Time Warner Cable last week intimated the only thing keeping faster cable modem speeds from Kansas City customers is consumer demand and they are not worried about the arrival of Google Fiber’s 1Gbps broadband speeds.
Time Warner Cable last week intimated the only thing keeping faster cable modem speeds from Kansas City customers is consumer demand and they are not worried about the arrival of Google Fiber’s 1Gbps broadband speeds.
The cable operator claims they have the advantage in Kansas City, as the first provider to offer a triple play package of voice, broadband, and television service. Time Warner also says they are constantly working on new, innovative services, including the much-touted “tablet remote” the company says it already offers customers in Kansas City in the form of apps available on the Android and iOS platforms.
“We always have the ability to adjust our network to keep up with demands from consumers [for faster broadband speeds],” Time Warner Cable said.
Cable operators and phone companies have traditionally argued there is little consumer demand for gigabit broadband speeds because the services most customers access online don’t need or cannot support that level of speed. Cost has also usually been a factor, and many operators point out the majority of their customers are satisfied with speeds of 20Mbps or less.
“We’re ready to compete any day, anytime, anywhere, with anyone,” said Time Warner Cable spokesman Mike Pedelty.
 AT&T, which has been providing U-verse in parts of Kansas City since 2007 says it isn’t threatened by Google Fiber either.
AT&T, which has been providing U-verse in parts of Kansas City since 2007 says it isn’t threatened by Google Fiber either.
Chris Lester from AT&T Media Relations notes AT&T now offers U-verse to more than 400,000 households in and around Kansas City and claims the company has gotten a “great response” from consumers, but declined to specify exactly how many of those households have actually signed up for service.
Both the dominant cable and phone company in Kansas City are betting on subscriber loyalty and consumer resistance to change to maintain their subscriber numbers. Statistically, they have a good chance of holding most of their current customers, at least for now.
The threat of Google’s fiber fast speeds may not be limited only to Kansas City, however. The Wall Street Journal has learned Google may be intending to bring its fiber network to other American cities, as long as they are not already served by Verizon’s FiOS fiber-to-the-home network.
Incumbent cable operators facing new competition from phone company IPTV (AT&T U-verse, Verizon FiOS) have not lost as much business as they first anticipated. In most cases, only 25-35% of customers eventually left for a satellite or phone company competitor. The older the subscriber, the less likely that customer is to consider a change, unless the service is poor or the price becomes unaffordable.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KCTV Kansas City Competition for Google Fiber 7-26-12.mp4[/flv]
KCTV in Kansas City talks with AT&T and Time Warner Cable about their newest competitor. (2 minutes)

No cable operator has reported alarming results from subscriber defections, either from competition or cord-cutting behavior, and Wall Street analysts are watching subscriber numbers closely.
So far, reports on the ground indicate AT&T and Time Warner Cable are following the playbook first established when any new broadband provider arrives on their turf — aggressively market discounts tied to a contract with a stiff early termination fee to discourage customers from switching. At least one local provider has been reportedly sending salespeople door to door to try and lock customers in with a multi-year service contract. When that does not work, both companies use their customer retention departments to offer customers cheaper service in a last ditch effort to keep them from heading for the door.
Even with those defensive measures, some investors still see Google’s new fiber service as something new and different in the broadband marketplace — “the most disruptive thing since Gmail,” concludes Business Insider‘s Matt Rosoff.
Rosoff says Google Fiber could completely change the broadband landscape in the United States much the same way Gmail changed e-mail.
Back when Gmail launched, the other free email providers like Hotmail and Yahoo Mail were offering less than 5MB of storage — that’s five megabytes,” Rosoff writes. “Google trumped them all with 1GB of free storage. With so much storage, there was no need to trash anything. You could archive it and keep it forever.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Fox Business News Google Stirs It Up 7-26-12.flv[/flv]
Fox Business News explores Google Fiber and finds phone companies telling reporters consumers don’t need 1Gbps broadband. (2 minutes)
Gmail has since captured a large share of the email market, while also paving the way for Google’s increasingly profitable business apps. Some also argue Google’s “save everything online” approach was like training wheels for the cloud computing concept, where consumers think less about local storage and more about going online to access content. Google Fiber’s speeds make accessing online content effortless, and with no usage caps, customers need not ration their usage.
