C Spire, a wireless phone company serving the southeastern United States today announced ambitious plans to deploy a gigabit fiber to the home network in the state of Mississippi, now considered to be one of the worst states for broadband speed and availability.
C Spire, a wireless phone company serving the southeastern United States today announced ambitious plans to deploy a gigabit fiber to the home network in the state of Mississippi, now considered to be one of the worst states for broadband speed and availability.
C Spire Fiber to the Home was introduced by company executives at a news conference this morning attended by community leaders. C-Spire intends to build a fiber network offering 1,000/1,000Mbps broadband, telephone and television service at a competitive price starting in 2014 in select communities in the state.
“As a brand that’s been pushing the envelope of innovation our entire existence, it’s only natural for us to want to provide the ‘what’s next’ to the customers we serve,” said Hu Meena, president and CEO of C Spire Wireless. “The ‘what’s next’ is now here and we’re ready to release the power of 1 Gig fiber to communities that want to experience the immediate and lasting benefits of 100 times the speed and 100 times the opportunities.”
C Spire will use its existing 4,000 miles of fiber optic infrastructure now providing backhaul connectivity to the company’s cell tower network and its commercial customers. An additional 1,500 miles of fiber is scheduled for installation next year.
The cell phone company will follow the lead of Google Fiber, giving Mississippi communities a chance to compete with one another for C Spire’s fiber network. C Spire will be accepting applications from neighborhoods, towns and cities in the state presenting their best case why they should be the first to get fiber to the home service. The communities that want it most, and move quickest, will get it first, promised company officials.
 C Spire claimed its proposed fiber to the home network will expand faster and deeper into Mississippi than Google Fiber’s limited network in Kansas City and nearby suburbs.
C Spire claimed its proposed fiber to the home network will expand faster and deeper into Mississippi than Google Fiber’s limited network in Kansas City and nearby suburbs.
“While we know some of the tangible benefits that fiber offers to individuals, families, businesses and entire communities, we’ve only scratched the surface of what’s possible with 100-times-faster Internet,” Meena said. “Similar to the transition from dial-up to broadband, no one could fathom that people would one day be able to shop online, download software and watch endless hours of video on YouTube. The undiscovered potential of fiber is what’s most exciting and compelling about our plans.”
Competing communities will be expected to explain how they intend to cut as much bureaucratic red tape as possible to win consideration. The company’s “Request for Information” (RFI) document prominently mentions “streamlined construction,” “advantageous access to public rights-of-way,” and “an attractive local franchise agreement” as the types of help most needed from local governments.
C Spire will likely not entertain franchise proposals that require the company to serve every possible resident. C Spire’s fiber business plan depends on rolling out the service only to neighborhoods where enough demand exists.
Other conditions:
- C Spire will not give away free service to schools or government buildings;
- Sizable local participation in the pre-registration process is required;
- The RFI hints that communities might be in a better position to win if they waive permit fees, issue permits within five business days, offer tax waivers, don’t require a local office for customer interaction, waive any “unacceptable ordinance provision or regulation as requested by C Spire,” and aid in rallying sign-ups for the fiber service.
Competitors, including AT&T, CableONE, Suddenlink, and Comcast may raise questions about local governments committing to rally for sign-ups. Some of those competing providers may also complain about their own franchise agreements, which often require widespread service deployment whether there is established demand for service or not.
C Spire is among a handful of companies that have recognized their existing fiber-to-cell-tower and institutional fiber broadband networks are underutilized and have the capacity to support both commercial and residential broadband applications.
C Spire is expected to announce the winning communities later this year or in early 2014.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/C Spire Fiber to the Home 9-24-13.mp4[/flv]
C Spire introduces Fiber to the Home service and explains the transformational benefits fiber broadband can deliver users. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
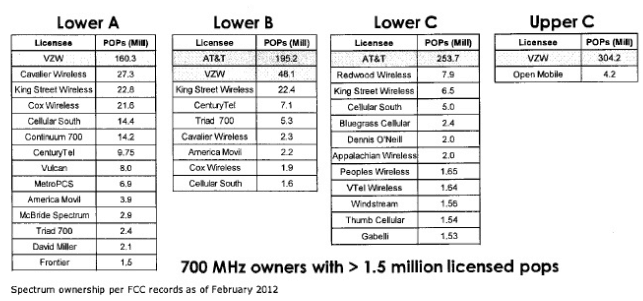
Subscribe Corr’s coverage area has not been a priority for larger carriers like Verizon Wireless and AT&T. The acquisition, which includes multiple PCS and 700MHz “C-Block” licenses, will bolster AT&T’s weak coverage in the region, which includes Huntsville, Oneonta, Decatur, Cullman, Hartselle, and Arab, Ala.
Corr’s coverage area has not been a priority for larger carriers like Verizon Wireless and AT&T. The acquisition, which includes multiple PCS and 700MHz “C-Block” licenses, will bolster AT&T’s weak coverage in the region, which includes Huntsville, Oneonta, Decatur, Cullman, Hartselle, and Arab, Ala.