AT&T will pay $60 million to compensate unlimited data customers that found their data speeds throttled without warning because AT&T deemed them ‘heavy users’ that were slowing down AT&T’s wireless network.
AT&T will pay $60 million to compensate unlimited data customers that found their data speeds throttled without warning because AT&T deemed them ‘heavy users’ that were slowing down AT&T’s wireless network.
“AT&T baited subscribers with promises of unlimited data, trapped them in multi-year contracts with punishing termination fees, and then scammed them by choking off their access unless they moved to a more expensive plan,” claimed FTC Commissioner Rohit Chopra. “The AT&T throttling scandal is an important case study into how dominant firms operating without meaningful competition can easily renege on their contractual obligations and cheat consumers who have almost no recourse.”
The $60 million in compensation is part of a settlement with the Federal Trade Commission that accused the company of false and misleading advertising after marketing an unlimited data plan subject to severe speed reductions after as little as 2 GB of usage. AT&T also agreed to a permanent injunction forbidding the company from advertising unlimited data plans without clear disclosures that such plans were subject to speed throttling. AT&T will have to prominently disclose such limitations in the future and not in the fine print.
“AT&T promised unlimited data—without qualification—and failed to deliver on that promise,” said Andrew Smith, director of the FTC’s Bureau of Consumer Protection. “While it seems obvious, it bears repeating that Internet providers must tell people about any restrictions on the speed or amount of data promised.”
AT&T’s throttling came to light in 2011 after the company was found to be slashing “unlimited data” smartphone users’ speeds to as low as 128 kbps — roughly 2-3 times the speed of dial up data, after a customer reached 2 GB of usage during a billing month. The FTC claims over 3.5 million AT&T customers were subjected to AT&T’s speed throttle as of October 2014 when the federal agency filed a formal complaint against the wireless carrier.
 AT&T fought the FTC in and out of court for five years, claiming the FTC had no jurisdiction over its wireless business. The Ninth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals disagreed in 2018, when it ruled that the FTC did have jurisdiction to pursue its false advertising claims against the company. Observers believed this court ruling forced AT&T to move towards a settlement.
AT&T fought the FTC in and out of court for five years, claiming the FTC had no jurisdiction over its wireless business. The Ninth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals disagreed in 2018, when it ruled that the FTC did have jurisdiction to pursue its false advertising claims against the company. Observers believed this court ruling forced AT&T to move towards a settlement.
AT&T’s past and current wireless customers targeted for speed throttling will automatically receive compensation without having to file a claim. The settlement provides customers throttled to 128 kbps an equal share of $13.8 million set aside to compensate current and former customers for the loss of value of their unlimited plan, plus interest. Those throttled to 256 or 512 kbps will split $46.2 million. Current customers will be provided a bill credit, former customers will receive a check in the mail, assuming AT&T can locate your current address. Any unclaimed funds will be sent to the FTC and will not be kept by AT&T. Customers can expect refunds within the next 90 days.
Wireless carriers selling “unlimited data” routinely bury restrictions on such plans in their fine print. Most limit customers to between 20-50 GB of usage per month, after which the company reserves the right to dramatically reduce your data speeds until the next billing cycle begins. The FTC is increasingly concerned that advertising unlimited service while burying important restrictions in the fine print is false advertising. The FTC is sending a message to wireless companies it wants hidden disclosures stopped.
The Commission vote approving the stipulated final order was 4-0-1. Commissioner Rebecca Kelly Slaughter was recused.
FTC Commissioner Deepak Chopra issued a scathing statement about how AT&T does business:
Chopra
AT&T’s Nationwide Bait-and-Switch Scam
When any business, big or small, offers an unlimited service for a fixed fee, that business is taking a risk. If customers use much more of the service than projected, the company will take a hit. Conversely, if customers use less than projected, the company will haul in even larger profits. This is how business works.
As detailed in the Commission’s complaint, AT&T wanted the rewards without the risks, so it turned its offer of an “unlimited” data plan into a bait-and-switch scam that victimized millions of Americans.
Subscribers were lured in with promises of unlimited data service for a fixed fee, trapped into multiple years of service by punitive termination fees, and then forced to switch to a more expensive tiered plan with overage fees to actually receive the unlimited data they were promised.
This scam went hand-in-hand with AT&T’s early monopoly in the iPhone market. In 2007, Apple and AT&T inked a major deal that gave purchasers of the iPhone only one choice for a mobile carrier.
