Ajit Pai Starts FCC Chairmanship by Clear-Cutting Pro-Consumer Policies, Cheap Internet for the Poor

Pai
Like President Donald Trump, Ajit Pai is a busy man. He’s spent his first month as FCC chairman gutting his predecessor’s legacy, reversing pro-consumer policies, ending forays into set-top box competition, fair pricing for inmate phone calls, cheap internet access for the poor, ending reviews of data caps and zero rating practices, and threatening to terminate Net Neutrality with extreme prejudice.
No wonder Bob Quinn, AT&T senior executive vice president of external & legislative affairs applauded President Trump’s appointment of Pai, proclaiming he will “quickly and decisively put back in place the commonsense regulatory framework necessary to support the President’s agenda for job creation, innovation and investment. We look forward to working with him and his team and the FCC to support President Trump’s growth agenda.”
AT&T’s only growth agenda is sending customers ever-increasing bills, and with Mr. Pai at the helm of the FCC, they are sure to get their wish.
Over their terms at the FCC under the Obama Administration, Republican Commissioners Ajit Pai and Michael O’Rielly frequently complained their minority voices on the Commission were ignored and newly proposed regulations or policies would come before the FCC so quickly, there was inadequate time for public review. But since Pai teamed up with O’Rielly to abolish many of the most important achievements of his predecessor, Chairman Thomas Wheeler, they have reportedly all but ignored the sole remaining Democrat currently serving on the Commission — Mignon Clyburn.
Last Friday, Clyburn accused Pai of hypocrisy for complaining about policies being rushed for a vote without explanation before doing the same thing himself late last week.

Clyburn
“Today is apparently ‘take out the trash day.’ In an eponymous episode of the West Wing, White House Chief of Staff Josh Lyman stated: ‘Any stories we have to give the press that we’re not wild about, we give all in a lump on Friday . . . Because no one reads the paper on Saturday,'” Clyburn said in a statement. “Today multiple Bureaus retract—without a shred of explanation—several items released under the previous administration that focus on competition, consumer protection, cybersecurity and other issues core to the FCC’s mission. In the past, then-Commissioner Pai was critical of the agency majority for not providing sufficient reasoning behind its decisions.”
Clyburn’s office asked for more than the allotted two days to review a dozen items that suddenly appeared on the FCC’s agenda.
“We were rebuffed,” Clyburn wrote.
Clyburn then accused Pai of violating the Administrative Procedure Act, which requires adequate public notice and a comment period for public input. When she asked the chairman to comply with the “reasoned decision-making requirements of the APA,” she was told ‘No deal.’
Mr. Pai’s regulatory rollback agenda has moved with breathtaking speed, according to some FCC observers. Consumer group Free Press today called Pai’s progress “Orwellian.” Over less than a month, Pai — with the help of Commissioner O’Rielly — has:
 Announced the formation of a Broadband Deployment Advisory Committee that is expected to be stacked with industry stakeholders that will recommend reform the FCC’s pole attachment rules, identify “unreasonable” regulatory barriers to broadband deployment, encourage local governments to adopt “deployment-friendly” policies, and develop a “model code” for local franchising, zoning, permitting, and rights-of-way regulations for telecom infrastructure like cell towers. Few expect the eventual “model code” to stray far from Big Telecom companies’ wish lists;
Announced the formation of a Broadband Deployment Advisory Committee that is expected to be stacked with industry stakeholders that will recommend reform the FCC’s pole attachment rules, identify “unreasonable” regulatory barriers to broadband deployment, encourage local governments to adopt “deployment-friendly” policies, and develop a “model code” for local franchising, zoning, permitting, and rights-of-way regulations for telecom infrastructure like cell towers. Few expect the eventual “model code” to stray far from Big Telecom companies’ wish lists;- Near-unilaterally loosened rules allowing AM radio stations to continue making their presence felt on the overcrowded FM band through the use of low-power FM “translator” stations that rebroadcast the AM station’s programming;
- Changed FCC policies to give broader notice of upcoming agenda items and policy proposals, ostensibly to improve public access to FCC rulemaking procedures. But observers suggest the change will primarily benefit industry lobbyists who will have advance detailed notice about the FCC’s upcoming agenda items, allowing them time to lobby for or against the proposals, or suggest changes;
- Rescinded “Improving the Nation’s Digital Infrastructure,” a policy paper promoting rural broadband deployment and other broadband improvements released just prior to the inauguration of President Trump. On Feb. 3, the FCC set “aside and rescinds the Digital Infrastructure Paper, and any and all guidance, determinations, recommendations, and conclusions contained therein. The Digital Infrastructure Paper will have no legal or other effect or meaning going forward.”
