Making America Great for Robber Barons Again
The president-elect’s choice for chairing the Federal Communications Commission may conclude there is little reason to even have a regulatory agency for telecommunications.
Donald Trump has gone farther to the right than any president-elect in modern history, at least in how he has chosen to staff his transition team. Having a place on that team is traditionally seen as a fast track to getting a plum cabinet position or leadership role in Washington’s bureaucracy, and Mr. Trump’s choices for overseeing tech and telecom policy have more in common with Ayn Rand than Ralph Nader.
Two of the top picks for his FCC transition team are true believers in the “laissez-faire/the free market always knows best” camp, but both have also been on the payroll of Big Telecom companies that believe special favors are perfectly acceptable.
The notorious D.C. revolving doorman Jeffrey Eisenach, now a leading contender for the next chairman of the FCC, is a man with so many hats that the New York Times published an exposé on him, noting it has become hard to tell whether Eisenach’s views are his own, those of his friends at the corporate-friendly American Enterprise Institute (AEI), or those of various telecom companies like Verizon that have had him on the payroll.
Eisenach has been heavily criticized for his especially close ties to telecom companies, fronting their positions at various Washington events often under the cover of his role as a “think tank scholar” at AEI. Eisenach despises Net Neutrality with a passion, and has used every opportunity to attack the open internet protection policies as overregulation. At the same time, Eisenach’s consulting firm was also doing work on behalf of the cellular telephone industry, including Verizon and other cell companies.
Eisenach is exceptionally casual about disclosing any paid financial ties, and has received criticism for it. His prominence as a member of the Trump transition team is therefore curious, considering incoming vice president Mike Pence has tried to clean the transition team of lobbyists.

Eisenach
Trump’s other leading contender is Mark Jamison, a former lobbyist for Sprint who now works for AEI. Jamison has received less attention and scrutiny from the telecommunications press, but in some cases his views, well-represented on his blog, are even more extreme than those of Mr. Eisenach.
In a 2013 report to the Florida Public Service Commission, Jamison looked down on consumer involvement in creating and enforcing telecom regulations:
Does customer involvement in regulation improve outcomes? Not always, according to PURC Director Mark Jamison. Speaking at the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission annual conference in Brisbane, Australia, Dr. Jamison explained that the key question is, “Who do we expect to change when regulators and customers engage?” Most discussion on customer engagement is about customers informing regulators about customer preferences and utility practices. Learning by regulators is important, but so are the building legitimacy, ensuring regulator integrity, and engaging in adaptive learning that are largely about changing customers. An over emphasis on changing regulators can result in pandering to current norms, which hinders institutional strengthening and adaptive work.
In that same report, Jamison echoed some of the same sentiments he has made on his blog, questioning the wisdom of regulating telecommunications policies, providing subsidies to ensure affordable telephone service (Lifeline), subsidizing rural broadband expansion, and maintaining the core concept of universal service, which means assuring every American that wants utility service can affordably get it.
Jamison even questioned the need for the FCC in its current form, particularly overseeing rate regulation, fair competition, and enforcing rules that overturn the telecom industry’s cartel-like agreement on mandated set-top boxes (and rental fees), Net Neutrality and interconnection agreements and fees, and consumer protection:
Most of the original motivations for having an FCC have gone away. Telecommunications network providers and ISPs are rarely, if ever, monopolies. If there are instances where there are monopolies, it would seem overkill to have an entire federal agency dedicated to ex ante regulation of their services. A well-functioning Federal Trade Commission (FTC), in conjunction with state authorities, can handle consumer protection and anticompetitive conduct issues.
Content on the web competes well with content provided by broadcasters, seeming to eliminate any need for FCC oversight of broadcasters. Perhaps there is need for rules for use of the airwaves during times of emergency, but that can be handled without regulating the content providers themselves.
The only FCC activity that would seem to warrant having an independent agency is the licensing of radio spectrum. Political interference in spectrum licenses would at least dampen investment and could lead to rampant corruption in the form of valuable spectrum space being effectively handed out to political cronies.

