After spending millions to kill net neutrality, AT&T today called on Congress to pass a new national law protecting AT&T’s idea of a free and open internet by regulating internet websites like Facebook, Google, and Amazon.
Full page newspaper ads taken out in several nationally known newspapers proclaimed AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson’s support for the first “Internet Bill of Rights,” conceived by some of the same lawyers and lobbyists AT&T paid to destroy the FCC’s net neutrality rules put into effect during the Obama Administration.
“Congressional action is needed to establish an ‘Internet Bill of Rights’ that applies to all internet companies and guarantees neutrality, transparency, openness, non-discrimination and privacy protection for all internet users,” Stephenson wrote in the ad.
AT&T’s proposal would attempt to include content regulation of websites under the guise of fairness, claiming that while internet service providers are expected to treat all content fairly, large websites like Google and Facebook currently do not. Critics of AT&T’s proposal call that a distraction that has nothing to do with ISPs seeking the right to establish paid internet fast lanes and favoring partnered websites with exemptions from data caps or speed throttles.

AT&T doesn’t inform readers of its own complicity in the “confusion” over net neutrality policies that have faced constant legal and political challenges from AT&T and other telecom companies. The telecom industry has furiously lobbied Congress and regulators to keep net neutrality from taking effect. Once it did, AT&T took the FCC to court to overturn the rules.

AT&T wants their own law for their own version of net neutrality.
AT&T’s campaign comes with some urgency as the company works to block states from enacting their own net neutrality laws to replace the rules abandoned by the Republican majority controlling the FCC. Despite assurances from FCC chairman Ajit Pai that the Commission would sue to pre-empt any state law that would re-establish net neutrality, AT&T and other large cable and phone companies prefer the regulatory certainty available from the quick passage of a federal law that would establish AT&T’s definition of net neutrality indefinitely. AT&T is also trying to rush passage with support from Republican congressional majorities and President Trump before the midterm elections threaten a Democratic takeover of the House, Senate, or both.
AT&T attempted to assuage customers of its good intentions by claiming it doesn’t block websites.
“We don’t censor online content. And we don’t throttle, discriminate, or degrade network performance based on content, period,” AT&T wrote (emphasis ours). But that claim opens the door to important loopholes:
- Speed throttles, data caps, and zero rating do not impact network performance. They impact your ability to equally access internet content, something AT&T does not promise here.
- AT&T only claims it won’t interfere with websites based on their content, but that was never the premise ISPs have used to demand additional payments from content creators. It isn’t the content ISPs are concerned with — it is the traffic those websites generate and, in the eyes of many net neutrality supporters, whether those websites compete with an ISPs own offerings. AT&T could have said it doesn’t throttle, discriminate, or degrade websites, period. But it didn’t.
AT&T alarmingly suggests that without predictable rules, next generation applications like virtual reality, telemedicine, and the Internet of Things will be threatened. Except that is not the message AT&T gives shareholders, arguing AT&T has robust capacity both now and into the future for next generation applications. AT&T has long promoted how lucrative it expects the Internet of Things marketplace will be.
Allowing the telecom industry to write its own “Internet Bill of Rights” met with harsh criticism from the consumer groups AT&T claims it wants to enlist in its efforts.
“Zero real net neutrality supporters are fooled by this,” wrote Fight for the Future executive director Evan Greer. “We had an Internet Bill of Rights. It was called Title II and AT&T’s army of lobbyists did everything in their power to burn it down.”
“AT&T’s hypocrisy knows no bounds,” said Free Press policy director Matt Wood. “Its phony bill of rights argument makes no sense based on the law, the policies, or the politics in play. AT&T’s head fake towards one-size-fits-all rules for all websites and content providers should fool no one. As soon as AT&T wants to stop lobbying against net neutrality, broadband privacy, and the other rights it has worked to kill at the Trump FCC and in this Congress, maybe people will stop laughing at desperate tactics like this. For now, all we can do is point out the company’s audacity in pretending that this hyper-partisan Congress can step in to fill the void of the net neutrality repeal by writing a new law tailor-made for AT&T.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Verizon will spend most of the benefits gained from the Trump Administration’s tax cuts on writing off investments that will reduce the company’s tax exposure and boosting its dividend to shareholders.
