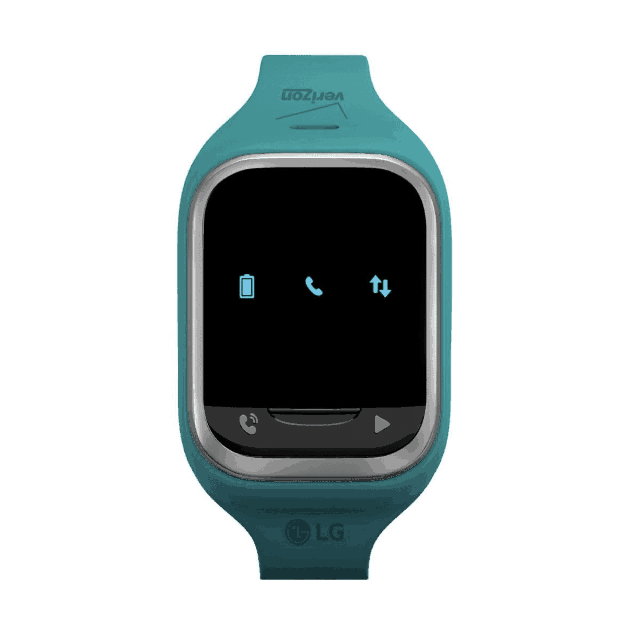

Times up. Legacy devices like the GizmoPal watch will stop connecting to Verizon after the company shuts down its CDMA/3G network at the end of the year.
Customers with older phones and devices that are dependent on Verizon Wireless, take note: those devices may stop working at the end of this year as Verizon Wireless mothballs its legacy CDMA network and 3G mobile data. Verizon originally announced it was planning to shut down CDMA and 3G service last summer, and stopped activating new devices that did not support the current 4G LTE standard. Since that time, the company has been gradually replacing CDMA and 3G-dedicated frequencies to 4G LTE to relieve congestion.
As this transition continues, some customers with older basic phone are noticing call issues and a lack of adequate mobile data service. That happens when a tower has re-dedicated almost all of its available spectrum to 4G LTE service, and those using older devices share a quickly declining number of frequencies. Some smartphone owners are also affected, even if their device supports 4G LTE data, because it may still rely on Verizon’s CDMA network to make and receive phone calls.
One of the biggest impacts of the shutdown will be felt by General Motors’ OnStar customers driving vehicles made before 2015, which rely on Verizon CDMA and 3G technology to support GPS, crash detection, diagnostics, and voice calling. Starting with 2015 models, GM moved its OnStar platform in new vehicles to AT&T’s 4G LTE network. Some GM vehicle owners, but not all, have the option of upgrading to OnStar over AT&T’s 4G LTE network with a retrofit kit, which also supports an in-vehicle hotspot. If this option is not available, service is expected to sunset for older vehicles on Dec. 31, 2019.
Some medical monitoring devices that rely on Verizon’s legacy CDMA network will also cease working unless a retrofit or upgrade is made available by the manufacturer.
Affected devices include:
- CDMA (3G)-only devices, including 3G basic phones and 3G smartphones
- 4G LTE smartphones that do not support HD Voice
- Apple iPhone 5s or prior including the Apple iPhone 5c
- Connected devices with CDMA (e.g,, GizmoPal, GizmoPal2, GizmoGadget and some Hum + models).
- In-car telematics devices like GM’s OnStar on pre-2015 model year vehicles
- Certain medical monitoring devices
Verizon had originally planned to mothball its CDMA network in late 2021, but the carrier needed to repurpose existing spectrum to meet growing data demands on its network, so it moved the drop dead date forward to Dec. 31, 2019.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Verizon has decided to treat its emerging mobile 5G network as a premium service that customers should pay more to access.
Verizon has decided to treat its emerging mobile 5G network as a premium service that customers should pay more to access.

 Verizon, the country’s leading provider of millimeter wave 5G wireless broadband, is promising to expand service nationwide, but admits it will only service urban areas where the economics of small cell/fiber network infrastructure makes economic sense.
Verizon, the country’s leading provider of millimeter wave 5G wireless broadband, is promising to expand service nationwide, but admits it will only service urban areas where the economics of small cell/fiber network infrastructure makes economic sense.

 Pai’s office this week released
Pai’s office this week released 