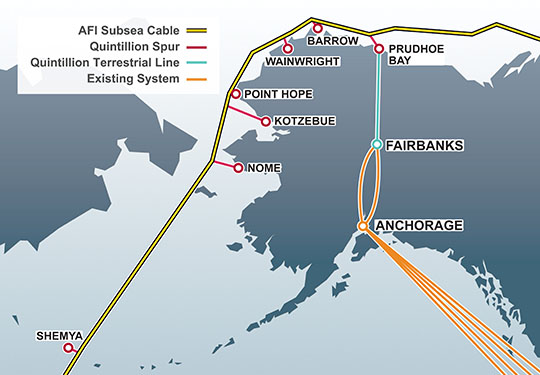
Quintillion, a new underseas fiber provider, is expected to vastly expand Alaska’s internet backbone, but there are not enough terrestrial middle mile networks to allow all Alaskans to benefit.
A federal taxpayer-funded effort to improve broadband access in rural Alaska will instead improve the bottom lines of Alaska’s telecommunications companies who helped collectively “consult” on a plan that will pay $365 million in taxpayer subsidies to companies building profitable and often redundant 4G wireless networks.
The Alaska Plan, which took effect Nov. 7, is a decade-long effort to subsidize telecom companies up to $55 million annually to encourage them to expand broadband service to 134,000 Alaskan households that get either no or very little internet service today. The Alaska Telephone Association (ATA) — an industry trade association and lobbying group, claims if the plan is successful, only 758 Alaskans will still be waiting for broadband by the year 2026.
But critics of the plan claim taxpayers will give millions to help subsidize private telecom companies that have plans to spend much of the money on redundant, highly profitable 4G wireless data networks that will cost most Alaskans large sums of money to access.
One company — AT&T, which refused to participate in the plan, is still taken care of by the plan, receiving $15.8 million dollars from taxpayers for doing absolutely nothing to improve broadband service in Alaska. The plan directs the money to AT&T to provide phase-down, high-cost support, which drew a sharp rebuke from Republican FCC commissioner Ajit Pai, who questioned why taxpayers had to subsidize AT&T for anything.
“The order claims this a ‘reasonable’ accommodation but cannot explain why the nation’s second largest wireless carrier needs ‘additional transition time to reduce any disruptions,’” Pai wrote.
 The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
Instead of subsidizing the development of middle mile networks for this purpose, the authors of The Alaska Plan have instead favored wireless connectivity, including the very lucrative 4G wireless networks cellular providers want to expand. By definition, the broadband plan accommodates the limitations of wireless by easing broadband speed requirements for providers. To earn a subsidy, providers need not offer the FCC’s minimum speed to qualify as broadband — 25Mbps.
 Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Commissioner Pai complained those are broadband speeds reminiscent of the internet a decade ago and hardly represents a vision for a faster future.
In a rare moment of bipartisanship at a divided FCC, Commissioner Mignon Clyburn joined Commissioner Pai dissenting from Alaska’s plan.
“It is clear that Alaska’s ‘majestic geography’ makes deployment difficult, but without affordable middle-mile connectivity, high-cost program support spent on the last mile does little to improve communications service to Alaskans,” Clyburn wrote. “Commissioner Pai and I supported an approach that would have taken the $35 million a year in duplicative universal service money and use[d] it to support a middle-mile mechanism that would enable many Alaskans in the Bush to receive broadband for the very first time. The status quo is simply not good enough, and the cost of doing nothing is far too high.”

