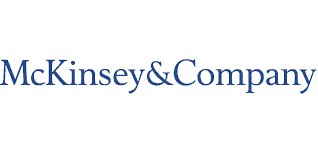 Investors are not buying into the substantial hype surrounding the forthcoming 5G revolution and many remain unconvinced about the benefits of spending billions of investor dollars to deploy the next generation in wireless.
Investors are not buying into the substantial hype surrounding the forthcoming 5G revolution and many remain unconvinced about the benefits of spending billions of investor dollars to deploy the next generation in wireless.
A survey by telecom analyst McKinsey & Co., picked up a clear drag on proposed spending, especially outside of North America, as carriers are finding investors reluctant about the business case for 5G technology.
The survey found 60% of wireless operators cited selling investors on the merits of 5G to be their greatest challenge. Only 25% were confident they could successfully prove a substantial return on investment for shareholders who typically want short-term results. Investors are demanding detailed evidence that 5G networks, the most costly requiring large fiber optic networks and neighborhood small cell antennas, will pay off with increased revenue and customer demand. Unlike earlier cellular standards which required incremental upgrades usually on existing cell towers, the fastest iteration of 5G will require providers to construct costly new fiber networks with a very large number of short-range antennas expected to be placed on top of utility or light poles.
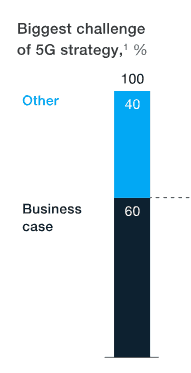 Customer demand for 5G is anticipated to be low until new devices are introduced capable of connecting to it, and investors already recognize consumers are increasingly delaying device upgrades since the industry dropped two-year service contracts with device subsidies. Ongoing upgrades to existing 4G LTE networks may ultimately dampen demand even for less costly 5G networks that will be deployed on existing cell towers. McKinsey’s survey found less than 35% of respondents are planning quick launches of 5G on gigabit-speed capable millimeter wave spectrum, citing the high cost of deploying small cell networks.
Customer demand for 5G is anticipated to be low until new devices are introduced capable of connecting to it, and investors already recognize consumers are increasingly delaying device upgrades since the industry dropped two-year service contracts with device subsidies. Ongoing upgrades to existing 4G LTE networks may ultimately dampen demand even for less costly 5G networks that will be deployed on existing cell towers. McKinsey’s survey found less than 35% of respondents are planning quick launches of 5G on gigabit-speed capable millimeter wave spectrum, citing the high cost of deploying small cell networks.
“Until th[e business case emerges], most operators will tread cautiously, leveraging 5G for near-term objectives and waiting for a clearer view on the use cases’ economics to accelerate,” the McKinsey report concluded. “Given the expense required to prove those significant use cases, it could be an uncomfortably long wait. And for operators in countries that don’t see 5G as a matter of strategic and economic importance, there is a greater risk of falling behind.”
In early 2019, most network operators will focus on network planning and funding, with the first significant wave of launches expected in the U.S. coming later this year. Just over half of U.S. operators plan to have “large-scale 5G deployments” completed by late this year, and U.S. carriers are the most optimistic 5G can make good business sense, at least for some applications. Other U.S. carriers expect their networks to launch by the end of 2022. But in neither case are those launches expected to be widespread across the country. Competing with cable and phone company internet with fixed wireless service is also a non-priority for most operators.
“At least at the outset, the majority see enhanced mobile broadband and the Internet of Things (IoT), rather than fixed wireless access or mission-critical applications, as the most prevalent applications,” McKinsey’s survey found. Among early potential applications are smart utility meter connectivity, traffic sensing, and connected public infrastructure like lighting and traffic control signals. Giving consumers a way out of choosing between Verizon and Comcast for home internet service is not going to be an early priority for companies like AT&T. In fact, starting a price war is the last thing investors want to see.
 “Although commercially in its infancy, 5G technology is ready, and in most markets its presence will be felt from 2020 on,” McKinsey’s report states. “Yet the fact that commercial models are not ready cannot be minimized; the business case is marginal, and the investments to enable new business models are not currently planned.”
