 Despite the massive amount of extra money from the Trump Administration’s corporate tax cuts generating huge revenue spikes for America’s telecom companies, Frontier Communications disappointed investors with today’s news it was suspending its quarterly cash dividend to shareholders after reporting a net loss of $1.03 billion on revenue of $2.2 billion during the fourth quarter of 2017, despite a $830 million tax benefit resulting from the reduction in federal tax rates.
Despite the massive amount of extra money from the Trump Administration’s corporate tax cuts generating huge revenue spikes for America’s telecom companies, Frontier Communications disappointed investors with today’s news it was suspending its quarterly cash dividend to shareholders after reporting a net loss of $1.03 billion on revenue of $2.2 billion during the fourth quarter of 2017, despite a $830 million tax benefit resulting from the reduction in federal tax rates.
Frontier saw revenue declines across almost every product category: Data and Internet services, $939 million (down 7.3%); Voice services, $687 million (down 11.2%); Video services, $310 million (down 15.1%), but the company slightly improved its churn rate (customers coming and going) to 1.83% for Frontier Legacy service areas (areas not acquired from Verizon or AT&T) and 2.22% for customers in California, Texas, and Florida acquired from Verizon (compared with 1.92% and 2.33% respectively in the third quarter of 2017).
The losses are attributable to:
- Frontier DSL is not competitive with cable broadband in most Frontier Legacy service areas. Cable companies continue to steal customers away with better value broadband packages at much faster speeds;
- Frontier FiOS delivers much better internet speeds, but customers in former Verizon service areas are upset about poor customer service and on-time repair visits and billing errors;
- Frontier landline customers have been disconnecting for years, especially in copper-only service areas.
- Frontier FiOS TV customers are getting better pricing and promotional deals from competing cable and satellite providers, or are cutting the cord entirely.
The average Frontier Legacy customer pays $65.11 a month. Customers with Frontier FiOS in California, Texas, and Florida pay an average of $107.35 a month.
Despite the anemic results, Frontier CEO Daniel McCarthy was optimistic.
“Our fourth quarter results highlight the ongoing progress on our key initiatives to improve customer retention, enhance the customer experience, and align our cost structure,” McCarthy said in a press release. “We are pleased with continued improvement in subscriber trends and churn in our California, Texas and Florida (CTF) markets, and the continued operating efficiencies achieved in the fourth quarter.”
But McCarthy rattled investors with news Frontier’s board of directors had voted to suspend the company’s dividend payout to shareholders, one of the key reasons investors buy Frontier common stock. Frontier intends to use the $250 million it would have handed shareholders to pay down the company’s massive debts.
In 2018, Frontier will pay more in interest on its outstanding debt ($1.5 billion) than it will spend on network upgrades and other capital expenditures ($1.0 billion to $1.15 billion). Most of the company’s debt comes from Frontier’s aggressive history of acquisitions, buying landline service areas from Verizon and AT&T.
Despite predictions by Frontier’s executives that its $10+ billion acquisition of Verizon service areas in California, Texas and Florida would deliver dramatically better results for Frontier and its shareholders, a botched transition and ongoing complaints about poor customer service and billing errors alienated Frontier’s adopted customers. Many canceled service and have no plans to return.
With Frontier’s financial condition concerning some financial analysts, Frontier is considering selling off its newest service areas to raise money.


 Subscribe
Subscribe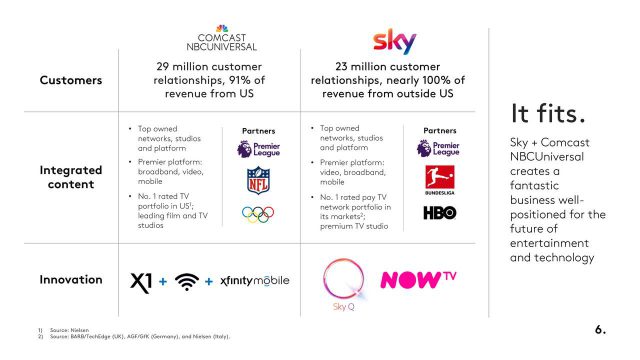
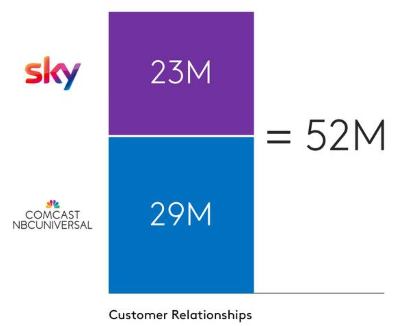 That three American companies are now competing to acquire Europe’s largest media company and biggest pay-TV broadcaster, with more than 23 million subscribers, could create concern among some regulators about foreign ownership of the media. A bid from Comcast is likely to be less controversial than dealing with Rupert Murdoch, however, who already has extensive media holdings in the United Kingdom.
That three American companies are now competing to acquire Europe’s largest media company and biggest pay-TV broadcaster, with more than 23 million subscribers, could create concern among some regulators about foreign ownership of the media. A bid from Comcast is likely to be less controversial than dealing with Rupert Murdoch, however, who already has extensive media holdings in the United Kingdom.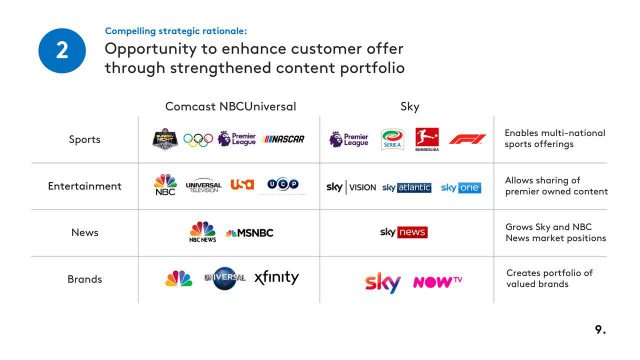
 AT&T’s attempt to avoid oversight and enforcement of consumer protection laws by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
AT&T’s attempt to avoid oversight and enforcement of consumer protection laws by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)  “AT&T promised its customers ‘unlimited’ data, and in many instances, it has failed to deliver on that promise,” said former FTC Chairwoman Edith Ramirez in 2014. “The issue here is simple: ‘unlimited’ means unlimited.”
“AT&T promised its customers ‘unlimited’ data, and in many instances, it has failed to deliver on that promise,” said former FTC Chairwoman Edith Ramirez in 2014. “The issue here is simple: ‘unlimited’ means unlimited.”

 “They basically said that until we agree that they don’t have to contribute to our pension and health plan, they won’t talk about anything else,” Chris Erikson, business manager of Local 3,
“They basically said that until we agree that they don’t have to contribute to our pension and health plan, they won’t talk about anything else,” Chris Erikson, business manager of Local 3,  The Trump Administration is
The Trump Administration is 