 The Justice Department and FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler are prepared to accept a massive $55 billion merger between Charter Communications, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks, but at a cost of stringent conditions governing the creation of America’s second largest cable conglomerate.
The Justice Department and FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler are prepared to accept a massive $55 billion merger between Charter Communications, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks, but at a cost of stringent conditions governing the creation of America’s second largest cable conglomerate.
In a joint agreement with the U.S. Department of Justice and the FCC, Charter executives have agreed to do nothing to harm online video competition or implement usage caps or usage-based billing for at least seven years. Charter will also be forced to broaden its cable service to reach at least two million additional homes, some already served by other providers, setting the stage for potential head-to-head competition between two closely-matched competitors.
The deal will directly affect 19.4 million customers of the three companies, which will eventually combine under the Charter Communications brand name and marketing philosophy — selling customers simplified television, phone, and broadband packages that reduce customer options. Little is expected to change for the rest of 2016, however, with Time Warner Cable and Bright House likely to continue operations under existing packaging and pricing until sometime in 2017. Technicians told Stop the Cap! earlier in April they were told not to acquire new outfits with the Time Warner Cable logo and branding, and the cable company is also making preparations to gradually repaint its massive fleet of vans and service vehicles with the Charter logo.

Wheeler
Most of the concessions seemed to have originated from FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler, who has been one of the strongest proponents of online video competition, improved broadband, and direct head-to-head competition between cable operators. The Justice Department focused its attention on challenging the cable industry’s almost-united front against online video competition. Under former CEO Glenn Britt’s leadership, Time Warner Cable was considered “the industry leader” in contract language that guaranteed it would share the lowest price negotiated by any other cable, satellite, telephone company or online video provider. Those agreements also often included clauses that restricted programmers from putting streamed programming online for non-subscribers. That explains why cord-cutters frequently run into barriers watching networks online unless they can prove they are already a pay-TV customer.
Under conditions from the Justice Department, those sections of agreements with Charter, Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks will become invalid and unenforceable. But that doesn’t mean restrictions will disappear overnight. Comcast, Cox, Cablevision, and other cable companies also enforce similar conditions which will be unaffected by the Justice Department decision, at least for now. But the precedent has sent shudders across an industry concerned about protecting its still-profitable cable TV business, under assault from increased programming costs and a greater reluctance by consumers to tolerate annual rate increases.
 Gene Kimmelman, chief executive of consumer interest group Public Knowledge, told the Wall Street Journal the conditions were “a clear signal to the content industry and entertainment companies that the enforcement agencies are giving them a green light to grow online video and experiment as a direct competitor to cable, and they will prevent cable from interfering.”
Gene Kimmelman, chief executive of consumer interest group Public Knowledge, told the Wall Street Journal the conditions were “a clear signal to the content industry and entertainment companies that the enforcement agencies are giving them a green light to grow online video and experiment as a direct competitor to cable, and they will prevent cable from interfering.”
Of greater interest to consumers are the deal conditions proposed by Chairman Wheeler. As Stop the Cap! reported almost a year ago, sources told us the FCC would “get serious” about data caps if companies like Comcast imposed them on customers nationwide. At the moment, Comcast is testing caps affecting just under 15% of their total customer base, already generating thousands of customer complaints with the FCC in response. Although Charter promised three years of cap-free service, Wheeler and his staff obviously felt it was important to send a message that they agree with cap opponents that data caps are more about preventing competition than technical need. By making long term data cap prohibition a core part of a settlement agreement with Charter, Wheeler sends a strong message to Comcast that the FCC isn’t drinking cable industry Kool Aid about the rationale for usage caps and usage billing.

