 When inclement weather forces Wayne County, Mo. schools to close, some area businesses in Piedmont also send employees home because their Windstream Communications’ DSL Internet speeds slow to a crawl.
When inclement weather forces Wayne County, Mo. schools to close, some area businesses in Piedmont also send employees home because their Windstream Communications’ DSL Internet speeds slow to a crawl.
“People feel they are paying for a service they are not getting,” Missouri state Rep. Paul Fitzwater told Windstream. “I get emails every day, letters, telephone calls. The other day there was a water main break and school was closed. Some of the businesses had to shut down because of reduced Internet speeds because the kids were online playing games.”
Fitzwater complained to Windstream officials that broadband issues are so bad in the region, it is affecting the local economy.
“McAllister Software is a major employer, employing around 140 people,” Fitzwater said. “They are vital to the local economy and they need Internet service. There were about 45 hours last year that they had to shut their doors because they had no Internet.”

Fitzwater
Windstream plans broadband feast or famine for southeast Missouri’s Wayne County, with well-populated communities getting some broadband service improvements while more rural areas continue to go without high speed Internet.
“Windstream has made it clear that they have no plans to invest in areas where they don’t feel they can be profitable,” said Piedmont Area Chamber of Commerce president Scott Combs.
With no cable broadband competition in rural parts of Missouri, customers can take Windstream DSL or leave it. With no major competitive pressures, Windstream has taken its time to manage capacity upgrades and extend service.
When the kids are home from school, browsing speeds crawl because Windstream lacks sufficient capacity in the region. The company’s last fiber backbone upgrade made little difference, according to the Journal-Banner. Customers regularly find DSL speeds in the Piedmont area slow to 80-100kbps, about twice what dial-up customers receive. The speeds also degrade during evenings and weekends, when more users are online.
“Obviously, this is a problem in the area,” Fitzwater said. “There are a lot of people that come through the Piedmont area annually due to tourism—two to three million each year. When I was going door-to-door campaigning, Internet speed was the number one issue of constituents. Everyone I met with, the Internet was all they wanted to talk about.”
At the local Wal-Mart, customers compete to tell the worst Windstream DSL horror story.
Windstream’s rural service area in southeast Missouri is served by 11 remote switches. Only one — provisioned for McAllister Software — is fed by fiber. The others are served by copper. The city of Piedmont is served by three D-SLAMS which help extend Internet to more distant sections of town. Even Windstream admits their current infrastructure is inadequate and plans to improve Piedmont’s broadband service in the near future.
But after Piedmont’s service is upgraded, the rest of southeast Missouri will just have to grin and bear it. Windstream says it plans no further upgrades in 2013 and beyond because spending money on extending improved Internet service costs too much and is not financially feasible.
 For rural customers who remain without service, Windstream suggests they sign up for satellite broadband service, which also delivers slow speeds and very low usage allowances.
For rural customers who remain without service, Windstream suggests they sign up for satellite broadband service, which also delivers slow speeds and very low usage allowances.
In 2009, Windstream won a $10.3 million grant for rural broadband projects. The money was not spent in Piedmont, however. Instead, Windstream used the funds for projects in Greenville and Wappapello, which also suffer from inadequate service.
Without further upgrades, customers are guaranteed additional speed degradation throughout the county. Those customers are angry.
Combs says Windstream is effectively engaged in bait and switch broadband marketing, promising customers 3Mbps service and delivering a small fraction of that speed during peak usage periods.
“I believe that Windstream, by taking money from customers that are being billed for 3Mbps download service (and greater), are obligated to provide that service,” Combs writes. “It is unethical and possibly illegal to charge customers for services that you have no capability or intention of delivering.”
Despite admissions from the company it faces growing usage and capacity issues, Windstream keeps marketing its broadband service to new customers, and charges voice-only customers more than those who bundle both voice and broadband, which only increases demand further.
“[Windstream has] no qualms about selling new accounts or ‘upgrading’ services on a system [it knows] cannot handle the additional pressure. How can this possibly be anything short of fraud?” asks Combs.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Kentucky Resources Council is appealing to Kentucky residents and elected officials to stop AT&T’s plan to abandon rural landline service in the state with the passage of a bill now before Kentucky lawmakers
The Kentucky Resources Council is appealing to Kentucky residents and elected officials to stop AT&T’s plan to abandon rural landline service in the state with the passage of a bill now before Kentucky lawmakers 
 The Internet Innovation Alliance this week unveiled its
The Internet Innovation Alliance this week unveiled its 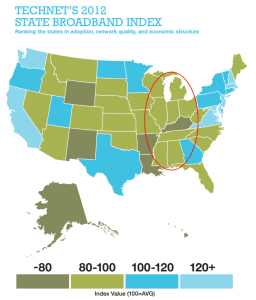

 North Carolina has achieved a new low. It is now tied with bottom-rated Mississippi as America’s least-connected state, at least in terms of broadband adoption.
North Carolina has achieved a new low. It is now tied with bottom-rated Mississippi as America’s least-connected state, at least in terms of broadband adoption. When inclement weather forces Wayne County, Mo. schools to close, some area businesses in Piedmont also send employees home because their Windstream Communications’ DSL Internet speeds slow to a crawl.
When inclement weather forces Wayne County, Mo. schools to close, some area businesses in Piedmont also send employees home because their Windstream Communications’ DSL Internet speeds slow to a crawl.
 For rural customers who remain without service, Windstream suggests they sign up for satellite broadband service, which also delivers slow speeds and very low usage allowances.
For rural customers who remain without service, Windstream suggests they sign up for satellite broadband service, which also delivers slow speeds and very low usage allowances.