Jamison
Jamison’s theories are interesting, but in the real world they are impractical and frankly untrue. Readers of Stop the Cap! have long witnessed the impact of the insufficiently competitive telecom marketplace — higher broadband fees, data caps, and relentlessly terrible customer service. The costs to provide service have declined, but prices continue to rise. For many consumers, there is barely a duopoly for telecom services with cable companies taking runaway victory laps for providing 21st century broadband speeds while an area’s phone company continues to try to compete with underinvested DSL. The FTC has been a no-show on every important telecom issues of our time, in part because the industry got itself deregulated, leaving oversight options very limited.
It wasn’t the FTC that halted AT&T’s attempted buyout of T-Mobile and Comcast didn’t lose its struggle to acquire Time Warner Cable because of the FTC either. Pushback from the FCC and Department of Justice proved to be the only brakes on an otherwise consolidation-crazed telecom sector.
Oversight of broadcasting remains important because unlike private networks, the airwaves are a publicly owned resource used for the good of the American people. Jamison would abandon what little is left of regulations that required broadcasters to serve the public interest, not just private profit motives. Programming content is not the only matter of importance. Who gets a license to run a television or radio station matters, and so does the careful coordination of spectrum. It is ironic Jamison theorizes that a lack of regulation (of spectrum) would lead to political interference, rampant corruption, and cronyism. Anyone who has followed our experiences dealing with many state regulatory bodies and elected officials over telecom mergers and data caps can already use those words to describe what has happened since near-total deregulation policies have been enacted.
Public and private broadband competitors like local communities and Google have been harassed, stymied, and delayed by organized interference coordinated by incumbent telecom companies. Allowing them off the leash, as Jamison advocates, would only further entrench these companies. We have a long history in the United States dealing with unfettered monopoly powers and trusts. Vital infrastructure and manufacturing sectors were once held captive by a handful of industrialists and robber barons, and consumers paid dearly while those at the top got fabulously rich. Their wealth and power grew so vast and enduring, we are still familiar with their names even today — Rockefeller, Vanderbilt, Morgan, Schwab, Mellon, Duke, and Carnegie, just to name a few.
Jamison wrote a blog entry mapping out how to ultimately destroy the effectiveness of the FCC:
- Take direction from politicians,
- Promote partisan divides,
- Change the language in orders after the FCC votes,
- Ignore the facts, or at least manipulate them.
Jamison intended to argue that represented the current state of the Obama Administration’s FCC, but it is just as easy to ponder what comes after the Trump-lit bonfire of burned regulations and oversight, leaving only Big Telecom companies and their paid mouthpieces to manipulate the facts.
Jamison also undercuts his own argument in two other ways: first by declaring Michael Powell one of the great FCC chairmen of the modern era (after leaving the FCC he became president of the country’s biggest cable industry lobbying group) and second by relying extensively on quoting people with direct and undisclosed financial ties to the telecom companies that will directly benefit from implementing Jamison’s world views.

