 Time Warner Cable executives brushed away Charter Communications’ first public offer to acquire the second largest cable company in the country in a debt-financed deal that Time Warner considers a lowball offer.
Time Warner Cable executives brushed away Charter Communications’ first public offer to acquire the second largest cable company in the country in a debt-financed deal that Time Warner considers a lowball offer.
“[Charter’s] proposal is grossly inadequate,” Time Warner Cable said in a statement. “We are confident in our standalone plan and we are not going to let Charter steal the company.”
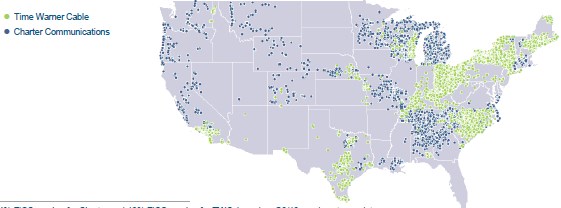
Charter’s combined service areas, if they win control of Time Warner Cable.
On Tuesday, Charter violated a long-standing, informal Code of the Cable Cartel that keeps cable companies from attacking each other.
 Charter Communications chief operating officer John Bickham launched an investor presentation that trashed Time Warner Cable and its leadership, and contended fixing the cable company will take more work than first envisioned.
Charter Communications chief operating officer John Bickham launched an investor presentation that trashed Time Warner Cable and its leadership, and contended fixing the cable company will take more work than first envisioned.
Bickham claimed Time Warner has exhibited a decade of a “failed operating strategy revealed by fact that they are losing customers at an alarming rate,” while Charter has a proven track record of performance.

Bickham
Historians recollect Charter’s recent past differently. In 2009, mired in debt and lacking a disciplined business plan, Charter declared Chapter 11 bankruptcy, wiping out shareholders and stiffing creditors.
Bickham capitalized on Time Warner’s 2013 summer of discontent, when a dispute with CBS resulted in the loss of the network from Time Warner Cable lineups (along with Showtime) in some of the biggest cities in the country. Combined with rate increases, subscribers began switching to the competition, especially where Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse gives cable operators stiff competition from money-saving new customer promotions.
Bickham described TWC as a company in shambles:
On Time Warner Cable TV: “It appears that Time Warner didn’t want to spend the money to go all-digital,” adding that the quality of TWC’s TV signal is poor and the company still lacks enough HD channels that could have been on the lineup if the cable company dropped analog service long ago.
On Time Warner Cable Internet: Bickham complained Time Warner is offering deep discounts on slow Internet packages, particularly its campaign targeting DSL customers with 2Mbps service for $14.99 a month. Bickham complains the large variety of Internet speed tiers are unnecessary, resulting in “nickel-and-dime charges to customers.” He argues Time Warner needs to simplify its offering by adopting a digital lineup and boost Internet speeds, so customers get at least 30Mbps service. Bickham did not mention Charter Communications also has a usage cap on its broadband products. TWC does not on most offerings.
On Time Warner Cable employees: “TWC never had a vision on high standards” for how the company manages its 50,000 employees. Bickham feels the workmanship of TWC installers leaves a lot to be desired.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Time Warner Cable Rejects Charter Offer 1-15-14.flv[/flv]
Time Warner Cable rejected an acquisition offer from Charter Communications valued at more than $61 billion including debt, spurning the biggest unsolicited takeover bid since 2008. Manus Cranny examines why the offer was rejected on Bloomberg Television’s “Countdown.” (2:06)
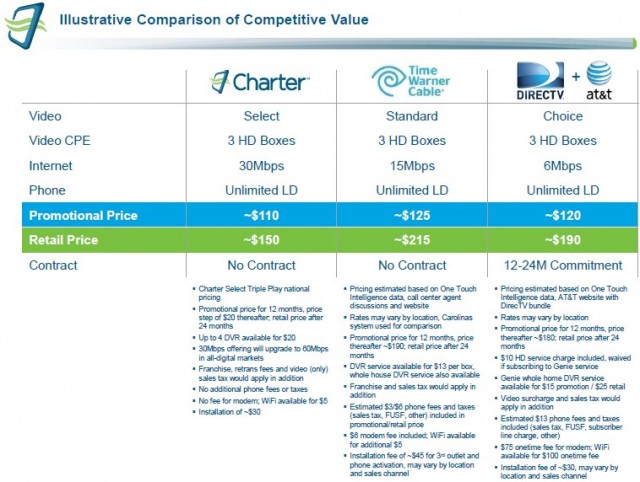
Charter’s proposed price comparison chart, produced for the benefit of Time Warner Cable shareholders, assumes worst-case pricing almost no Time Warner Cable customer actually has to pay.
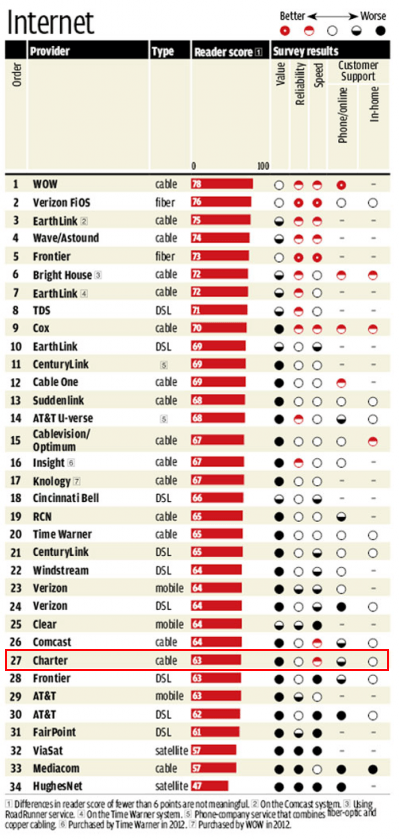
Charter is America’s second worst rated cable company. (Consumer Reports, 2013)
On its face, Charter’s plan for Time Warner Cable doesn’t look all bad, but execution is critical and Charter has a long-standing and very poor record of customer satisfaction, typically ranked in consumer surveys as America’s second worst cable operator year after year.