Pai
Both Clyburn and Pai also complained federal tax dollars will be used to build duplicative 4G wireless networks that will primarily benefit providers. From Commissioner Clyburn’s statement:
We do not subsidize competition. We do not provide duplicative high-cost support to carriers in the same area and we do not subsidize carriers where other unsubsidized carriers are providing service. That underlying principle should be applied here as well. With Alaska’s “sublime scale,” we should instead be directing support to areas that are unserved, not subsidizing competition in areas that already receive mobile service. And just what is the cost to the American consumer of continuing to support overlap in these areas? About $35 million a year!
The companies benefiting from federal tax subsidies include: ASTAC, Copper Valley Wireless, Cordova Wireless, GCI, OTZ Wireless, which covers Northwest Alaska, TelAlaska Cellular, covering Interior and Northwest Alaska, and Windy City Cellular, covering Adak.

Clyburn
Pai called many of the spending priorities a waste of money that will still leave 21,000 Alaskans without 4G LTE broadband and another 46,000 without 25Mbps fixed broadband:
All together these wasted payments total $365 million, or about one quarter of the total Alaska Plan pot. That’s $365 million that could be used to link off-road communities to urban Alaska as requested by the Alaska Federation of Natives, the Bering Straits Native Corporation, the Chugachmiut rural healthcare organization, and many others. That $365 million is more than eight times the $44 million grant from the Broadband Initiatives Program that launched the TERRA Southwest middle-mile network that connected 65 off-road communities in 2011.
With the federal government now pouring federal tax dollars into Alaskan broadband, the state government has been using that as an opportunity to slash state investments in internet access.
A bill from Rep. Neal Foster (D-Nome) to upgrade all rural school districts to 10Mbps broadband for $6.2 million died in committee without any hearings, according to the Alaska Commons. State Rep. Lynn Gattis (R-Wasilla) proposed killing a $5 million broadband grant to schools, and the House Education subcommittee also recommended eliminating the Online with Libraries (OWL) program. Both programs ultimately survived, but not before the state legislature significantly cut the budgets of both programs.

Guttenberg
State Rep. David Guttenberg (D-Fairbanks) hopes the results from last week’s election in Alaska will allow him to position stronger broadband-related legislation in the state legislature.
Guttenberg wants to reinstate a long-cut Broadband Task Force and Working Group while also creating a public Broadband Development Corporation that would build and own middle mile broadband infrastructure and sell it to telecommunications companies that have refused to build those types of networks on their own.
A lot of members of the ATA are lining up in opposition, the newspaper notes, because they won’t directly own the infrastructure. Guttenberg’s view is that the needs of the many outweigh the needs of deep-pocketed telecom companies.
“If you want to build a strong state, if you want to build a strong community, we need to start putting those pieces together,” Guttenberg said of broadband infrastructure last year. “If you give a kid a laptop or a pad in a school district, it’s pointless if he can’t get online.”



 Subscribe
Subscribe Starting tomorrow, new customers signing up for AT&T’s 100+ channel streaming television package will pay $60 a month, up from the $35 promotional price AT&T has been advertising during the holidays.
Starting tomorrow, new customers signing up for AT&T’s 100+ channel streaming television package will pay $60 a month, up from the $35 promotional price AT&T has been advertising during the holidays.


 The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point. Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.


 At least 54,000 Time Warner Cable customers downgraded or canceled their cable TV service in the last three months as Charter Communications continues to take a harder line on offering or renewing customer retention discounts for customers unhappy with their bill.
At least 54,000 Time Warner Cable customers downgraded or canceled their cable TV service in the last three months as Charter Communications continues to take a harder line on offering or renewing customer retention discounts for customers unhappy with their bill.

 Rutledge made clear that despite any product changes or rebranding, the long term goal of Charter Communications is to see revenue grow. Whether that will come from gradual repricing of cable products and services to a higher rate or from improved products and services that attract new upgrade business is not yet certain. But Rutledge outlined key areas Charter expects to focus on in the next few years:
Rutledge made clear that despite any product changes or rebranding, the long term goal of Charter Communications is to see revenue grow. Whether that will come from gradual repricing of cable products and services to a higher rate or from improved products and services that attract new upgrade business is not yet certain. But Rutledge outlined key areas Charter expects to focus on in the next few years: