
Verizon’s FiOS expansion is still dead.
Verizon Communications does not see its remaining landline customers as part of the company’s future growth and customers should not be surprised if Verizon sells more of its legacy network to other telephone companies including Frontier, Windstream, and CenturyLink.
Speaking at the Morgan Stanley Technology, Media and Telecom Conference 2015 on March 2, Verizon chief financial officer Fran Shammo made it clear to investors Verizon will dump “non-core” assets that do not align with the company’s future long-term growth strategy, even in areas where FiOS predominates.
Shammo told investors Verizon’s growth strategy is predicated on Verizon Wireless, which will continue to get most of the company’s attention and future investment.
“It’s all around the wireless network and I’ve consistently said before, you should anticipate that wireless CapEx continues to trend up while wireline continues to trend down,” Shammo said.
The bulk of Verizon’s investments in its wired network are being made in areas that are already designated as FiOS fiber to the home service areas. Shammo explained that the company is required to invest in FiOS expansion to comply with agreements signed in cities like New York and Philadelphia to make the service widely available in those communities. Beyond those commitments, Shammo signaled the company isn’t planning any significant new spending to upgrade the rest of its legacy copper network.
“We continue to invest in those things that we believe are the future growth of the company,” Shammo said, and anything involving its wired networks outside of Verizon’s core FiOS service area in the northeast and Mid-Atlantic states probably doesn’t qualify.
 What will happen in Verizon service areas that are not considered priorities?
What will happen in Verizon service areas that are not considered priorities?
“For the right price and right terms, if there’s an asset we don’t believe is strategic to Verizon and can return shareholder value, we’ll dispose of that asset,” Shammo said.
An example of that strategy was Verizon’s sudden announcement in February it would sell its wireline assets in Florida, California, and Texas to Frontier Communications for $10.54 billion. Although a significant part of those service areas are served by FiOS after Verizon invested more than $7 billion on upgrades, Verizon still plans to abandon customers and walk away from that investment because it is not part of Verizon’s future growth strategy.
“If you look at Florida, Texas, and California, these are three island properties,” Shammo told investors. “FiOS is a very small footprint of those properties compared to the copper [except in] Florida because it was just Tampa. But you look at that and you say strategically there’s really not much we can do with those properties because they are islands.”
Verizon will spend the proceeds from its latest landline sale on the wireless spectrum it just acquired and will pay down some of the debt incurred after buying out Vodafone’s former ownership stake in Verizon Wireless. The company has also undertaken a massive share repurchase program, planning to buy back 100 million shares by 2017 to help its shareholders. To ease investor concerns about some of Verizon’s latest strategic moves, it also announced plans to buy back an extra $5 billion worth of shares in the second quarter of this year.
A close review of the latest Verizon sale to Frontier shows the extent Verizon believes in its wireless business at the cost of its legacy copper and FiOS networks. That comes as no surprise to Verizon observers who note its current CEO used to run Verizon Wireless.

Shammo, as featured on a recent cover of CFO Studio magazine.
“It’s been clear for years that Verizon has wanted out of the copper business,” said Doug Dawson from CCG Consulting. “They first sold off large portions of New England to Fairpoint. Then in 2010 they sold a huge swath of lines in fourteen states to Frontier including the whole state of West Virginia. And now comes this sale. It’s starting to look like Verizon doesn’t want to be in the landline business at all, perhaps not even in the fiber business.”
Verizon’s latest sale involves “higher margin properties than the rest of our wireline business,” Shammo said, in part because large parts of the urban service areas involved were previously upgraded to FiOS.
“So if you look at Dallas, we were over 50% penetrated both in TV and broadband,” said Shammo. “So, it was a very highly penetrated market that was delivering a lot of cash flow and delivering a lot of earnings. So by just divesting of the three properties, if you just did it on an apples-to-apples basis, there would be dilution.
Giving up that amount of cash flow — needed to win back the $7 billion in FiOS upgrade investments Verizon made in the three states — would normally concern investors worried about the “stranded costs” left over from investments that were never fully repaid. But Verizon has a plan for that: an “Involuntary Separation Plan” (ISP) for more than 2,000 Verizon employees, a polite way to describe job-cutting layoffs.
“We have a year to plan for this and the plan is similar to what we did with the last time we rolled properties out from Frontier,” Shammo said. “We will plan to offset the stranded cost and those plans are already being worked. You saw a little bit of that in the fourth quarter where we gave some ISPs to the represented employee base and we had 2,100 people come off payroll.”
Verizon’s growing preoccupation with Verizon Wireless leaves some analysts questioning the company’s wisdom giving up high-profit FiOS broadband in favor of wireless at a time when competition among wireless companies is finally emerging.
“Verizon reports an overall 41% market penetration for its data product on FiOS networks,” said Dawson. “Data has such a high profit margin that it’s hard to think that FiOS is not extremely profitable for them. The trend has been for the amount of data used by households to double every three years, and one doesn’t have to project that trend forward very far to see that future bandwidth needs are only going to be met by fiber or by significantly upgraded cable networks.”
Considering the wireless market is maturing and most everyone who wants a cell phone already has one, there are questions about where Verizon sees future growth in a business where it is getting harder to attract new customers.
“Verizon was a market leader getting into the fiber business. FiOS was a bold move at the time,” Dawson reflects. “It’s another bold move to essentially walk away from the fiber business and concentrate on wireless. They obviously think that wireless has a better future than wireline. But since they are already at the top of pile in cellular one has to wonder where they see future growth?”