Verizon will spend most of the benefits gained from the Trump Administration’s tax cuts on writing off investments that will reduce the company’s tax exposure and boosting its dividend to shareholders. If you are a resident of New York City, you can now stream 15 over the air local television stations for free, at least until the station owners send their lawyers after the coalition running the new service.
If you are a resident of New York City, you can now stream 15 over the air local television stations for free, at least until the station owners send their lawyers after the coalition running the new service.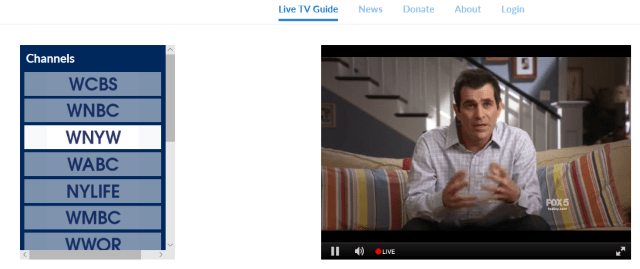
 In 1999, iCraveTV provided more than a dozen Canadian and American television stations received over the air in Toronto made available to a nationwide online audience. The over-the-air stations (and the networks they affiliated with) in Buffalo, N.Y., promptly launched legal action against the company, challenging its claim it was entitled to offer the service because it was effectively a cable operator. International copyright law claims led to a preliminary injunction against the service and the threat of costly ongoing litigation convinced the owner of iCraveTV to stop the service in return for dropping lawsuits.
In 1999, iCraveTV provided more than a dozen Canadian and American television stations received over the air in Toronto made available to a nationwide online audience. The over-the-air stations (and the networks they affiliated with) in Buffalo, N.Y., promptly launched legal action against the company, challenging its claim it was entitled to offer the service because it was effectively a cable operator. International copyright law claims led to a preliminary injunction against the service and the threat of costly ongoing litigation convinced the owner of iCraveTV to stop the service in return for dropping lawsuits. Broadcasters ran up large legal bills to defeat Aereo in two major court cases. In 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court
Broadcasters ran up large legal bills to defeat Aereo in two major court cases. In 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court  The Republican-pushed corporate tax rollback will bring a $14.4 billion increase in available cash flow for Comcast to use for future mergers and acquisitions or share buybacks by 2021, even as the cable company has no plans to share its tax savings bonanza with subscribers in the form of lower rates.
The Republican-pushed corporate tax rollback will bring a $14.4 billion increase in available cash flow for Comcast to use for future mergers and acquisitions or share buybacks by 2021, even as the cable company has no plans to share its tax savings bonanza with subscribers in the form of lower rates. Rogers Communications’ call center workers treated customers as adversaries and allegedly placed unauthorized charges on customer bills, didn’t disclose service fees, and avoided downgrading or disconnecting service while managers encouraged these practices and lectured workers it was not their job to worry about what customers thought.
Rogers Communications’ call center workers treated customers as adversaries and allegedly placed unauthorized charges on customer bills, didn’t disclose service fees, and avoided downgrading or disconnecting service while managers encouraged these practices and lectured workers it was not their job to worry about what customers thought. In its original report, CBC News quoted a Rogers spokesperson who denied knowledge of these practices and declared there was no tolerance for employees who mistreated customers. But the latest group of employees to come forward consider the abuses systematic and occurred with the full knowledge of company managers and supervisors.
In its original report, CBC News quoted a Rogers spokesperson who denied knowledge of these practices and declared there was no tolerance for employees who mistreated customers. But the latest group of employees to come forward consider the abuses systematic and occurred with the full knowledge of company managers and supervisors.
