[Important Update — 7:53am ET 4/7 — Because of a technicality, it is important for everyone to reference H.129 when calling your state senators. Members of the Senate Finance Committee are still evaluating the House version of the bill — H.129, so senators will more readily identify the bill we are opposing when we reference the House version (and not S.87). You can also call it the “Level Playing Field” bill, but with disgust. Include the fact you found the name highly ironic, since the only thing it will “level” are the state’s community broadband networks — right to the ground. If you already called, why not just send a follow-up e-mail opposing H.129.]
Stop the Cap! has learned lobbyists for North Carolina’s cable and phone companies are growing concerned over increasing opposition to their custom-written duopoly protection bill that will ruin community broadband developments across the state and threaten ones already up and running. Now they’re in a mad dash to push S.87 (the Senate version of H.129) through the Senate Tuesday before you have a chance to call and express outrage over this corporate protectionism.
Our sources tell us the bill has been yanked from the Senate Commerce Committee and is moving faster than North Carolina’s cable and DSL broadband to the Finance Committee, where bill sponsors hope for a quick voice vote and no public comment allowed.
The engineer of the legislative railroad in the Senate is Sen. Tom Apodaca (R) who serves the western North Carolina counties of Buncombe, Henderson, and Polk — areas with broadband challenges of their own. Apodaca’s lead role pushing an anti-broadband bill is ironic considering his campaign website lists his priorities as:
- “Great schools for our children.” Western N.C. residents without broadband service at home are forced to resort to sitting in their cars in school parking lots or spend hours at overburdened public libraries to access Wi-Fi networks to complete homework assignments. Great schools in a digital economy require great broadband – both in school and at home
- “Better paying jobs.” Digital economy jobs are always in demand and bring good salaries. But those with inadequate broadband will find the kind of entrepreneurial experience and independent study required to excel in these fields hampered by satellite fraudband service or dial-up that limits possibilities and leaves North Carolina behind.
- “Let people keep more of the money they earn.” It’s a great idea, and competition for big cable and phone companies guarantees it. In Wilson, consumers don’t face annual rate hikes for their cable service. Can your community say that? When their network is paid off, Wilson’s GreenLight will start paying off for local residents as well, keeping money in the community.
- “And access to quality health care.” As Google intends to prove in Kansas City, Kansas — great health care and excellent broadband go hand-in-hand to deliver better patient outcomes at a cheaper price. Every health care provider wants faster broadband to increase efficiency and reduce costs and medical care errors. S.87 delivers the equivalent of just another metal filing cabinet and fax machine to the back office. Allowing communities to build fiber broadband changes everything.
What has proven so perplexing to consumers across the state is how a bill written by and for the cable and phone companies that does not deliver a single new broadband connection is getting such love and care from a legislature that is supposed to represent the interests of voters, not multi-billion dollar out of state corporations. It confuses some of America’s high tech companies as well, including Google, Alcatel-Lucent, and Intel. They’ve all signed a joint letter opposing H.129/S.87.
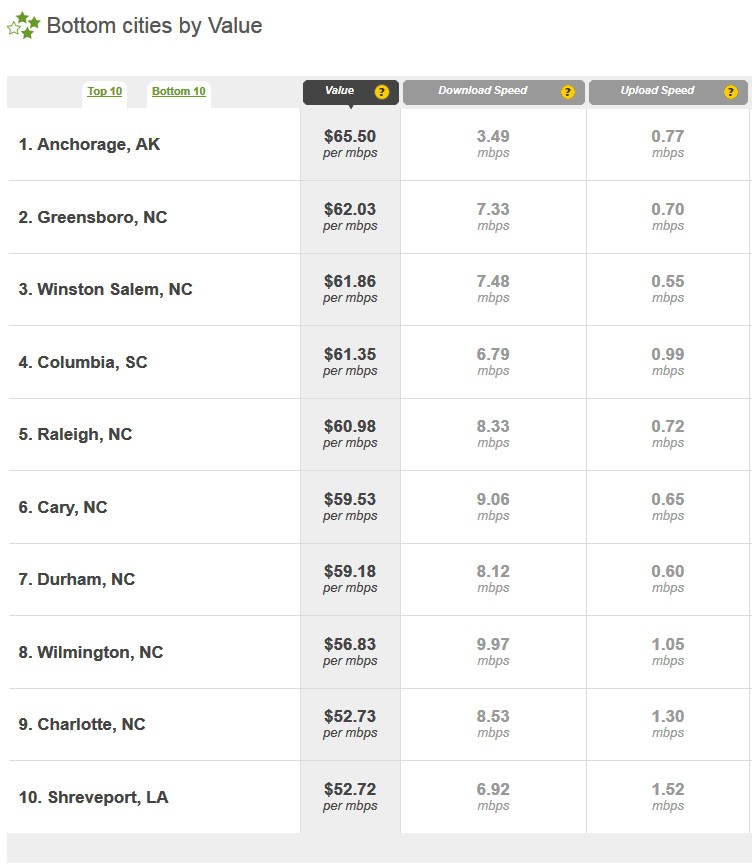
In fact, one of the reasons Google picked Kansas City, Kansas for its 1Gbps network is the friendly working relationship it has established with local utilities, which are all owned by the community of Kansas City. It no doubt speaks volumes to Google that the North Carolina legislature would rather be at war with their towns and cities for the benefit of Time Warner Cable, AT&T and CenturyLink, than allowing communities to build their own broadband networks. At a time when the FCC has ranked North Carolina worst in the nation, members of the Senate are being asked to guarantee that will remain so for years to come.
So What Should I Do?
Get on the phone -and- e-mail your state senator and demand a NO vote on S.87. If you are shy, you can call before or after business hours and leave a message on their voicemail. It takes less than five minutes. Your calls make a huge difference because so few constituents ever call state legislators. Here are your talking points:
1. At a time when we need all the broadband improvements this state can muster, S.87 destroys those efforts for the benefit of a handful of out of state phone and cable companies. It’s classic protectionism — the same companies that helped write this bill are fully exempted from its onerous requirements. The practical reality for rural North Carolina is either waiting for existing companies to deliver service they were always free to provide (and won’t), or allowing communities to do it themselves where appropriate. Why should rural North Carolina have to depend on out of state corporations for basic broadband service many still don’t have?
2. Not a single company has been harmed by community broadband projects in North Carolina. In fact, it has created incentive to improve products and services while keeping prices stable, a welcome relief for consumers enduring annual rate increases far outpacing inflation. Why is the state Senate trying to pass legislation that will guarantee higher bills and worse service?
3. North Carolina’s fiber networks are not economic failures risking taxpayer dollars. In fact, protections for taxpayers are already a part of the state code. The General Assembly has already established: (1) rules governing Public Enterprises (NCGS Chapter 160A, Article 16); (2) strict rules in the Budget and Fiscal Control Act governing all municipal budgets and expenditures, including hearing and disclosure requirements (NCGS Chapter 159, Article 3); and (3) strict oversight of municipal borrowing by the Local Government Commission (NCGS Chapter 159). S.87 attempts to micromanage public projects to the point where they simply cannot function and pay off bondholders and will, for future projects, ensure they never get off the ground.
4. Now that the FCC ranks North Carolina dead last in broadband, isn’t it be time to allow new entrants to shake up the market and deliver some competition? Since when is legislating for less broadband better for this state? The communities of Wilson and Salisbury now have the tools to compete with any wired city in America to attract new digital economy business and jobs. S.87 sends exactly the wrong message — telling business the state wants to wait for the cable or phone company to eventually (if ever), deliver service other states now take for granted. Businesses cannot wait. We cannot wait.
5. Provisions of this bill are unconstitutional. By placing illegal regulatory burdens on only public providers of communications services (defined broadly) H.129/S.87 will harm municipal convention centers, public safety networks, smart grid systems, tower leasing contracts, and even make seemingly free public Wi-Fi networks vulnerable to lawsuits if the large incumbents want in on those services.
6. The only real level playing field in broadband is the one that already exists without S.87. Tell your senator you are tired of seeing these cable company-written bills come up in the Legislature year after year when the state has more important matters to worry about. Time Warner Cable will do just fine without S.87, just as they do well in every other state where these kinds of bills would never get passed into law (or even proposed).
Senate Representation By County
2011-2012 Session
(click on your member’s name for contact information)


 Subscribe
Subscribe