 Subscribe
Subscribe More than three years after Canadian regulators required Bell Canada’s northern subsidiary, Northwestel, to undertake a
More than three years after Canadian regulators required Bell Canada’s northern subsidiary, Northwestel, to undertake a 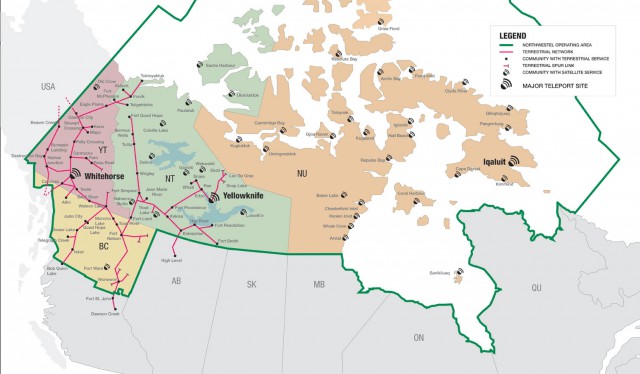
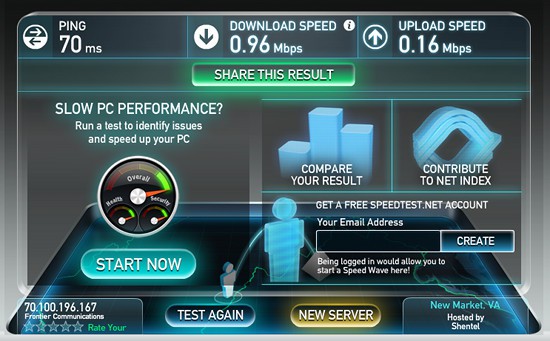
 “The DSL package that I pay for out at Lake Lebarge is absolutely ridiculous in comparison to high-speed in town,” said Jeremy Jones. “[Northwestel charges] $90 for [5Mbps DSL with a usage cap of] 125GB. The only way to increase it would be to put in another phone line and second modem and that would have ended up being another $100+ per month. We’ve decided it is cheaper just to go over it if we need to.”
“The DSL package that I pay for out at Lake Lebarge is absolutely ridiculous in comparison to high-speed in town,” said Jeremy Jones. “[Northwestel charges] $90 for [5Mbps DSL with a usage cap of] 125GB. The only way to increase it would be to put in another phone line and second modem and that would have ended up being another $100+ per month. We’ve decided it is cheaper just to go over it if we need to.”
 Wilderotter is expected to leave the CEO role by April, replaced by Daniel McCarthy. She will stay with the company as executive chairman of the Board of Directors.
Wilderotter is expected to leave the CEO role by April, replaced by Daniel McCarthy. She will stay with the company as executive chairman of the Board of Directors.
 The Republican leadership of West Virginia’s House of Delegates is alleged to have quietly placed a ban on considering any bill that could potentially offend Frontier Communications, frustrating state lawmakers attempting to introduce broadband improvement and consumer protection measures.
The Republican leadership of West Virginia’s House of Delegates is alleged to have quietly placed a ban on considering any bill that could potentially offend Frontier Communications, frustrating state lawmakers attempting to introduce broadband improvement and consumer protection measures.


 Welcome to the 2015 Time Warner Cable Winter Policy Conference, held Jan 22-23 at the remodeled resort and spa where a stay during the summer can cost $500 a day.
Welcome to the 2015 Time Warner Cable Winter Policy Conference, held Jan 22-23 at the remodeled resort and spa where a stay during the summer can cost $500 a day. The thought of competition is enough to give any cable lobbyist indigestion, especially if the new entrant provides fiber to the home service, something almost unknown among commercial providers in Maine.
The thought of competition is enough to give any cable lobbyist indigestion, especially if the new entrant provides fiber to the home service, something almost unknown among commercial providers in Maine. “If we want good public policy, there’s reason for all of us to be worried,” utilities expert Gordon Weil, the state’s first Public Advocate, who represented the interests of ratepayers before regulators, told the Maine Center for Public Integrity. Such treatment of legislators is “obviously intended to persuade them by more than the validity of the arguments; it’s intended to persuade by the reception they’re given.”
“If we want good public policy, there’s reason for all of us to be worried,” utilities expert Gordon Weil, the state’s first Public Advocate, who represented the interests of ratepayers before regulators, told the Maine Center for Public Integrity. Such treatment of legislators is “obviously intended to persuade them by more than the validity of the arguments; it’s intended to persuade by the reception they’re given.” Scott Pryzwansky, Time Warner Cable’s director of public relations for the eastern U.S., declined to answer any specific questions but replied by email: “As one of Maine’s leading employers and telecommunications companies, we designed this second biannual educational forum to help policymakers and others better understand some of the complex telecommunications issues confronting Maine and the nation.”
Scott Pryzwansky, Time Warner Cable’s director of public relations for the eastern U.S., declined to answer any specific questions but replied by email: “As one of Maine’s leading employers and telecommunications companies, we designed this second biannual educational forum to help policymakers and others better understand some of the complex telecommunications issues confronting Maine and the nation.” A highly slanted (
A highly slanted (