“Although commercially in its infancy, 5G technology is ready, and in most markets its presence will be felt from 2020 on,” McKinsey’s report states. “Yet the fact that commercial models are not ready cannot be minimized; the business case is marginal, and the investments to enable new business models are not currently planned.”
McKinsey believes what will ultimately drive a gradual rollout of 5G technology is network congestion which can no longer be managed through existing traditional cell tower networks, known as “macro sites.”
“In rural and suburban areas, as well as along roadways, operators can handle increased traffic simply by densifying existing networks with macro sites,” McKinsey shared. “In many highly populated urban areas, by contrast, they’ll need to rely on small-cell solutions for two reasons: a higher concentration of traffic, as measured by traffic load per square kilometer, and the use of higher spectrum bands (greater than 3 gigahertz).”
But making the jump from the traditional large cell tower to a network of small cells scattered around neighborhoods will require a great deal of money. Operators will need to build fiber optic connectivity to each small cell, which can be managed either with a newly constructed fiber project or leasing existing fiber optic networks, presumably from cable operators which already have a significant fiber presence. In either scenario, rural areas will largely be left out, because all-important network traffic density is generally inadequate to support the business case for 5G, and cable operators are unlikely to have fiber networks available to lease in those areas.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast and Charter Communications have no real interest in competing head-to-head in wireless with AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, or Sprint. Instead, the two cable companies hope to trap you in a bundled package of services too inconvenient to cancel.
Comcast and Charter Communications have no real interest in competing head-to-head in wireless with AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, or Sprint. Instead, the two cable companies hope to trap you in a bundled package of services too inconvenient to cancel.
 Charter is expecting it can distribute more of its revenue to shareholders, share buybacks, and debt payments as a result of the completion of its all-digital conversion project, which eliminated analog television signals from cable systems to make more room for revenue-enhancing internet service. The company also gets to lease more set-top boxes to customers seeking to view digital television signals on older analog TV sets.
Charter is expecting it can distribute more of its revenue to shareholders, share buybacks, and debt payments as a result of the completion of its all-digital conversion project, which eliminated analog television signals from cable systems to make more room for revenue-enhancing internet service. The company also gets to lease more set-top boxes to customers seeking to view digital television signals on older analog TV sets.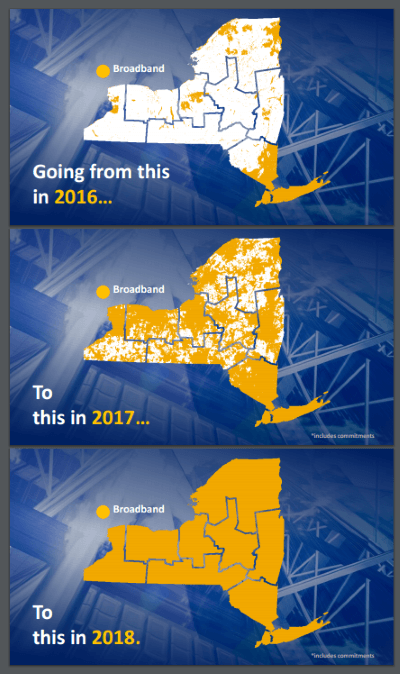 Tens of thousands of rural New York families were hopeful after Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced in 2015 his intention to bring true broadband to every corner of the state by the year 2018. At the time, it was the largest and most ambitious broadband investment of any state in the country, putting $670 million in lawsuit settlement money and rural broadband funds from the FCC on the table to build out rural broadband service other states only talk about.
Tens of thousands of rural New York families were hopeful after Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced in 2015 his intention to bring true broadband to every corner of the state by the year 2018. At the time, it was the largest and most ambitious broadband investment of any state in the country, putting $670 million in lawsuit settlement money and rural broadband funds from the FCC on the table to build out rural broadband service other states only talk about.
 D’Agostino fears that tens of thousands of additional satellite users will dramatically slow down HughesNet across upstate New York unless the company finds a way to get more shared bandwidth to serve the state’s rural broadband leftovers.
D’Agostino fears that tens of thousands of additional satellite users will dramatically slow down HughesNet across upstate New York unless the company finds a way to get more shared bandwidth to serve the state’s rural broadband leftovers. AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5G
AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5G Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research,
Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research, 