Around this time, AT&T faced a major threat to its wireless business: the company was losing exclusivity over the iPhone. Analysts warned that the company could be “demolished,” potentially losing millions of customers to Verizon.
To prevent this from happening, AT&T aimed to lock down existing subscribers into new long-term contracts by “grandfathering” them in to their unlimited plans when they upgraded their phones. Since data usage can be unpredictable and hard to track, an unlimited plan without risk of overage fees created certainty for cost-conscious consumers.
How low can AT&T go? Some wireless customers were throttled to 128 kbps speed after using just 2 GB of data on their AT&T Unlimited Plan.
AT&T is a sophisticated company. It knew it needed to invest in enough capacity to deliver service for subscribers who used a lot of data under their unlimited plans, especially since the company had claimed its network was the “fastest” in the nation.
Instead of living up to its promises, AT&T pulled a bait-and switch.
First, to hold on to customers who might switch to the competition, AT&T marketed an unlimited data plan that was not actually unlimited. AT&T subscribers who signed up for newer phones with unlimited service were likely those who intended to use the most data. Instead, these subscribers were throttled the most, and ended up receiving the slowest, most unreliable data coverage.
According to the FTC’s complaint, roughly 3.5 million customers victimized by AT&T’s fraud saw their speeds go down by up to 95 percent. The iPhone’s internet-intensive functions were practically unusable on AT&T’s network at the diminished speeds. This Swiss-cheese service was not the unlimited deal that was promised. Americans in rural areas without broadband connections, as well as those who depended on the service for their livelihood, got a particularly raw deal.
Second, AT&T made it hard to walk away, trapping subscribers in contract terms. Until 2011, AT&T was the only carrier offering the iPhone and the only network the iPhone worked on. As the exclusive iPhone carrier, AT&T dictated the terms of access, which included signing long-term contracts with big penalties for leaving early. After AT&T lost iPhone exclusivity, new carriers entered the market promising better coverage. But most existing iPhone users were stuck with AT&T until their contracts ran out, unless they paid the expensive early termination fee. And when their contracts did run out, AT&T induced them to renew with false promises of “unlimited” service.
Third, AT&T pushed subscribers into switching to more expensive plans. AT&T allocated the most data and most reliable service to capped data plans with overage fees, while imposing arbitrary limits on subscribers in “unlimited” plans. Unlimited data subscribers who wanted reliable service could pay a big fee to switch carriers, or they could switch for free to a capped data plan with no throttling. While these plans might have been cheaper upfront than the unlimited plan, their low data cap, the high cost of overages, and the expanding capabilities of smartphones made a service price hike inevitable for Americans who wanted what they signed up for. The only truly unlimited data service was therefore available solely through capped plans with expensive overages.
AT&T’s bait-and-switch scam is a good window into the many harms that result from dominant companies operating without the discipline of meaningful competition. Their market power, financial resources, and one-sided information gives them license to ignore their own contractual obligations while aggressively enforcing every little clause in the fine print. Consumers can accept the bad deal, walk away, or fight it, but each choice carries a cost, with dominant firms prevailing almost every time.
In my view, AT&T profited by using its dominance to force customers to keep their end of the deal even as the company failed to deliver and then changed the terms. AT&T’s unlimited data subscribers could have kept paying for limited, unreliable service, paid the penalty to switch to a carrier with better service, or paid a price hike to get the unlimited data service they had been promised. But none of those are good options.
Wireless companies are spending more money on stock buybacks than they are investing in their networks.
AT&T’s broken promises were not inevitable. The company could have upheld its obligations to its customers by making the right infrastructure investments. It certainly had the money to do so. From 2011 to 2015, AT&T paid tens of billions of dollars in dividends and share buybacks. In 2012, as the company boasted to investors that customers were fleeing its unlimited plan for tiered plans, it spent more on share buybacks than it invested in its wireless network. The bottom line is that AT&T fleeced its customers to enrich its executives and its investors.
Scrutiny for Scammers of All Sizes
The FTC sued AT&T in 2014, and an exceptional group of staff litigators racked up big wins in this case. Our staff even prevailed in the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals, when AT&T tried to sidestep accountability for this massive fraud by claiming it was immune from the FTC’s oversight. I am extremely grateful to our litigators and investigators who persisted, and I am glad to see money being returned to consumers. No settlement is perfect. While I would have liked to see AT&T pay more for the company’s scheme, I fully appreciate the risks and resources associated with litigation.
