Truth or Consequences: Does privatizing a government-owned telephone company encourage innovation and efficiency or serve to enrich a handful of executives and shareholders at the cost of customer service? Two essentially equal telephone companies serving the Canadian prairie provinces offer some useful insights.
 The provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan are remarkably similar in their landscape and their sparse populations — 1.29 million in Manitoba and 1.13 million in Saskatchewan. Today, most are concentrated in or near a few large cities with many small agricultural towns scattered across great distances.
The provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan are remarkably similar in their landscape and their sparse populations — 1.29 million in Manitoba and 1.13 million in Saskatchewan. Today, most are concentrated in or near a few large cities with many small agricultural towns scattered across great distances.
At the dawn of the 1900s, the “Sunny way” of Prime Minister Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier and his Liberal party was to push open the western frontiers and lay new railways across Canada. Part of the zeal for expansion came from a sense of growth and optimism, but there were also pervasive fears that without significant settlements in central Canada, the Americans could end up annexing huge swaths of empty Canadian agricultural lands for its own interests.
To prevent this and enhance its own national identity, Canada threw its doors open to immigration, especially to hard-working Americans from the midwest who were inundated with government-sponsored advertisements about a new life and opportunities that waited in the Canadian prairies.
The campaign worked. Between 1901 and 1906, the population of Saskatchewan surged from 91,279 to 257,763, 86.8% settled in rural farming areas. By 1911, the population almost doubled again to 492,432 with over 80% located away from the cities of Regina and Saskatoon. Next door in Manitoba, many new residents preferred areas south of Winnipeg, closer to the American border.
 Serving this population boom depended heavily on Canadian railroads, which delivered settlers and laborers, medicine, farming equipment, and the latest news from Ottawa. The trains returned east with part of the harvest and various meats.
Serving this population boom depended heavily on Canadian railroads, which delivered settlers and laborers, medicine, farming equipment, and the latest news from Ottawa. The trains returned east with part of the harvest and various meats.
It was no surprise Canada’s telecommunications infrastructure (along with more than a few new towns) would grow up along its railway lines.
With Bell Canada preoccupied with its larger client base in Ontario and Quebec, both the governments of Manitoba and Saskatchewan established provincial, publicly owned, phone companies to take control of their telecommunications future. In 1908, the Manitoba Telephone System (MTS) was born, made up mostly of former Bell customers. In 1909, SaskTel was established as a publicly owned operation as well, again comprising former Bell customers in the province. Both MTS and SaskTel quickly bought out all the remaining private telephone companies still operating in their midst.
The Winnipeg Free Press notes both MTS and SaskTel successfully served their respective customers for nearly 90 years. In 1997, Manitoba’s Progressive Conservative premier Gary Filmon broke his pledge to keep hands off MTS and privatized the company, claiming it would be more innovative in private hands.
That move would not be repeated in Saskatchewan, where every political party in office usually treated SaskTel as sacrosanct to the province’s economic development. Even the conservative Saskatchewan Party, which held power in the province from 1982-1991, never got around to privatizing the phone company, and a pledge to privatize crown corporations in the near future was just one of several issues that led to the party’s downfall in the election of 1991.
 For the last 18 years, Canadians have been able to see which province made the wisest choice. The newspaper concluded after nearly two decades, there is strong evidence MTS’ main priorities are to satisfy shareholders and commercial business customers, while rewarding their executives with handsome pay packages.
For the last 18 years, Canadians have been able to see which province made the wisest choice. The newspaper concluded after nearly two decades, there is strong evidence MTS’ main priorities are to satisfy shareholders and commercial business customers, while rewarding their executives with handsome pay packages.
“Meanwhile, SaskTel appears to focus on customer service and satisfaction, being a good employer and on providing returns to their public shareholder: the people of Saskatchewan,” the Winnipeg Free Press concluded.
Evidence of SaskTel’s service ethic could be found last week when SaskTel was acknowledged as western Canada’s most dependable wireless carrier, according to a new study by market researcher J.D. Power.
“SaskTel ranks highest in overall network quality and performs particularly well in call quality, messaging quality and data quality,” J.D. Power said in its report.
SaskTel has never been reserved about its own accomplishments, particularly its success delivering innovative new services to sparsely populated regions across Saskatchewan:
- SaskTel was the first telecommunications company in Canada to complete its rural individual line service program, eliminating all party lines in 1990;
- SaskTel was at the forefront of Internet provision as the first in Canada to remove the long distance charges on dial-up Internet and the first in North America to offer high-speed service on phone lines through DSL technology;
- SaskTel was among the first commercial users of fiber-optics in the world, today offering customers competitive cable television, broadband, and phone service.

Filmon
MTS has not turned out to be the innovator it was promised to be as a private company. While SaskTel was becoming a world leader in converged fiber optic networks, supplying voice, data and video across a strand of fiber, MTS was raising rates on landline customers.
Today, a basic landline in Saskatchewan costs around $8 a month — 27% less than the cheapest MTS home phone service. Everything at MTS usually costs more, which has turned out very well for shareholders and executives. While MTS earns roughly double the profit of SaskTel, almost all goes to major shareholders and top executives. SaskTel has returned $497 million over the last five years to the provincial government as well as customers through an annual dividend payment. Over in Manitoba, MTS has proved to be innovative in avoiding its tax bill — only paying corporate taxes once in 10 years — and that was just $1.2 million in 2010. Creative accounting at MTS has allowed the profitable company to pay “a big fat zero in federal and provincial corporate income taxes,” according to the newspaper, and MTS does not expect to owe a penny in income taxes until 2020 at the earliest.
So where do MTS profits go? Last year, MTS former CEO Pierre Blouin received $7.8 million in compensation, well above his five-year average of $4.8 million. Blouin’s salary was more than 10 times higher than what SaskTel’s CEO receives annually.
The newspaper adds MTS directors are paid more than 10 times what SaskTel’s directors are paid. But even more disturbing, the man who made the Money Party possible for MTS — former premier Gary Filmon — had a cozy, well-compensated home waiting for him on the MTS board after he lost his re-election bid. He has used his time at MTS to feather his own nest with more than $1.4 million in director fees and compensation over 10 years, along with hundreds of thousands of dollars worth of shares.
“None of this is meant to suggest SaskTel is an ideal company, but it appears abundantly clear this publicly owned and operated company provides better service at lower costs to its customers than the privatized MTS, and it also provides much larger benefits to the people of the province from its profits,” writes economist Toby Sanger. “Despite all this, the Saskatchewan government may be laying the groundwork for privatization of SaskTel. If this is what we can expect from the privatizations of other public utilities — higher fees for the public, lower-quality service, much higher compensation for CEOs and executives, higher corporate profits but much lower returns for the provinces — we can see why Bay Street [Canada’s Wall Street] is so excited about the privatization of Hydro One — and why the people of Ontario should be very worried.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 The Federal Communications Commission’s Net Neutrality rules took full effect Friday, after a three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit denied petitions for a temporary stay of the rules made in separate lawsuits by AT&T and other telecom industry opponents.
The Federal Communications Commission’s Net Neutrality rules took full effect Friday, after a three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit denied petitions for a temporary stay of the rules made in separate lawsuits by AT&T and other telecom industry opponents. A Prattsburgh, N.Y. family-owned company has picked up where Verizon left off and is busily wiring up small communities across western New York and the Southern Tier with fiber to the home service, giving both Verizon and Time Warner Cable some competitive headaches.
A Prattsburgh, N.Y. family-owned company has picked up where Verizon left off and is busily wiring up small communities across western New York and the Southern Tier with fiber to the home service, giving both Verizon and Time Warner Cable some competitive headaches.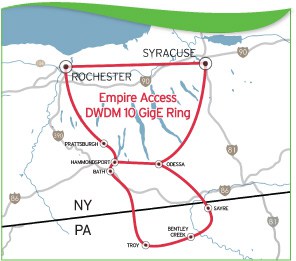 With the help of public and non-profit broadband infrastructure, residents in small communities across a region extending from Sayre, Pa., north to Batavia, N.Y., will have another choice besides Verizon or Frontier DSL, Comcast or Time Warner Cable.
With the help of public and non-profit broadband infrastructure, residents in small communities across a region extending from Sayre, Pa., north to Batavia, N.Y., will have another choice besides Verizon or Frontier DSL, Comcast or Time Warner Cable. The arrival of Empire reminds some of the days when the first cable company arrived to wire their village. Word of mouth is often enough to attract new customers, but a handful of local sales agents are also on hand to handle customer signups. From there, one of the company’s 80+ employees in New York handle everything else.
The arrival of Empire reminds some of the days when the first cable company arrived to wire their village. Word of mouth is often enough to attract new customers, but a handful of local sales agents are also on hand to handle customer signups. From there, one of the company’s 80+ employees in New York handle everything else.