One of the side benefits of Google getting into the broadband provider business is learning first-hand what is reality and what represents provider spin and marketing nonsense used to justify high prices and usage limits.
As Google Fiber slowly spreads across Kansas City, the search engine giant is gaining first hand-experience in the broadband business. Google understands what cable operators endured in the 1980s and what Verizon was coping with until it pulled the plug on FiOS expansion: the upfront costs to build a new network that reaches individual subscribers’ homes and businesses can be very high. But once those networks are paid off, revenue opportunities explode, particularly when delivering broadband service.
Milo Medin, a former cable Internet entrepreneur and now vice president of access services at Google, presented a cogent explanation of why Google can make gigabit broadband an earner once construction costs are recouped. He demonstrated the economics of fiber broadband at a meeting of the San Jose chapter of the IEEE.
In addition to a long term investment in fiber, and the new business opportunities 1,000Mbps Internet provides, Google has learned from the mistakes other utilities have made and is trying to establish close working relationships with local governments to find ways to cut costs and bureaucracy.
In Kansas City, Google has placed staff in the same office with city zoning and permit officials. Working together in an informal public-private partnership to cut red tape, local inspectors have agreed to coordinate appointments with Google installers to reduce delays. That alone reportedly saves Google two percent in construction expenses.
“Governments have policies that can make it easy or hard, so I say, ‘if you make it hard for me, enjoy your Comcast,’” Medin said.
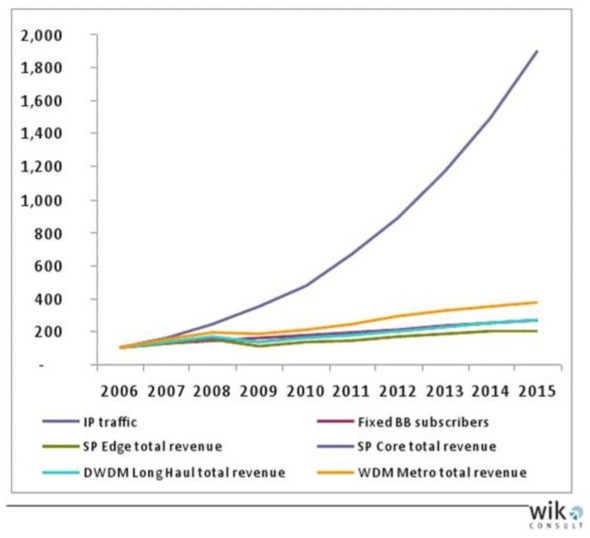
Internet traffic vs. costs
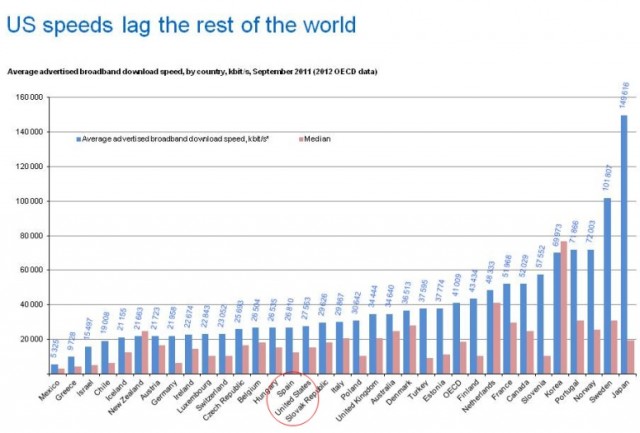
Medin notes broadband adoption and expansion in the United States is being artificially constrained by the marketplace, where wired providers are resting on their laurels.
More than a decade ago, people paid $40 a month for 4-5Mbps service, Medin noted.
Providers have kept the price the same, arguing they create more value for subscribers with ongoing speed increases.
But Medin notes overseas, prices are falling and speeds are increasing far faster than what we see in North America.
“Broadband in America is not advancing at nearly the pace it needs to be,” Medin argues. “Most of you have seen dramatic changes in wireless, but there’s never been a real step function increase in wired. That’s what’s needed for us to retain leadership in technology — and not having it is a big problem.”