There are also important lessons from this matter that I hope the entire agency can learn.
Scammers come in all sizes. During my tenure as a commissioner, I have raised concerns about disparate treatment of small firms, where the agency is quick to call out their fraud and where resolutions can include crippling consequences and individual liability. In contrast, the agency is quick to deem large firms as “legitimate” and apply a more soft-touch approach. AT&T’s massive scam is a reminder that we must focus on the practices of a business, rather than the size of a business.
Rigorous analysis yields better results. The Commission must do more to support our litigators and investigators with rigorous analysis of the many ways that companies profit from illegal conduct.
Commission economists typically develop estimates of consumer injury, but this is just one facet of the relief we can seek in court. Economic analysis of consumer injury is not a complete financial analysis, so we must be wary of overly relying on this narrow methodological approach. To arm our litigators effectively, we must conduct rigorous financial analysis that goes beyond the out-of-pocket losses that consumers experience. We also need to ensure we conduct a comprehensive review of a firm’s business model, which can allow us to assess what led to the wrongdoing in order to inform what injunctive relief we should pursue.
It will be critical for the Commission to closely scrutinize AT&T’s moves under order. If the company violates any aspect of this settlement, the agency should seek a contempt judgment in federal court and hold both the company and any appropriate individuals responsible for flouting the order. Given AT&T’s aggressive enforcement of arbitration clauses that ban consumers from taking the company to court, it is critical to be vigilant in our oversight of AT&T under this order.
Conclusion
If consumers don’t pay up when a company fails to live up to its promises, they are often pummeled with late fees, collection calls, and negative credit reporting. Yet when dominant companies don’t deliver on their end of the bargain, too often they can turn a profit, as their customers feel powerless to do anything about it. Cheating is not competing. Without effective government and private enforcement, we will not achieve all of the benefits that competitive markets can deliver.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 T-Mobile is gradually expanding its new fixed wireless home broadband service, prioritizing rural areas next to major highways where the mobile provider has strong 4G LTE service.
T-Mobile is gradually expanding its new fixed wireless home broadband service, prioritizing rural areas next to major highways where the mobile provider has strong 4G LTE service.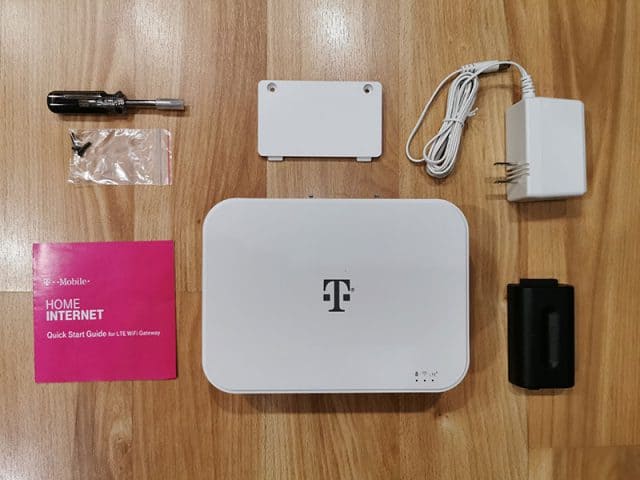
 Many of the same civil rights groups that regularly advocate their support of giant corporate telecom mergers are back once again to
Many of the same civil rights groups that regularly advocate their support of giant corporate telecom mergers are back once again to  In a joint statement, the groups urged the FCC to approve the T-Mobile/Sprint merger “so the combined New T-Mobile can definitively launch these enhanced diversity efforts and expansion of service to all communities included in the MOU.”
In a joint statement, the groups urged the FCC to approve the T-Mobile/Sprint merger “so the combined New T-Mobile can definitively launch these enhanced diversity efforts and expansion of service to all communities included in the MOU.”

 WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018.
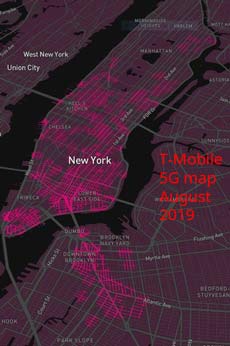
WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018. Verizon and T-Mobile are redlining their up and coming 5G wireless services to target wealthy neighborhoods and business districts while shunning the urban poor.
Verizon and T-Mobile are redlining their up and coming 5G wireless services to target wealthy neighborhoods and business districts while shunning the urban poor.