Should Charter win control of Time Warner Cable, big changes will be in store for TWC customers under the Charter umbrella:
- Analog television would be phased out, along with “limited basic” packages. Charter wants to repurpose analog spectrum for faster Internet speeds, but that also means video customers will be required to get more set-top boxes;
- Eliminate “Switched Digital Video” technology now in place on TWC systems. SDV is a bandwidth saver – only delivering digital TV signals customers in a particular neighborhood are actively watching. But those using inexpensive digital-to-analog set-top boxes on analog-only televisions can’t watch SDV channels, inconveniencing customers;
- Increase the number of HD channels to 200+;
- All residential set-top boxes would now support HD signals at no added cost and customers will be able to get up to four DVR boxes for $20 a month;
- Time Warner Cable’s new minimum Internet speed would be 30Mbps with much faster added-cost tiers available, but usage caps will apply;
- Time Warner Cable’s phone product would be repriced at $30 a month in the first year, $20 in the second with all calling features and voicemail included;
- No term contracts will be offered and modem rental fees, regulatory surcharges, added taxes on Internet and Phone, and service visit fees will no longer be charged.
Charter customers can expect aggressive sales pitches for their “high value” triple-play bundle which may include services customers don’t want at a price that is largely non-negotiable. The more boxes and services you add, the greater the discount you will receive. In contrast, Time Warner Cable began de-emphasizing its triple play promotions in early 2012 and now aggressively promotes single and double play packages that typically omit phone service.
Unlike TWC, Charter has been more difficult when trying to negotiate customer retention discounts. Charter generally charges the same prices everywhere.
Their proposed offer for Time Warner customers will be a triple play offer starting at $110 a month for the first 12 months, then increase $20 in the second year to $130 a month and in year three the price will rise again to $150 a month. Charter’s typical “step-up” pricing is in $20 increments.
Charter is reluctant to allow customers to add or drop package components, so for most customers packages will be all-inclusive with no discounts for dropping channels or features. That means customers will likely end up with more television channels, more phone features, and faster Internet speeds, but at the cost of an eventually higher cable bill.
Any buyout could also mean some Time Warner Cable territories could be put up for sale to a third-party. Charter is especially interested in the New York and Los Angeles markets, but may have little interest in western New York and Ohio, New England, Kentucky and Wisconsin. Any orphaned TWC customers would likely be snapped up by companies like Comcast, which may join Charter’s takeover bid.
Any sale would need approval by the Federal Communications Commission and potentially the Justice Department’s Antitrust Division, especially in Comcast becomes involved.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNBC Tom Rutledge Explains Charter Offer for TWC 1-15-14.mp4[/flv]
Time Warner Cable rejected a merger proposal from Charter Communications. Tom Rutledge, Charter Communications president and CEO, explains the offer as he describes as “rich and fair.” We feel like we’ve come a far way and have not received a serious response, Rutledge says. A CNBC exclusive. (4:35)
 “The future is a ring, a community ring connecting around the community that allows data to be transmitted both internally and externally,” said Fontenot.
“The future is a ring, a community ring connecting around the community that allows data to be transmitted both internally and externally,” said Fontenot.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Montana is among the bottom three states for Internet broadband performance and the state can partly blame Charter Communications for its poor service.
Montana is among the bottom three states for Internet broadband performance and the state can partly blame Charter Communications for its poor service. Comcast Corporation and Charter Communications are actively working on a deal to let Comcast acquire Time Warner Cable subscribers in New York, New England, and North Carolina, according to sources
Comcast Corporation and Charter Communications are actively working on a deal to let Comcast acquire Time Warner Cable subscribers in New York, New England, and North Carolina, according to sources  Comcast’s involvement in the deal could inject much-needed cash into a takeover bid financed largely by debt. It might also prompt Charter to sweeten its offer for TWC.
Comcast’s involvement in the deal could inject much-needed cash into a takeover bid financed largely by debt. It might also prompt Charter to sweeten its offer for TWC.
 $6.99 a month for one stream (SD only);
$6.99 a month for one stream (SD only); For Netflix, the increased revenue that can be earned by charging different rates for concurrent streams might prove a win-win proposition because many lurkers may be unwilling to buy their own account.
For Netflix, the increased revenue that can be earned by charging different rates for concurrent streams might prove a win-win proposition because many lurkers may be unwilling to buy their own account. Canadian investment analysts are recommending that Canada’s telecom giant Bell (BCE) should explore buying out Bell Aliant, Inc. the largest telephone company in the Maritimes, to further consolidate Canada’s telecommunications marketplace.
Canadian investment analysts are recommending that Canada’s telecom giant Bell (BCE) should explore buying out Bell Aliant, Inc. the largest telephone company in the Maritimes, to further consolidate Canada’s telecommunications marketplace. Time Warner Cable executives brushed away Charter Communications’ first public offer to acquire the second largest cable company in the country in a debt-financed deal that Time Warner considers a lowball offer.
Time Warner Cable executives brushed away Charter Communications’ first public offer to acquire the second largest cable company in the country in a debt-financed deal that Time Warner considers a lowball offer.
 Charter Communications chief operating officer John Bickham launched
Charter Communications chief operating officer John Bickham launched 