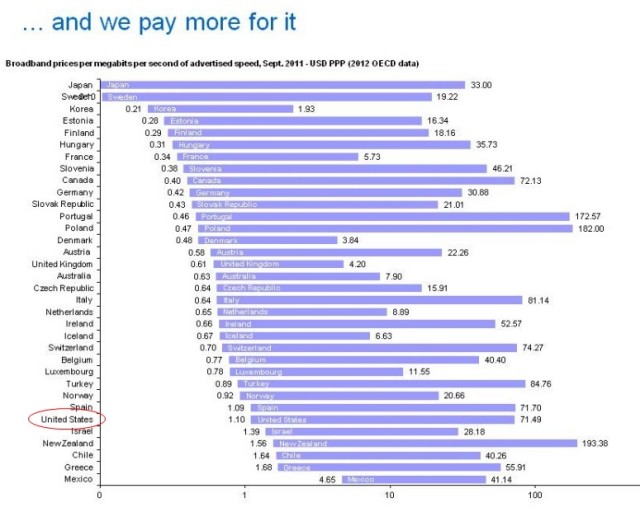
Medin points to OECD statistics that show the cost per megabit per month in the U.S. is the sixth highest among 34 OECD nations. Only Mexico, Chile, Israel, New Zealand, and Greece pay higher prices. Every other OECD nation pays less.
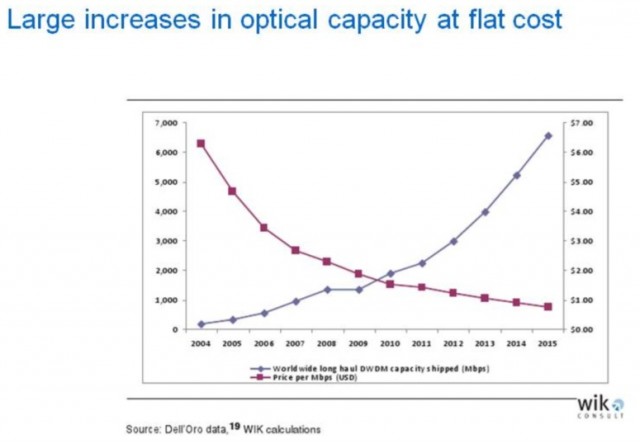
By leveraging fiber optics, which every provider uses to some extent, costs plummet after network construction expenses are paid off. In fact, despite the explosion in network traffic, provider bandwidth costs remain largely flat even with growing use, which makes the introduction of Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps and consumption-based pricing unjustified.
“Moving bits is fundamentally not expensive,” said Medin.
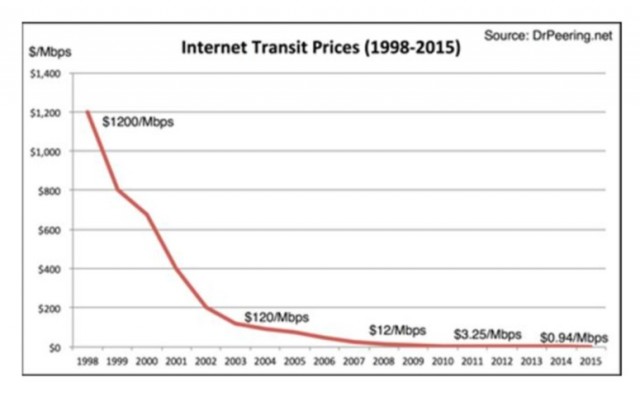
In 1998, when cable broadband first became available in many markets, the monthly price for the service was around $40 a month. Internet transit prices — the costs to transport data from your ISP to websites around the world averaged $1,200 per megabit that year. Today that cost has dropped below $4 per megabit and is forecast to drop to just $0.94 by 2015.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Both Time Warner Cable and Verizon don’t think you want or need gigabit fiber broadband — the kind of service now available in Kansas City from Google Fiber.
Both Time Warner Cable and Verizon don’t think you want or need gigabit fiber broadband — the kind of service now available in Kansas City from Google Fiber.





 Amazon.com today announced it is expanding its lineup of on-demand programming that will bring popular cable shows to Amazon’s Prime Instant Video service ($79/annually).
Amazon.com today announced it is expanding its lineup of on-demand programming that will bring popular cable shows to Amazon’s Prime Instant Video service ($79/annually).