 4GCommunity.org, a non-profit provider of unlimited 4G LTE wireless internet service, is ending the service by Nov. 30, 2017 for “circumstances beyond the organization’s control.”
4GCommunity.org, a non-profit provider of unlimited 4G LTE wireless internet service, is ending the service by Nov. 30, 2017 for “circumstances beyond the organization’s control.”
The service cost $250 for the first year, which included a mobile hotspot device, and $168 each year thereafter, which means many subscribers that started in the past year may lose some or all of their annual fee as the service closes down.
The company e-mailed its members this morning:
Dear 4GCommunity.org Members,
We are saddened to inform you that due to circumstances beyond the organization’s control the Internet connectivity benefit of membership will be ceasing no later than November 30, 2017. It may be sooner, so please begin looking for other Internet connectivity options right away.
The member online support center will remain a resource through this time next year. Member and support team volunteers will be providing their general assistance through the online support center to assist with questions about basic home computing, networking, and related technologies. It can be accessed through the Support Center page of the website, or directly at: https://4gcommunityorg.happyfox.com/
Respectfully yours,
Support Team
Sprint was 4GCommunity’s 4G service provider, and was potentially not enthusiastic about the partnership.
4GCommunity.org is one of several non-profit groups that have taken advantage of an agreement made years earlier with Clearwire, a company acquired by Sprint in 2013.

Non-profit groups offering inexpensive 4G wireless internet service are exploiting a loophole in a 2006 contract agreement between Clear (now owned by Sprint) and Educational Broadband Service licensees.
In 2006, Clearwire reached an agreement to lease wireless spectrum earmarked for Educational Broadband Service (EBS) providers including Mobile Citizen and Mobile Beacon. In return for the use of those frequencies, Clearwire agreed to sell wireless internet service on its WiMAX network at rock bottom prices to those two providers, their non-profit affiliates and dues-paying members. As a result, more than 1,800 nonprofits, 429 schools, and 61 libraries signed up for service at prices averaging $10 a month. A few of those non-profits creatively exploited a loophole in the agreement which guaranteed access “as long as you are a user, recipient or beneficiary of a non-profit programs or services, but not thereafter.” That provision was interpreted to mean non-profit groups attached to either Mobile Citizen or Mobile Beacon could resell the service to their own members.
A groups have turned up, including 4GCommunity.org, typically offer access to unlimited 4G LTE data on Sprint’s network for an annual fee. 4GConnection effectively charged only $14 a month after the first year. The service has been especially popular with those within Sprint coverage areas, but outside of range for DSL or cable broadband. It also attracted a large number of RV owners and frequent travelers looking for portable internet access.
Sprint and other wireless companies have had experience with all kinds of resellers before. Historically, many of those providers offering unlimited data have been suddenly notified their contract to resell service was canceled or modified, usually after the carrier discovered a surge in traffic and usage it did not originally expect.
4GCommunity did not reveal the specific reasons for the decision to cancel its internet offering, but does suggest the termination is connected to Sprint. The decision is causing customers to scramble to find a new service provider. Selling low-cost internet plans that depend on one of the four major carriers has proven a risky business for providers and customers, because a carrier can put a provider under just by canceling a service agreement.
4GCommunity obviously understood the risks of having their provider drop them, placing this warning (emphasis theirs) in their service agreement:
You understand your support and membership in the organization is not a guarantee of any particular benefit for any duration of time. You understand you are supporting an organization mission. You understand we reserve the right to cancel any Internet connectivity Service as a member benefit at any time without notice, for any reason. You understand that your membership charges may not be refunded or prorated if the Internet connectivity benefit is terminated or modified regardless of reason at any time.
Customers may be less forgiving, especially if they recently paid several hundred dollars for a year of service that may not be refunded.
Similar resellers still appear to be offering service, but potential customers should be cautious and not assume other service provision contracts won’t be similarly canceled. A customer could be out up to $679 if a service later disappears.
- Calyx Institute – Membership costs $500 the first year, which includes wireless mobile hotspot service. The renewal rate is $400.
- Freedata.io – First year prices range from $449 – $679 for three different tiers of service offering different hotspot devices (currently showing as out of stock) and different options to access 3G service, which can be more reliable in rural/fringe reception areas. The service has also been battling with its small business payment processors, which suggests this is a very small operation.
- PCs for People & Connectall.org – Provide service to those below the 200% poverty level or currently enrolled in an income-based government assistance program. Proof of income required.
One of the few remaining unlimited wireless data providers unlikely to be affected by these developments is Unlimitedville, which offers a variety of expensive plans that correspond to the carrier providing the service. The “Yellow” plan, powered by Sprint, is $99 a month. The “Pink” plan, powered by T-Mobile, is $149 a month. A “Blue” plan offering service from AT&T costs $199 a month, and a “Red” plan using Verizon’s network is $249 a month. All of the plans are free of caps and speed throttles and offer 4G LTE data without hotspot restrictions, but require a one-time $99 “membership fee.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe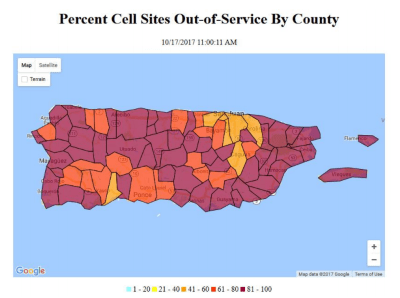 As Puerto Rico approaches the first month anniversary of Hurricane Maria, only small amounts of incremental progress have been made restoring the island’s telecommunications networks badly damaged by the storm.
As Puerto Rico approaches the first month anniversary of Hurricane Maria, only small amounts of incremental progress have been made restoring the island’s telecommunications networks badly damaged by the storm.

