 The arrival of Netflix north of the American border has sparked a potential video revolution in Canada that some fear could renew “an erosion” of Canadian culture and self-identity as the streaming video service floods the country with American-made television and movies. But anxiety also prevails on the upper floors of some of Canada’s biggest telecom companies, worried their business models are about to be challenged like never before.
The arrival of Netflix north of the American border has sparked a potential video revolution in Canada that some fear could renew “an erosion” of Canadian culture and self-identity as the streaming video service floods the country with American-made television and movies. But anxiety also prevails on the upper floors of some of Canada’s biggest telecom companies, worried their business models are about to be challenged like never before.
Two weeks ago, the country saw a remarkable Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) hearing featuring a Netflix executive obviously not used to being grilled by the often-curt regulators. When it was all over, Netflix refused to comply with a CRTC order for information about Netflix’s Canadian customers.
Earlier today, the CRTC’s secretary general, John Traversy, declared that because of the lack of cooperation from Netflix, all of their testimony “will be removed from the public record of this proceeding on October 2, 2014.” That includes their oral arguments.
“As a result, the hearing panel will reach its conclusions based on the remaining evidence on the record. There are a variety of perspectives on the impact of Internet broadcasting in Canada, and the panel will rely on those that are on the public record to make its findings,” Mr. Traversy wrote in a nod to Canada’s own telecom companies.
Not since late 1990’s Heritage Minister Sheila Copps, who defended Canadian content with her support of a law that restricted foreign magazines from infiltrating across the border, had a government official seemed willing to take matters beyond the government’s own policy.
CRTC chairman Jean-Pierre Blais threw down the gauntlet when Netflix hesitated about releasing its Canadian subscriber and Canadian content statistics to the regulator. Mr. Blais wanted to know exactly how many Canadians are Netflix subscribers and how much of what they are watching on the service originates in Canada.
With hearings underway in Ottawa, bigger questions are being raised about the CRTC’s authority in the digital age. Doug Dirks from CBC Radio’s The Homestretch talks with Michael Geist at the University of Ottawa. Sept. 19, 2014 (8:40) You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Netflix has operated below regulatory radar since it first launched service in Canada four years ago. The CRTC left the American company with an impression it had the right to regulate Netflix, but chose not to at this time. The CRTC of 2010 was knee-deep in media consolidation issues and did not want to spend a lot of time on an American service that most Canadians watched by using proxy servers and virtual private networks to bypass geographic content restrictions. But now that an estimated 30% of English-speaking Canada subscribes to Netflix, it is threatening to turn the country’s cozy and well-consolidated media industry on its head.
Ask most of the corporate players involved and they will declare this is a fight about Canada’s identity. After all, broadcasters have been compelled for years to live under content laws that require a certain percentage of television and radio content to originate inside Canada. Without such regulations, enforced by the CRTC among others, Canada would be overwhelmed by all-things-Americans. Some believe that without protection, Canadian viewers will only watch and listen to American television and music at the cost of Canadian productions and artists.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/BNN Netflix vs the CRTC 9-22-14.flv[/flv]
Kevin O’Leary, Chairman, O’Leary Financial Group is furious with regulators for butting into Netflix’s online video business and threatening its presence in Canada is an effort to protect incumbent business models. From BNN-Canada. (8:45)
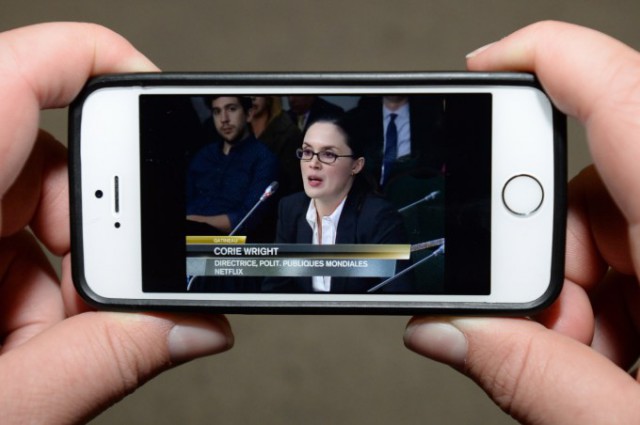

A viewer watches Netflix’s Corie Wright testify before the CRTC. (Image: Sean Kilpatrick, The Canadian Press)
But behind the culture war is a question of money – billions of dollars in fact. Giant media companies like Rogers, Shaw, and Bell feel threatened by the presence of Netflix, which can take away viewers and change a media landscape that has not faced the kind of wholesale deregulation that has taken place in the United States since the Reagan Administration.
Before Netflix, the big Canadian networks didn’t object too strongly to the content regulations. After all, CRTC rules helped establish the Canadian Media Fund which partly pays for domestic TV and movie productions. Canada’s telephone and satellite companies also have to contribute, and they collectively added $266 million to the pot in 2013, mostly collected from their customers in the form of higher bills. Netflix doesn’t receive money from the fund and has indicated it doesn’t need or want the government’s help to create Canadian content.
“It is not in the interest of consumers to have new media subsidize old media or to have new entrants subsidize incumbents,” added Netflix’s Corie Wright. “Netflix believes that regulatory intervention online is unnecessary and could have consequences that are inconsistent with the interests of consumers,” Wright said, adding viewers should have the ability “to vote with their dollars and eyeballs to shape the media marketplace.”
That is not exactly what the CRTC wanted to hear, and Wright was off the Christmas card list for good when she directly rebuffed Mr. Blais’ requests for Netflix’s data on its Canadian customers. Wright implied the data would somehow make its way out of the CRTC’s offices and end up in the hands of the Canadian-owned broadcast and cable competitors that know many at the CRTC on a first name basis.
Does Netflix pose a threat to Canadian culture? Matt Galloway spoke with John Doyle, the Globe & Mail’s television critic, on the Sept. 22nd edition of CBC Radio’s Metro Morning show. Sept. 22, 2014 (8:31) You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Mr. Blais, obviously not used to requests being questioned, repeated demands for Netflix’s subscriber data to be turned over by the following Monday and if Netflix did not comply, he would revoke Netflix’s current exemption from Canadian content rules and bring down the hammer of regulation on the streaming service.

Blais
The deadline came and went and last week Netflix defiantly refused to comply with the CRTC’s order. A Netflix official said that while the company has responded to a number of CRTC requests, it was not “in a position to produce the confidential and competitively sensitive information, but added it was always prepared to work constructively with the commission.”
Now things are very much up in the air. Many Canadians question why the CRTC believes it has the right to regulate Internet content when it operates largely as a broadcast regulator. Public opinion seems to be swayed against the CRTC and towards Netflix. Canadian producers and writers are concerned their jobs are at risk, Canadian media conglomerates fear their comfortable and predictable future is threatened if consumers decide to spend more time with Netflix and less time with them. All of this debate occurring within the context of a discussion about forcing pay television companies to offer slimmed down basic cable packages and implement a-la-carte — pay only for the channels you want — is enough to give media executives heartburn.
To underscore the point much of this debate involves money, American TV network executives also turned up at the CRTC arguing for regulations that would compensate American TV stations for providing “free” programming on Canadian airwaves, cable, and satellite — retransmission consent across the border.
Netflix does not seem too worried it is in trouble in either Ottawa or in the halls of CRTC headquarters at Les Terrasses de la Chaudière in Gatineau, Québec, just across the Ottawa River. Prime Minister Stephen Harper and Heritage Minister Shelly Glover have made it clear they have zero interest in taxing or regulating Netflix. Even if they were, the Canada-U.S. free trade agreement may make regulating Netflix a practical impossibility, especially if the U.S. decides to retaliate.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Canadian Press CRTC vs Netflix 9-19-14.mp4[/flv]
Dwayne Winseck, Carleton School of Journalism and Communication, defended the role the CRTC is mandated to play by Canada’s telecommunications laws. (1:41)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Three competing telephone companies in Singapore have launched an all-out price war on gigabit fiber to the home Internet access that shows what real competition can do for broadband pricing.
Three competing telephone companies in Singapore have launched an all-out price war on gigabit fiber to the home Internet access that shows what real competition can do for broadband pricing. Singapore’s largest phone company, SingTel, has its own unlimited gigabit offering for $55.13 a month, a price the company is now re-evaluating.
Singapore’s largest phone company, SingTel, has its own unlimited gigabit offering for $55.13 a month, a price the company is now re-evaluating. Rightscorp does not appear to be spending its limited resources actually pursuing suspected violators in court. The threat of further action alone appears to have been enough for many to voluntarily pay the firm after receiving their first violation notice. Little, if anything, has happened to those who ignore Rightscorp’s settlement messages unless their ISP suspends access.
Rightscorp does not appear to be spending its limited resources actually pursuing suspected violators in court. The threat of further action alone appears to have been enough for many to voluntarily pay the firm after receiving their first violation notice. Little, if anything, has happened to those who ignore Rightscorp’s settlement messages unless their ISP suspends access.

 Whether ISPs will grant unprecedented access to a third-party company trying to turn off their customers’ broadband while maintaining a financial interest in extracting settlements from those customers is doubtful.
Whether ISPs will grant unprecedented access to a third-party company trying to turn off their customers’ broadband while maintaining a financial interest in extracting settlements from those customers is doubtful. Comcast has strongly denied reports it threatened customers with service termination for using the Tor anonymous web browser, designed to obscure a web user’s identity or location.
Comcast has strongly denied reports it threatened customers with service termination for using the Tor anonymous web browser, designed to obscure a web user’s identity or location. But whether the messages reported by Deep.Dot.Web were simply the result of an overeager support employee or actual company policy is now in dispute.
But whether the messages reported by Deep.Dot.Web were simply the result of an overeager support employee or actual company policy is now in dispute.