New York Times: In a 2014 email, Mr. Eisenach encouraged Michael O’Rielly, a Republican FCC commissioner, to use an American Enterprise Institute event to “lay out the case against” internet regulations.
Who doesn’t ultimately matter much in this debate, according to Jamison, are customers and consumers, whose input in these discussions is dismissed as either trendy or misinformed. No similar conclusions are forthcoming from Mr. Jamison about the influence and misinformation emanating from huge telecommunications companies that keep more than a few of his self-interested sources in comfortable suburban Virginia homes, driving their nice cars to and from the offices of shadowy think tanks that receive direct corporate funding or go out of their way to hide their benefactors.
Appointing either Mr. Eisenach or Mr. Jamison to the Federal Communications Commission would be the ultimate rubber stamping of business as usual in Washington, exactly what Donald Trump ran against. That may make Verizon or Comcast “great again,” but it certainly won’t help the rest of the country.
 AT&T Mobility customers can now stream AT&T-owned DirecTV video on their mobile devices without fear of hitting their data allowance, because AT&T has exempted its own content from mobile data caps.
AT&T Mobility customers can now stream AT&T-owned DirecTV video on their mobile devices without fear of hitting their data allowance, because AT&T has exempted its own content from mobile data caps.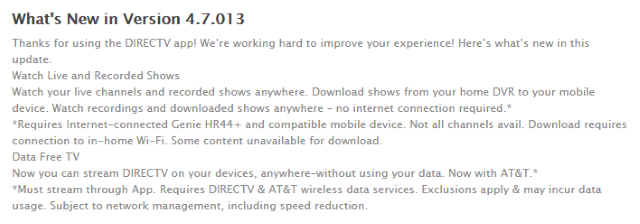



 Subscribe
Subscribe



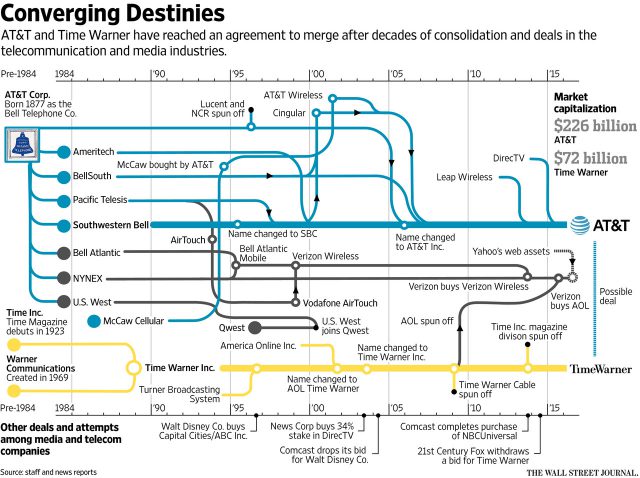
 It was a busy weekend for AT&T’s Randall Stephenson and Time Warner (Entertainment)’s Jeff Bewkes, culminating in an announcement from AT&T it was acquiring Time Warner
It was a busy weekend for AT&T’s Randall Stephenson and Time Warner (Entertainment)’s Jeff Bewkes, culminating in an announcement from AT&T it was acquiring Time Warner 

 Several years after wireless unlimited data plans became grandfathered or riddled by speed throttling, America’s third and fourth largest carriers have decided the marketplace wants “unlimited everything” after all and is prepared to give customers what they want, at least until they read the fine print.
Several years after wireless unlimited data plans became grandfathered or riddled by speed throttling, America’s third and fourth largest carriers have decided the marketplace wants “unlimited everything” after all and is prepared to give customers what they want, at least until they read the fine print.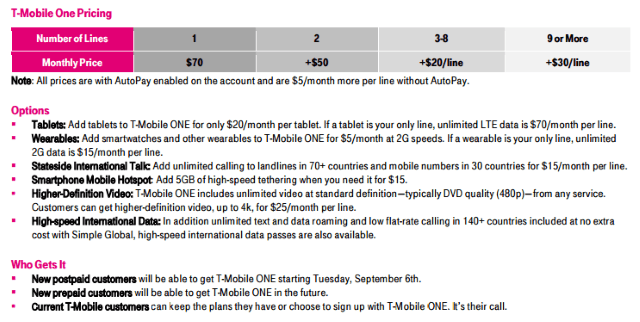

