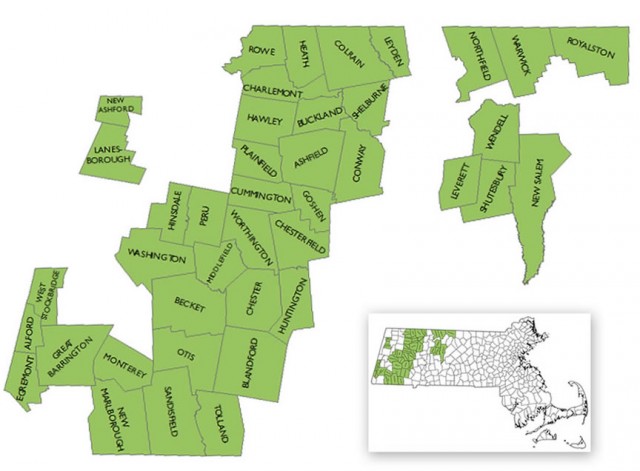
The WiredWest Cooperative
Towns shown above are official voting members of the WiredWest Cooperative. The town of Montgomery has also recently become a member. Requirements for new towns including being contiguous and directly accessible by road from another WiredWest member town, and less than 50% served by cable broadband.
Although plans to offer publicly owned fiber to the home service in 42 western Massachusetts communities are moving forward, a proposed $10 million taxpayer-funded incentive to encourage Comcast to expand cable service in western Massachusetts could mean the cable giant might get to some of those communities first.
Reps. Stephen Kulik (D-Worthington), Paul Mark (D-Cuba) and Sens. Stanley Rosenberg (D-Amherst) and Benjamin Downing (D-Pittsfield) have filed an amendment to Gov. Deval Patrick’s $40 million community broadband bond bill requesting a $10 million incentive be included to underwrite Comcast’s expenses to expand cable service into areas the company has long declared unprofitable.
“It’s challenging, because you cannot overbuild a new broadband network where there is existing service,” Kulik told The Recorder. “What we’re proposing is to add language to this bill, to provide incentive money to expand cable service. The partial cable towns aren’t eligible for federal funds. Carving out a way to reach out to these towns and extend cable seems a better way to do this.”
The dozens of communities participating in the WiredWest community broadband consortium have waited years for better broadband service. Rural western Massachusetts has been largely bypassed by Verizon, which only offers limited DSL service to some customers. Dominant cable provider Comcast primarily serves denser neighborhoods in selected towns.
Life is particularly complicated for the handful of communities that have some service from Verizon and/or Comcast, because almost all federal broadband grants are available only to communities that don’t have Internet access. These partially served areas, dubbed “cable towns,” are frustrated by government grants that only direct funding to areas where no service is available and are on the receiving end of endless complaints from local residents suffering broadband envy, knowing a neighbor up the street has had cable service for 30 years while many others are left in limbo.

Kulik
In August, Chris Saner of Huntington told the newspaper Comcast’s cable line ends 1.4 miles down the road from his house. The cable company would be happy to extend service to the roadway in front of his home for $24,000. If Saner had to sell his home, that investment might be mandatory to help find a buyer. Saner should know, as he works in real estate. Prospective buyers tell him, “don’t even show me anything where there’s no cable.”
Broadband access has become so critical, some don’t care whether they get it from WiredWest’s future fiber network or Comcast’s coax.
Fiber broadband “is lobster and filet mignon. Cable is hamburger, but give us hamburger —we’re starving out here,” Saner said.
The $10 million proposal from the four Massachusetts Democrats could bring faster cable Internet service for some residents, but could also potentially undercut fiber access down the road.
Comcast isn’t likely to expand service on its own, citing Return On Investment formulas that make expansion unprofitable. A $10 million incentive could resolve some of those cost concerns, but critics call it corporate welfare.
Robbie Leppzer, a Wendell documentary filmmaker who has been involved in the struggle to improve broadband in western Massachusetts for years, suggests that taxpayer funds would be better spent in the public sector, “where towns and their residents have more say in the process.”
 “Personally, I would love to see a nonprofit, community-based solution because it would be a more effective use of money, and it would keep it in the fiber-optic realm,” Leppzer told the newspaper. “While [coaxial cable] may be adequate for now, it will not meet the needs of the 21st century.”
“Personally, I would love to see a nonprofit, community-based solution because it would be a more effective use of money, and it would keep it in the fiber-optic realm,” Leppzer told the newspaper. “While [coaxial cable] may be adequate for now, it will not meet the needs of the 21st century.”
Ironically, western Massachusetts may eventually get the fastest Internet speeds in the state from the Massachusetts Broadband Institute’s $71.5 million middle-mile network, now 95 percent complete. MBI’s priority is to build the regional fiber network and provision it for institutional customers including municipal buildings, schools, hospitals, libraries, fire and police departments. Once complete, the network’s second phase involves expanding access to the public.
 The WiredWest consortium will be the public-facing part of the project, responsible for marketing high-bandwidth, affordable Internet, phone, high-definition television services and ancillary services to residents and businesses. WiredWest wants to build a 1,952-mile fiber-to-the-home network off MBI’s regional fiber backbone and institutional network.
The WiredWest consortium will be the public-facing part of the project, responsible for marketing high-bandwidth, affordable Internet, phone, high-definition television services and ancillary services to residents and businesses. WiredWest wants to build a 1,952-mile fiber-to-the-home network off MBI’s regional fiber backbone and institutional network.
 One of the most common questions from eager would-be customers is exactly when the fiber network will be finished and open for business to the public. Funding remains the biggest impediment. The cost of wiring residents for fiber service across the 42-town consortium ranges from $70 million to $130 million. It’s a substantial sum for small communities to cover, but the project does enjoy economy of scale that could ultimately save taxpayer dollars.
One of the most common questions from eager would-be customers is exactly when the fiber network will be finished and open for business to the public. Funding remains the biggest impediment. The cost of wiring residents for fiber service across the 42-town consortium ranges from $70 million to $130 million. It’s a substantial sum for small communities to cover, but the project does enjoy economy of scale that could ultimately save taxpayer dollars.
In Leverett, which has been building a fiber-to-the-home network on its own, the price tag for the 1,900 residents is $3.6 million — the amount of the bond secured to launch the project. Leverett residents will cover the costs of the fiber network through a tax increase that will amount to $295 a year over 20 years for a home assessed at $278,700.
The state can continue to budget about $40 million annually to gradually connect residents to the WiredWest fiber network or find Comcast expansion a better choice at a quarter of the price in some communities. It could even fund both. For some elected officials, getting broadband to communities using any means necessary is the primary goal. Downing thinks the western half of the state has waited long enough for broadband, noting the improvement initiative started in 2008. He wants the project finished before Patrick leaves office.
“We should all recognize that 18 months from now is the end of this administration,” Downing said. “And there is no guarantee that the next governor will share the same commitment for this project.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Viodi Broadband – Unique to Each Locale 11-13-13.mp4[/flv]
The western Massachusetts middle-mile/fiber to the home project is being developed in cooperation with Axia Technology Partners, a consulting, engineering, and construction firm. Tim Scott talks to Viodi.tv about Axia’s role as the operator for the Massachusetts community network. (7:45)
 “Use it or lose it” is the policy under which the Federal Communications Commission licenses scarce, publicly owned airwaves, but in practice companies warehousing unused spectrum can sell it off and make a handsome profit.
“Use it or lose it” is the policy under which the Federal Communications Commission licenses scarce, publicly owned airwaves, but in practice companies warehousing unused spectrum can sell it off and make a handsome profit.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Critics contend satellite broadband is not a good long-term solution except in the most rural of sparsely populated areas. Although providing wired service may be too costly, ground-based wireless services could be the most capable technology to contend with future demand and capacity concerns.
Critics contend satellite broadband is not a good long-term solution except in the most rural of sparsely populated areas. Although providing wired service may be too costly, ground-based wireless services could be the most capable technology to contend with future demand and capacity concerns.



 “Personally, I would love to see a nonprofit, community-based solution because it would be a more effective use of money, and it would keep it in the fiber-optic realm,” Leppzer told the newspaper. “While [coaxial cable] may be adequate for now, it will not meet the needs of the 21st century.”
“Personally, I would love to see a nonprofit, community-based solution because it would be a more effective use of money, and it would keep it in the fiber-optic realm,” Leppzer told the newspaper. “While [coaxial cable] may be adequate for now, it will not meet the needs of the 21st century.” The WiredWest consortium will be the public-facing part of the project, responsible for marketing high-bandwidth, affordable Internet, phone, high-definition television services and ancillary services to residents and businesses. WiredWest wants to build a 1,952-mile fiber-to-the-home network off MBI’s regional fiber backbone and institutional network.
The WiredWest consortium will be the public-facing part of the project, responsible for marketing high-bandwidth, affordable Internet, phone, high-definition television services and ancillary services to residents and businesses. WiredWest wants to build a 1,952-mile fiber-to-the-home network off MBI’s regional fiber backbone and institutional network. One of the most common questions from eager would-be customers is exactly when the fiber network will be finished and open for business to the public. Funding remains the biggest impediment. The cost of wiring residents for fiber service across the 42-town consortium ranges from $70 million to $130 million. It’s a substantial sum for small communities to cover, but the project does enjoy economy of scale that could ultimately save taxpayer dollars.
One of the most common questions from eager would-be customers is exactly when the fiber network will be finished and open for business to the public. Funding remains the biggest impediment. The cost of wiring residents for fiber service across the 42-town consortium ranges from $70 million to $130 million. It’s a substantial sum for small communities to cover, but the project does enjoy economy of scale that could ultimately save taxpayer dollars.
 The 1.5Mbps, 5Mbps, 8Mbps, 10Mbps, 12Mbps, & 50Mbps services (some plans grandfathered for existing customers) have a cap of 300GB per billing cycle, while the 60Mbps and 70Mbps services respectively have 400 and 500GB data caps per billing cycle. Surfing Internet has a 50GB cap.
The 1.5Mbps, 5Mbps, 8Mbps, 10Mbps, 12Mbps, & 50Mbps services (some plans grandfathered for existing customers) have a cap of 300GB per billing cycle, while the 60Mbps and 70Mbps services respectively have 400 and 500GB data caps per billing cycle. Surfing Internet has a 50GB cap.