
Verizon Wireless quietly admitted Tuesday its much-vaunted LTE network is suffering speed slowdowns so serious, some customers in New York, Chicago, and San Francisco are being randomly kicked off Verizon’s 4G network to slower 3G service until congestion eases.
Fran Shammo, Verizon’s chief financial officer, volunteered that online video was the likely culprit and he was surprised by usage growth well in excess of what Verizon predicted.
Current estimates from the company suggest Verizon’s LTE customers are responsible for 64% of all data traffic on Verizon’s wireless network nationwide. But in large cities, Shammo said traffic numbers are much higher.

Shammo
“There are certain pockets where we’re absolutely going to experience that down tick from the LTE network to 3G because of capacity constraints,” Shammo admitted.
The sudden revelation Verizon now has insufficient capacity for its LTE service is a significant reversal for Shammo, who has repeatedly told investors Verizon has enough wireless spectrum for the next 4-5 years.
In May 2013, Shammo told investors attending the JPMorgan Global Technology, Media and Telecom Conference:
As I have said before, our spectrum position right now is very good, with the AWS transaction that we completed with the cable carriers last year, with the sale of the spectrum that we are doing with AT&T later this year, obviously giving that spectrum to someone who can utilize it better than we can at this point in time. So I think our holdings are exactly where we need to be. And I have said before we really don’t need spectrum for the next four to five years, with the way that we deployed CDMA and how we will utilize that spectrum from our CDMA deployment over to the 4G network as we need it.
Later that same month, Shammo confidently repeated his assertion Verizon was all set for spectrum at Barclays Global Technology, Media and Telecommunications Conference:
Well, we have — from where we sit today, we have a very good spectrum portfolio which is why we went after the AWS spectrum, which is really going to be used for our capacity of LTE. The 700 megahertz that we have contiguous across the United States is used for the coverage piece. So we’re in pretty good shape for the next four to five years, even with reallocating our 3G spectrum over to our 4G network. […] And we think, look, we think that there will be enough spectrum there. We think that technology change — I mean, people are already talking about LTE advanced. Well, LTE advanced is nothing more than creating a bit more speed on the network. But really LTE advances around being able to utilize the spectrum much more efficiently within the network.
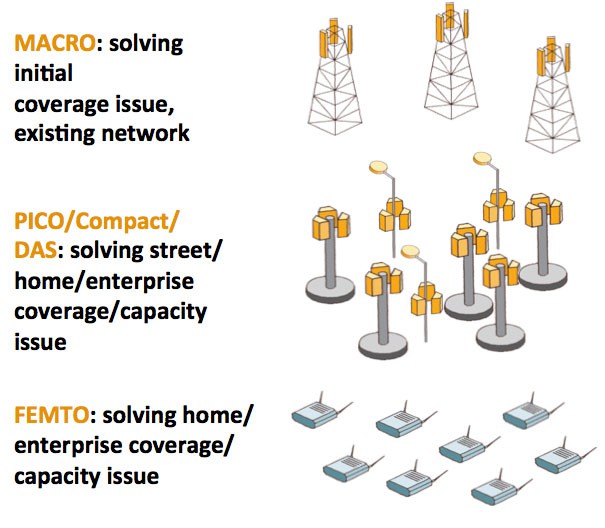
Carriers can boost coverage with more cell towers, street level picocells, or in-building femtocells.
Some critics suggest Verizon is ginning up a spectrum crisis as new FCC chairman Tom Wheeler begins to look at the current state of wireless spectrum and competition in the wireless industry. They also point to the fact Verizon has so much unused, warehoused spectrum, it has tried to sell the excess off to third parties.
“We have A band [unused spectrum] in our pocket today that we put for auction a year and a half ago and we did not get what we thought it was worth,” Shammo said yesterday. “We brought it back into the portfolio. But we can use that as a trade for some different spectrum. We put it up for auction so obviously it was on the block [and was] never taken off the block. But obviously it is not for fire sale. If a transaction makes sense then we will execute the transaction. If it doesn’t, then we will deploy it.”
In the short-term, Shammo promised customers the congestion issues were already being dealt with by “lighting up” acquired AWS spectrum formerly owned by cable operators, and adding data systems and small cell-type antennas in high congestion areas.
Shammo added that since Verizon was finished expanding its wireless network out to new, unserved areas, future investments would be directed at improving service within current coverage areas.
“I think by year-end you’re going to see us [concentrate] all of our CapEx around densification and then you will start to see us talk about things like VoLTE (Voice over LTE) and multicast (video) and some of these LTE advanced technologies that will come in the next year,” said Shammo.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Cord-cutting is a real, measurable phenomena and is especially common among those under 30 who don’t care about traditional cable television service.
Cord-cutting is a real, measurable phenomena and is especially common among those under 30 who don’t care about traditional cable television service.
 Are you getting the mobile broadband speeds your provider advertises for its whiz-bang 4G network? How do you know which carrier really delivers?
Are you getting the mobile broadband speeds your provider advertises for its whiz-bang 4G network? How do you know which carrier really delivers? AT&T has agreed to pay an extra $3.5 million in addition to the $18.25 million already paid to settle Justice Department claims the company knowingly overbilled the government for reimbursement of fraudulent international relay calls usually made by scammers originating from countries like Nigeria.
AT&T has agreed to pay an extra $3.5 million in addition to the $18.25 million already paid to settle Justice Department claims the company knowingly overbilled the government for reimbursement of fraudulent international relay calls usually made by scammers originating from countries like Nigeria.
