy and powerful have exercised disproportionate influence over how those laws are written, usually through well-funded think tanks, lobbying firms, and anti-tax astroturf efforts. Most Americans lack the resources to take advantage of loopholes and benefits that require sophisticated advisers prepared to withstand any scrutiny from the IRS.
An emboldened Liberty Global is even willing to publicly signal its next tax avoidance measure.
In a filing last April, Liberty disclosed that a U.S. subsidiary will pay at least $7 billion in tax-deductible interest to its new UK parent over the next decade. Such payments are known to tax lawyers as “earnings stripping,” because the big interest deductions strip profits out of the U.S., thus cutting any U.S. tax obligation.
The practice has become so common among inverted companies headquartered overseas, Democratic Sens. Charles Schumer and Richard Durbin authored a bill to ban the practice. It has gone nowhere in the legislature because of objections raised primarily by Republicans, who characterize loophole closing measures as disguised “tax increases” on business.
What is Malone doing with all the money he has successfully kept out of the hands of the U.S. Treasury? He bought an Irish castle and three major Irish hotel properties. He did it using a capital gains tax holiday offered by Ireland’s government to wealthy investors willing to buy Irish real estate and retain ownership for a minimum of seven years.
 While Comcast, Cox, Suddenlink, and a handful of other cable companies play games with usage caps and expensive broadband, Germany is getting some massive broadband speed improvements with no data caps, speed throttling, or rate increases.
While Comcast, Cox, Suddenlink, and a handful of other cable companies play games with usage caps and expensive broadband, Germany is getting some massive broadband speed improvements with no data caps, speed throttling, or rate increases.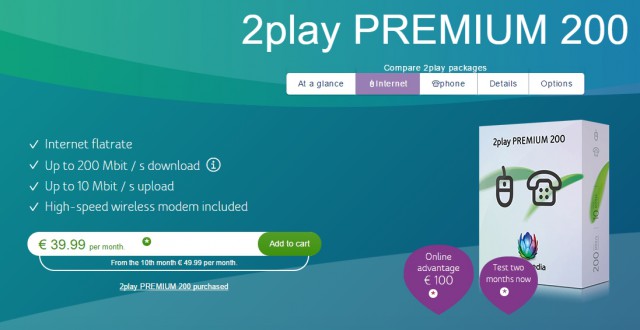


 Subscribe
Subscribe John Malone’s Liberty Global has bought out Puerto Rico’s second biggest cable television operator — Choice Cable TV — and will convert its customers to Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico.
John Malone’s Liberty Global has bought out Puerto Rico’s second biggest cable television operator — Choice Cable TV — and will convert its customers to Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico.
 The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
 The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets.
The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets. Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
 Not everyone can afford to move their assets overseas or set up complicated charitable trusts to shelter income, but the enormously wealthy Malone can. He recently passed Ted Turner as America’s biggest private landowner, owning 2.2 million acres of property in the United States, including more than 5% of the state of Maine.
Not everyone can afford to move their assets overseas or set up complicated charitable trusts to shelter income, but the enormously wealthy Malone can. He recently passed Ted Turner as America’s biggest private landowner, owning 2.2 million acres of property in the United States, including more than 5% of the state of Maine. Although the corporation escapes a tax bill, shareholders usually do not, subject to tax for shares converted from the old U.S.-based company to the new overseas entity. Faced with owing capital gains taxes at a rate of 23.8 percent, the day before the inversion was announced, Malone transferred almost $600 million of his shares to the Malone-controlled, tax exempt LG 2013 Charitable Remainder Unitrust, avoiding much of the tax. Not satisfied with the fact he still would owe tax on the remaining $260 million of his personal stake in Liberty, the company hired Shearman & Sterling LLP to devise a strategy to get Malone (and shareholders) off the hook for any tax liability.
Although the corporation escapes a tax bill, shareholders usually do not, subject to tax for shares converted from the old U.S.-based company to the new overseas entity. Faced with owing capital gains taxes at a rate of 23.8 percent, the day before the inversion was announced, Malone transferred almost $600 million of his shares to the Malone-controlled, tax exempt LG 2013 Charitable Remainder Unitrust, avoiding much of the tax. Not satisfied with the fact he still would owe tax on the remaining $260 million of his personal stake in Liberty, the company hired Shearman & Sterling LLP to devise a strategy to get Malone (and shareholders) off the hook for any tax liability.