- Rescinded “in its entirety and effective immediately, earlier guidance provided in a March 12, 2014, public notice, DA 14-330, “Processing of Broadcast Television Applications Proposing Sharing Arrangements and Contingent Interests,” which attempted to limit ongoing media consolidation controversies including allowing one TV station to effectively operate and provide content for so-called ‘competing’ stations in a local area.
- Closed the FCC’s investigation into wireless carriers’ zero-rating policies, which allow subscribers free access to “preferred provider content” without it counting against their data plan. Critics call zero rating an end run around Net Neutrality, because providers treat their own content as “preferred.” AT&T charges other content providers to participate in its zero rating program.
- Instructed the FCC’s legal team to stop defending court challenges to its authority to ensure fair and reasonable telephone rates for incarcerated prisoners held captive to using a single carrier to make phone calls at prices much higher than what the public pays. Those rates were as high as $5.70 for a 15-minute in-state collect call placed from an incarceration facility in Kentucky. In that state alone, consumers effectively paid $2.79 million in kickbacks to state prison systems or a county jail. In contrast, a similar 15-minute call placed from a West Virginia jail or prison would cost $0.48. As a result of Pai’s actions, companies like Global Tel*Link, Securus, and Telmate “can continue the practice of price gouging prisoners and their families,” according to Prison Phone Justice;
- Ended former FCC Chairman Wheeler’s attempt to force competition in the cable set-top box marketplace, allowing consumers to take a bite out of the $20 billion cable companies make in rental fees annually. At least 99% of subscribers now pay an average of $231 a year to lease the boxes, even after the company has fully recouped their original cost. Customers in Canada can buy their own set-top boxes and DVRs.
- Killed an expansion of the FCC’s Lifeline program to offer discounted internet access to the poor. Pai reversed approvals made to nine providers — none accused of waste, fraud, or abuse — including Kajeet, Spot On, Boomerang Wireless, KonaTel, FreedomPop, Applied Research Designs, Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico, Northland Cable Television and Wabash Independent Networks. Pai later defended the move claiming his predecessor rushed through approval of the providers and he was rescinding those “midnight rules” as current chairman. Many Republicans are seeking a complete elimination of the Lifeline program.
- Rescinded the latest progress report on modernizing the Universal Service Fund’s E-Rate program, which is designed to subsidize telecom services for schools and libraries. It could be the first step in eliminating or dramatically reforming the Fund;
- Gave two violators of the FCC’s rules on properly collecting and reporting information about the source of political advertising aired on stations air a free pass.
- Threw out a white paper from the FCC’s own Homeland Security Bureau advising the agency on cybersecurity issues. Pai doesn’t think the FCC should be involved in cybersecurity, so anything contrary to his agenda of reducing the role of the FCC is likely destined for the nearest wastepaper basket.

FCC letter to AT&T’s Bob Quinn letting him know the company is off the hook with the FCC on zero rating.