 While we’re happy to see unlimited data plans return to prominence, T-Mobile is continuing to punish high bandwidth applications, tethering, and usage outliers with frustrating speed throttles.
While we’re happy to see unlimited data plans return to prominence, T-Mobile is continuing to punish high bandwidth applications, tethering, and usage outliers with frustrating speed throttles.
 Another clue about the impact of online video on T-Mobile’s network is the same video throttling strategy is built into T-Mobile ONE and applies to all online video, whether the provider partners with T-Mobile or not. Also consider the extraordinary cost of the optional HD Video add-on, which defeats video throttling: a whopping $25 per month per device. That kind of pricing clearly suggests 1080p or even 4K video is a major resource hog for T-Mobile, and customers looking for this level of video quality are going to pay substantially to get it.
Another clue about the impact of online video on T-Mobile’s network is the same video throttling strategy is built into T-Mobile ONE and applies to all online video, whether the provider partners with T-Mobile or not. Also consider the extraordinary cost of the optional HD Video add-on, which defeats video throttling: a whopping $25 per month per device. That kind of pricing clearly suggests 1080p or even 4K video is a major resource hog for T-Mobile, and customers looking for this level of video quality are going to pay substantially to get it.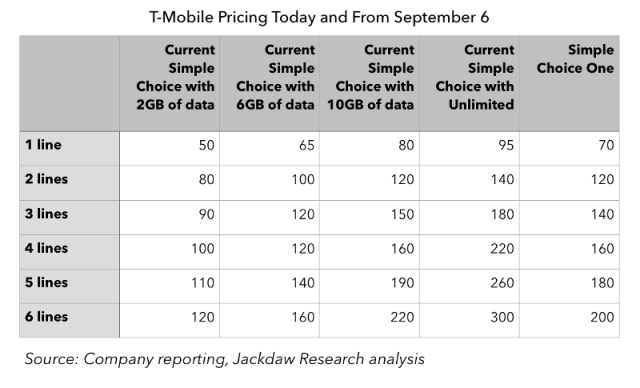
 Sprint: Unlimited Freedom: Two Lines of Unlimited Talk, Text, and Data for $100/month
Sprint: Unlimited Freedom: Two Lines of Unlimited Talk, Text, and Data for $100/month
 “Wireless customers want simple, worry-free and affordable wireless plans on a reliable network,” said Marcelo Claure, Sprint president and CEO. “There can be a lot of frustration and confusion around wireless offers, with too much focus on gigabytes and extra charges. Our answer is the simplicity of Unlimited Freedom. Now customers can watch their favorite movies and videos and stream an unlimited playlist at an amazing price.”
“Wireless customers want simple, worry-free and affordable wireless plans on a reliable network,” said Marcelo Claure, Sprint president and CEO. “There can be a lot of frustration and confusion around wireless offers, with too much focus on gigabytes and extra charges. Our answer is the simplicity of Unlimited Freedom. Now customers can watch their favorite movies and videos and stream an unlimited playlist at an amazing price.”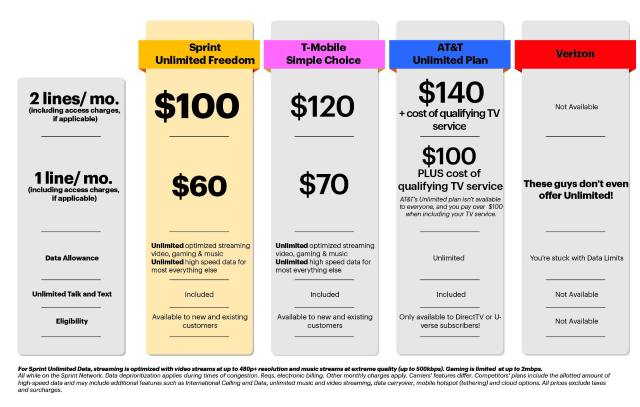
 Also, beginning Friday, Aug. 19, Sprint’s leading prepaid brand, Boost Mobile introduces its own unlimited offer, Unlimited Unhook’d:
Also, beginning Friday, Aug. 19, Sprint’s leading prepaid brand, Boost Mobile introduces its own unlimited offer, Unlimited Unhook’d: