Down the rabbit hole
Google has quietly announced an indefinite suspension of further fiber expansion as it prepares to downsize fiber division employees and re-evaluate its fiber business model.
In a blog post tonight from Craig Barratt, senior vice president of Alphabet and CEO of Google’s Access division, it becomes clear Google is rethinking its entire fiber strategy and is likely moving towards fixed wireless technology going forward:
Now, just as any competitive business must, we have to continue not only to grow, but also stay ahead of the curve — pushing the boundaries of technology, business, and policy — to remain a leader in delivering superfast Internet. We have refined our plan going forward to achieve these objectives. It entails us making changes to focus our business and product strategy. Importantly, the plan enhances our focus on new technology and deployment methods to make superfast Internet more abundant than it is today.
Barratt outlines the immediate implications of Google’s dramatic shift:
- In the cities where we’ve launched or are under construction, our work will continue;
- For most of our “potential Fiber cities” — those where we’ve been in exploratory discussions — we’re going to pause our operations and offices while we refine our approaches. In this handful of cities that are still in an exploratory stage, and in certain related areas of our supporting operations, we’ll be reducing our employee base.

Barratt
Barratt himself is jumping ship (or was pushed). He announced in his blog entry he is “stepping away” from his CEO role, but will remain as an “adviser.”
Observing Google’s recent fiber efforts and acquisitions, it seems clear Google no longer thinks fiber-to-the-home service is an economically viable solution in light of competitors like AT&T rolling out increasing amounts of fiber and the cable industry is on the cusp of launching DOCSIS 3.1, which will dramatically boost internet speeds without a substantial capital investment.
Google’s investors have been lukewarm about the company’s economic commitments relating to its fiber broadband networks. Often built from the ground up, Google’s fiber construction complexities also include trying to navigate costly roadblocks established by their competitors (notably Comcast and AT&T), dealing with bureaucracies and red tape even in states where near-total-deregulation was supposed to make competition easy. Google Fiber has also not proved to be a runaway economic success, and now faces more challenges in light of upgrades from their competitors. Cable companies have slashed prices for customers threatening to cancel and have added free services or upgrades to persuade customers to stay, and Google’s proposition of selling consumers $70 gigabit access has proved tougher than expected.
It is highly likely the future of Google’s Access business will be deploying wireless broadband solutions powered by Webpass, a company Google acquired earlier this year. Webpass uses a high-speed point to point wireless transmission system the company claims can deliver gigabit broadband access to customers in multi-dwelling buildings and other urban areas. Webpass sells access for $60 a month (discounted to $550/yr if paid in advance) for 100Mbps-1,000Mbps speed depending on network density and capacity in the customer’s building. So far, Webpass has not been able to guarantee speed levels, and some customers report significant variability depending on their location and network demand.
Webpass’ wireless infrastructure costs a fraction of what Google has coped with building fiber to the home networks, and the installation of point-to-point wireless antennas on participating buildings has been less of a regulatory nightmare than digging up streets and yards to lay optical fiber.
 But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference.
But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference.
There is room for wireless technology to grow and develop, as evidenced by the wireless industry’s excitement surrounding future 5G networks and their ability to offer a home broadband replacement. The emergence of 5G competition is almost certainly also a factor in Google’s decision. But even AT&T and Verizon acknowledge a robust 5G network will require a robust fiber backhaul network to support both speed and user demand. The more users sharing a network, the slower the speed for all users. No doubt Webpass has made the same assumption that cable operators did in the early days of DOCSIS 1 — current internet applications won’t tax a network enough to create a traffic logjam that would be noticed by most customers. The phone companies also learned a similar lesson trying to serve too many DSL customers from inadequate middle mile networks or traffic concentration points. (Some phone companies are still learning.)
Whether it was yesterday’s peer-to-peer file sharing or today’s online video, capacity matters. That is why fiber broadband remains the gold standard of broadband technology. Fiber is infinitely upgradable, reliable, and robust. Wireless is not, at least not yet. But technology arguments rarely matter at publicly-traded corporations that answer to Wall Street and investors, and it appears Google’s backers have had enough of Google Fiber.
Stop the Cap!’s View
 At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.
At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.
Not every product or service needs to earn Wall Street-sized profits. Nobody needs to get rich selling water, gas, and electricity… or broadband. Public broadband networks can and should be established wherever they are needed, and they should be priced to recover their costs as well as expenses that come from support, billing, and ongoing upgrades. Naysayers like to claim municipal broadband is socialism run wild or an instant economic failure, yet the same model has provided Americans with reliable and affordable gas, electricity, and clean water for over 100 years.
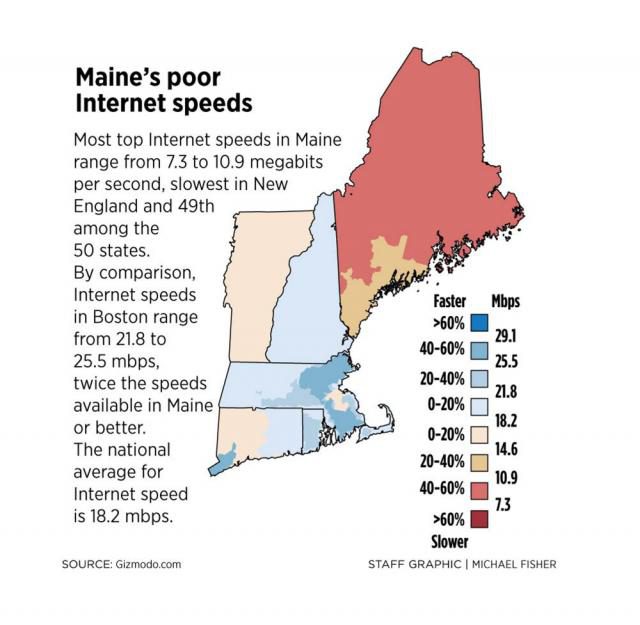
Maine was made for municipal broadband.
In New York, publicly owned/municipal utilities often charge a fraction of the price charged by investor-owned utilities. In Rochester, where Stop the Cap! is headquartered, one need only ask a utility customer if they would prefer to pay the prices charged by for-profit Rochester Gas & Electric or live in a suburb where a municipal provider like Fairport Electric or Spencerport Electric offers service. RG&E has charged customers well over 10¢ a kilowatt-hour when demand peaks (along with a minimum connection charge of over $21/mo and a “bill issuance charge” of 72¢/mo). Spencerport Electric charges 2.9¢ a kilowatt-hour and a connection charge of $2.66 a month, and they issue their bills for free. There is a reason real estate listings entice potential buyers by promoting the availability of municipal utility service. The same has proven true with fiber-to-the-home broadband service.
The economic arguments predicting doom and gloom are far more wrong than right. Municipal utilities are often best positioned to offer broadband because they already have experience providing reliable service and billing and answer to the needs of their local communities. Incompetence is not an option when providing reliable clean water or electricity to millions of homes and customers have rated their public utilities far superior to private phone or cable companies.
Google’s wireless future may prove a success, but probably only in densely populated urban areas where a point-to-point wireless network can run efficiently and profitably. It offers no solution to suburban, exurban, or rural Americans still waiting for passable internet access. Clearly, Google is not the “free market” solution to America’s pervasive rural broadband problem. It’s time to redouble our efforts for public broadband solutions that don’t need a seal of approval from J.P. Morgan or Goldman Sachs.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T
AT&T 
 Charter Communications has announced price changes and new fees for existing Time Warner Cable customers that will take effect Dec. 15, 2016:
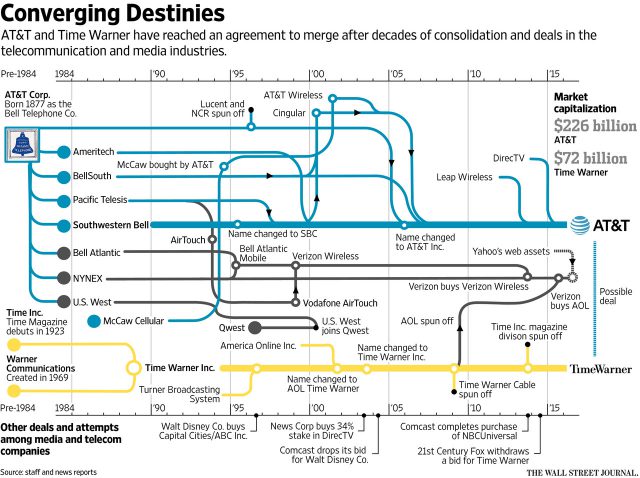
Charter Communications has announced price changes and new fees for existing Time Warner Cable customers that will take effect Dec. 15, 2016: It was a busy weekend for AT&T’s Randall Stephenson and Time Warner (Entertainment)’s Jeff Bewkes, culminating in an announcement from AT&T it was acquiring Time Warner
It was a busy weekend for AT&T’s Randall Stephenson and Time Warner (Entertainment)’s Jeff Bewkes, culminating in an announcement from AT&T it was acquiring Time Warner