“Ajit Pai has been on the wrong side of just about every major issue that has come before the FCC during his tenure,” said Craig Aaron, president of Free Press. “He’s never met a mega-merger he didn’t like or a public safeguard he didn’t try to undermine. He’s been an inveterate opponent of Net Neutrality, expanded broadband access for low-income families, broadband privacy, prison-phone justice, media diversity and more. If Trump really wanted an FCC chairman who’d stand up against the runaway media consolidation that he himself decried in the AT&T/Time Warner deal, Pai would have been his last choice — though corporate lobbyists across the capital are probably thrilled.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Higher bills, confusing and conflicting services and pricing, and badly trained customer service representatives are just a few of the problems afflicting customers transitioning from Bright House Networks and Time Warner Cable to service plans being gradually introduced around the country by Charter Communications/Spectrum. Stop the Cap! has collected more than 50 reports from customers experiencing problems, bill shock, lost access to Wi-Fi hotspots, and
Higher bills, confusing and conflicting services and pricing, and badly trained customer service representatives are just a few of the problems afflicting customers transitioning from Bright House Networks and Time Warner Cable to service plans being gradually introduced around the country by Charter Communications/Spectrum. Stop the Cap! has collected more than 50 reports from customers experiencing problems, bill shock, lost access to Wi-Fi hotspots, and 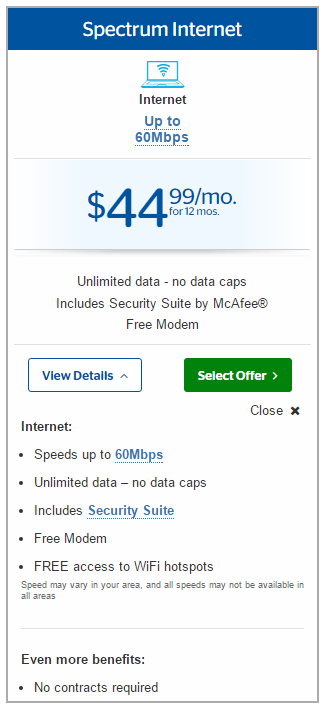
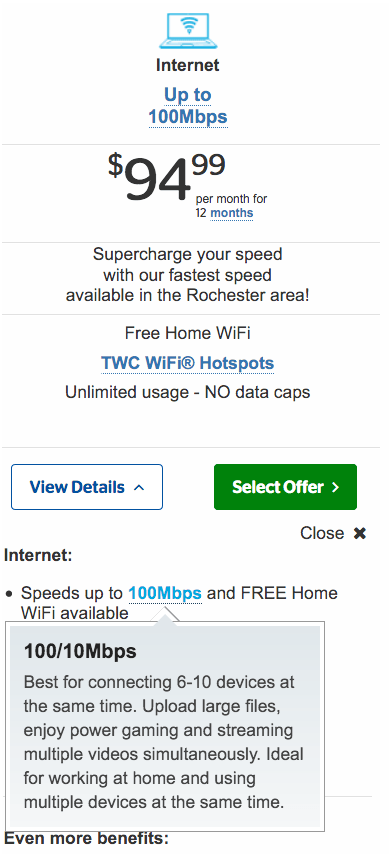
 Bright House Networks customers are also experiencing transition troubles. Residential customers reportedly lost any static IP addresses they signed up for when they converted to a Charter Spectrum residential plan. Static IP addresses are still available for Spectrum commercial plans. More troubling for many is the loss of access to Bright House Network’s secure Wi-Fi network.
Bright House Networks customers are also experiencing transition troubles. Residential customers reportedly lost any static IP addresses they signed up for when they converted to a Charter Spectrum residential plan. Static IP addresses are still available for Spectrum commercial plans. More troubling for many is the loss of access to Bright House Network’s secure Wi-Fi network. In Indianapolis, former Bright House Networks customers
In Indianapolis, former Bright House Networks customers  Former AT&T customers who dumped their former carrier for T-Mobile in return for a free year of DirecTV Now are getting a sweeter deal with a free year of Hulu with Limited Commercials as well.
Former AT&T customers who dumped their former carrier for T-Mobile in return for a free year of DirecTV Now are getting a sweeter deal with a free year of Hulu with Limited Commercials as well.


 The most notable phone that no longer has access to AT&T’s network is the original Apple iPhone, first released ten years ago. It will still work on Wi-Fi, but mobile data over AT&T’s network no longer functions.
The most notable phone that no longer has access to AT&T’s network is the original Apple iPhone, first released ten years ago. It will still work on Wi-Fi, but mobile data over AT&T’s network no longer functions.
 McAdam originally planned to use Verizon’s acquisition of Yahoo! as a way to broaden the phone company’s content library, but that yet-to-be-finished deal has been in turbulence since media reports exposed major security breaches of Yahoo’s e-mail and portal sites.
McAdam originally planned to use Verizon’s acquisition of Yahoo! as a way to broaden the phone company’s content library, but that yet-to-be-finished deal has been in turbulence since media reports exposed major security breaches of Yahoo’s e-mail and portal sites.