Some consumer groups worry Charter has overextended itself in debt over-acquiring other cable companies.
“New Charter will not be permitted to charge usage-based prices or impose data caps,” Wheeler said in a statement. “Second, New Charter will be prohibited from charging interconnection fees, including to online video providers, which deliver large volumes of internet traffic to broadband customers. Additionally, the Department of Justice’s settlement with Charter both outlaws video programming terms that could harm online video distributors (OVDs) and protects OVDs from retaliation– an outcome fully supported by the order I have circulated today. All three seven-year conditions will help consumers by benefitting OVD competition. The cumulative impact of these conditions will be to provide additional protection for new forms of video programming services offered over the Internet. Thus, we continue our close working relationship with the Department of Justice on this review.”
Wheeler is also intent on proving there is a viable market for cable operators overbuilding into new territories. To prove that point, Wheeler has gotten an agreement that Charter will introduce service to one million new customers where it will intrude on another operator’s service area and directly compete with it. The other provider has to already offer service at 25Mbps or greater. That could mean Charter competing directly with a cable company like Comcast or building service into an area already served by Verizon FiOS, AT&T U-verse, or another provider offering something beyond traditional DSL.

Copps
Another million customers just outside of areas served by the three cable companies may also finally get service, as Charter will be compelled to wire at least another million homes for cable service for the first time.
Despite the conditions, many consumer groups and former public officials remain unhappy the merger won approval.
“Creating broadband monopoly markets raises consumer costs, kills competition, and points a gun at the heart of the news and information that democracy depends upon,” said Michael Copps, a former Democratic commissioner at the FCC and a special adviser to the Common Cause public interest group. “FCC approval of this unnecessary merger would be an abandonment of its public interest responsibilities.”
“There’s nothing about this massive merger that serves the public interest. There’s nothing about it that helps make the market for cable TV and Internet services more affordable and competitive for Americans,” said Craig Aaron, president and CEO of Free Press. “Customers of the newly merged entity will be socked with higher prices as Charter attempts to pay off the nearly $27 billion debt load it took on to finance this deal. The wasted expense of this merger is staggering. For the money Charter spent to make this happen it could have built new competitive broadband options for tens of millions of people. Now these billions of dollars will do little more than line the pockets of Time Warner Cable’s shareholders and executives. CEO Rob Marcus will walk away with a $100 million golden parachute.”
Wheeler’s draft order is likely to receive a final vote in the coming days before the Commission. The only remaining holdout is California’s telecom regulator, which is expected to reach a decision by May 10.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications is in talks with Amazon.com about joining Comcast to pitch cable service to the online retailer’s giant customer base.
Charter Communications is in talks with Amazon.com about joining Comcast to pitch cable service to the online retailer’s giant customer base.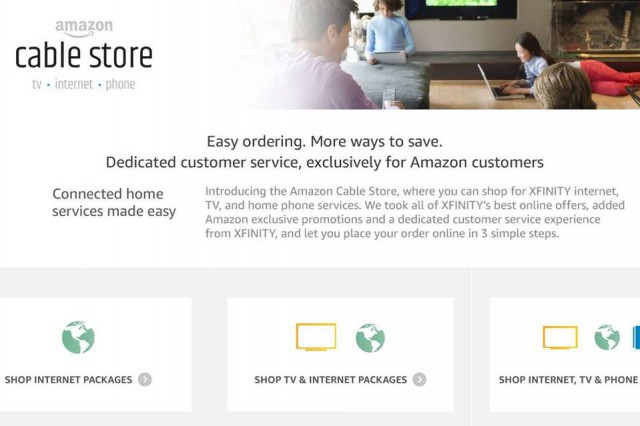


 The local hero? Rep. Art Swann (R-Maryville) who voted yes (
The local hero? Rep. Art Swann (R-Maryville) who voted yes ( Entrenched telecom industry lobbyists and a legislature enriched by their campaign contributions chose the interests of AT&T, Comcast, and Charter Communications over the broadband needs of rural Tennessee, killing a municipal broadband expansion bill already scaled down to little more than a demonstration project.
Entrenched telecom industry lobbyists and a legislature enriched by their campaign contributions chose the interests of AT&T, Comcast, and Charter Communications over the broadband needs of rural Tennessee, killing a municipal broadband expansion bill already scaled down to little more than a demonstration project.