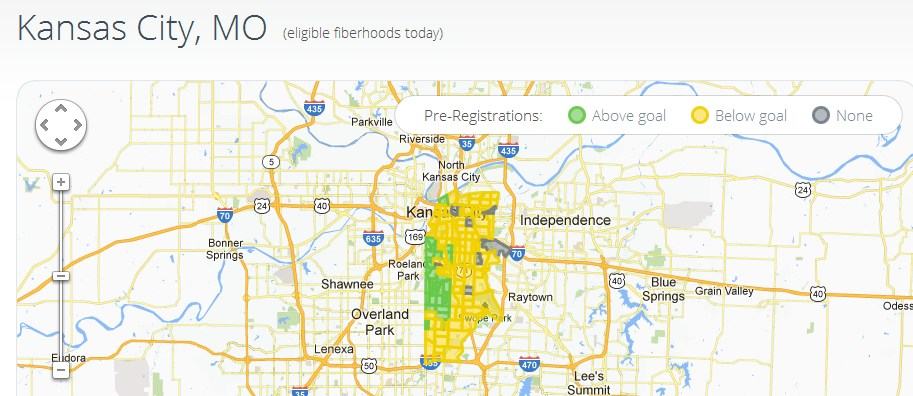
As of Monday, Google has already achieved the minimum number of needed homes to install Google Fiber in several, mostly affluent, Kansas City neighborhoods.
Rosoff says much like Gmail exposed the weaknesses of former email leaders like Hotmail, Google Fiber embarrasses incumbent Internet Service Providers and illustrates just how slow they have been to innovate.
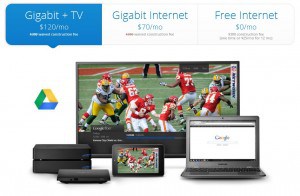
“Google Fiber makes the cable-based ISPs look pathetic,” says Rosoff. “It promises to offer speeds up to 1,000Mbps downstream and upstream, for only $70 a month.”
In comparison, Time Warner Cable charges $100 for 50/5Mbps service in Kansas City. AT&T’s U-verse can only offer up to 24/3Mbps service, and it charges well over $50 a month for that, except on a new customer promotion. Both Time Warner and AT&T also sell “lite use” packages from 1-6Mpbs for $20-25 a month — service Google intends to give away for free after a $300 installation fee.
Many industry observers suggest Google is using its new fiber network in part as a hedge against market abuse from dominant cable and phone companies who are fiercely opposed to Net Neutrality and favor monetizing broadband usage. Both are serious threats to Google’s business model which seeks more usage, not less. The more time consumers spend online, the more likely they will be exposed to a Google ad, use a Google product, or purchase a current or forthcoming service owned or partnered with the search engine giant.
Early indications from Kansas City show the cable and phone companies do have something to be concerned about. In more affluent areas of Kansas City, Google passed the minimum number of households willing to commit to the fiber service in just two days. Enthusiasm has been so overwhelming, tech entrepreneurs drooling for fiber service are hiring door-to-door promoters to visit nearby residents to encourage them to show their interest, in some cases even paying Google’s $10 pre-registration fee on their behalf.
More than 20 percent of the eligible “fiberhoods” in Kansas City, Mo. have already passed their signup goals. In poorer, mostly minority neighborhoods, Google is still waiting for their first pre-registration. In less affluent Kansas City, Kan., Google is finding considerably less interest, and pre-registrations are running below goal in all but three “fiberhoods.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WDAF Kansas City Competitors Gear Up For Google’s Challenge 7-26-12.flv[/flv]
WDAF says competing cable and phone companies cannot deliver the speeds Google Fiber will offer, but they are betting consumers don’t need or care about faster broadband speeds. (3 minutes)
 Subscribe
Subscribe