 As the wireless industry awaits an announcement that T-Mobile and Sprint have an agreement to merge, some on Wall Street are skeptical the merger deal will win approval, especially if Republicans lose their majority in the House and Senate in the 2018 mid-term elections.
As the wireless industry awaits an announcement that T-Mobile and Sprint have an agreement to merge, some on Wall Street are skeptical the merger deal will win approval, especially if Republicans lose their majority in the House and Senate in the 2018 mid-term elections. Wall Street analysts are debating exactly how many tens of thousands of jobs will be lost in a merger, and the numbers are staggering.
Wall Street analysts are debating exactly how many tens of thousands of jobs will be lost in a merger, and the numbers are staggering.

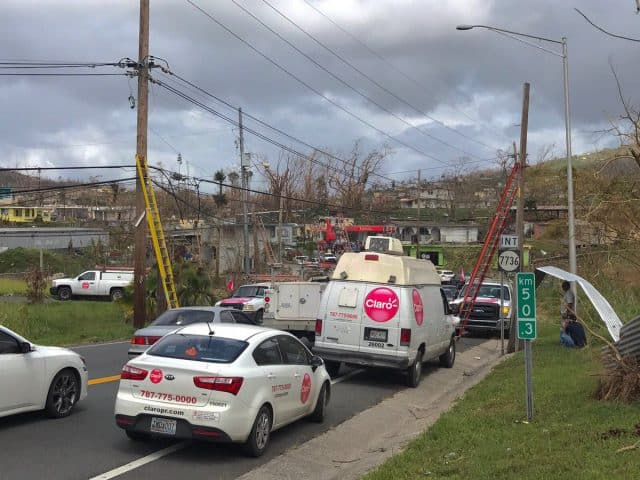
 U.S. cell phone providers are facing increasing criticism they are dragging their feet on restoring cell service in Puerto Rico while Mexican-owned Claro has now successfully restored service in 28 of the territory’s 78 municipalities.
U.S. cell phone providers are facing increasing criticism they are dragging their feet on restoring cell service in Puerto Rico while Mexican-owned Claro has now successfully restored service in 28 of the territory’s 78 municipalities.

