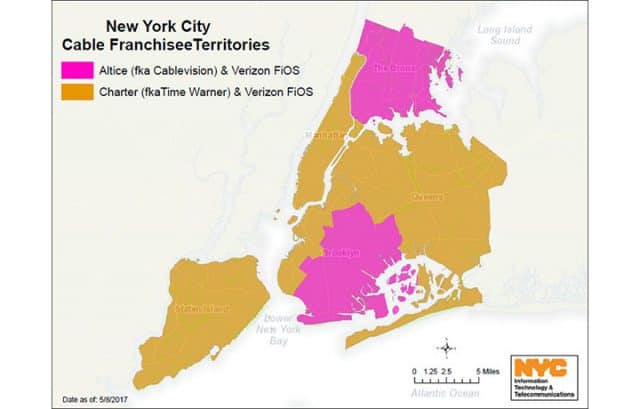
New York City’s cable franchise territories
A proposal to replace Charter Communications’ Spectrum cable systems in New York with a workers co-op, owned and self-managed by its workers, would offer a bundle of television, phone, and broadband service price-capped at $100 a month for residential customers.
Developed by several dozen striking Charter/Spectrum workers, the 18-page proposal, “New York City Communication July 2018 Business Plan” would, for now, address only the five boroughs of New York City and nearby Bergen, N.J. But Troy Walcott, a striking member of the International Brotherhood of Electric Workers (IBEW) Local 3, says the current proposal was written as “a proof of concept” that can be adopted across New York State.
“The best time is now,” Walcott told LaborPress, noting that if the city (or state) decided not to renew Charter Communications’ franchise agreements in the city, there will still be a few years left before it expires, giving the proposed co-op time to develop its own network or plan to overhaul what was originally Time Warner Cable’s system in places like Manhattan.
A citywide co-op would also introduce competitive service in boroughs presently serviced by Altice, formerly Cablevision. The group would have to build its own network in those areas. If New York revokes Charter’s franchise, the cable system would likely take the city and/or state to court, setting up years of litigation. Past precedent has shown that cable systems abandoning or forced from an area are exceptionally rare, and usually involve a friendly sale of the existing system to another provider. One example was Adelphia Communications Corporation, which ran the fifth largest cable company in the country until it filed bankruptcy in 2002 after investigators revealed internal executive corruption. Adelphia systems were sold to Comcast and Time Warner Cable in most areas, although the communities of Mooresville, Davidson, and Cornelius, N.C., acquired the bankrupt Adelphia system serving parts of the three communities in 2007 for $80 million, relaunching it as a community-owned cable provider with mixed results.

A workers co-op is owned and run by its workers in the public interest.
If New York does strip Charter of its Spectrum cable franchises in the state, and if that effort survives the inevitable court challenges, Charter would likely sell its systems in New York to Comcast, an obviously motivated buyer. Another possible, but less-likely buyer is Altice, which acquired Cablevision and already provides service in parts of downstate New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
Charter is facing multiple investigations in New York over its business conduct. In New York City, where its franchise agreement is set to expire July 18, 2020, the company is under fire for its creative interpretation of “located in New York City” — language in Article 17 of the franchise agreement which requires Charter to use vendors registered to do business in New York, have a long-term commercial lease in New York, and more than 50% of its workforce living in New York.
With a substantial amount of its workforce on strike in the area for the last year and a half, and the industry’s trend to shift work to third-party contractors as a cost saving measure, the IBEW has been documenting instances of Charter-badged commercial vehicles parked overnight behind a Far Rockaway florist shop or in residential neighborhoods, often with out-of-state license plates.
Charter officials deny those accusations, and claim at least 75% of its vendors and contractors are located within New York City.
When Kate Blumm, assistant commissioner of the New York City Department of Information Technology & Telecommunications (DoITT) confronted Charter officials about its possible use of out-of-state vendors, the response from Charter was less than reassuring.
“Once we started to probe, we realized that Charter was essentially making the argument that if you are a worker and you are doing work in the city, therefore, you are located in the city,” Blumm said during the March 13 episode of the “Blue Collar Buzz” podcast. “They pointed us to a Macmillan online dictionary definition of what the word ‘located’ means — and we kind of looked at ourselves and were scratching our heads — this is not the spirit and intent of this provision. This provision says that Charter has to use best efforts to use vendors located in the city.”
As a result, the DoITT has pushed its franchise agreement audit one year earlier than normal, now scheduled to begin Sept. 1. The city’s concerns about Charter’s performance have been amplified at the state level by the New York Public Service Commission, which has hammered Charter executives for months about the company’s inability to meet its obligations under the 2016 Merger Order approving the takeover of Time Warner Cable.
Tell us what you think about your cable TV service – whether it’s @verizon , @Altice or @GetSpectrum – send us your comments so we can make sure New Yorkers get the best service possible 📺👉https://t.co/ic2cx3sAjW
— NYC IT & Telecomm (@NYCDoITT) July 11, 2018
“Not only has the company failed to meet its obligations to build out its cable system as required, it continues to make patently false and misleading claims to consumers that it has met those obligations without in any way acknowledging the findings of the Public Service Commission to the contrary,” said PSC Chairman John B. Rhodes. “Our patience with Charter has come to an end and now we must move to take much stronger actions.”

Mayor de Blasio
Backers of the cable co-op note many of those on their business plan development team have direct experience designing, surveying, building, and maintaining the existing Spectrum cable system originally owned by Time Warner Cable.
“We know the system because we built it,” Walcott said. “The system was already crumbling and the infrastructure needed to be redone. This is something that’s going to have to get done anyway. We’re saying, instead of letting them do it, let’s start doing it and rebuilding it ourselves — the people that are actually going to build it anyway.”
Finding enough money to proceed will be the co-op’s biggest challenge. New York City officials, like Mayor Bill De Blasio, are in favor of more cable competition in spirit, but are careful not to commit themselves, or the sizable sums required if the group decides to begin building a competing system or bid to acquire the current Spectrum system. So far, the New York City Council has committed to gradually increasing financial support for the development and cultivation of worker cooperatives, starting with $1.2 million in 2015 and increasing to $2.2 million last year. A full-scale acquisition of the existing infrastructure owned by Charter in New York would likely run into the billions of dollars.
The group hopes public demand and dislike of Charter/Spectrum will force elected officials to get involved in the effort.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
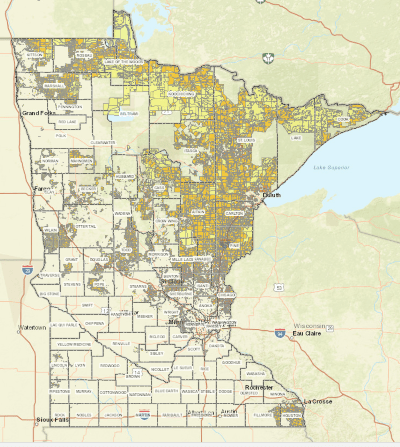


 REU is
REU is  Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.


 While parts of rural Tennessee languish with little or no broadband service, the state’s electric cooperatives are jumping to deliver internet access over fiber optic cables after the governor eased restrictions written into state law on rural co-ops offering public broadband service.
While parts of rural Tennessee languish with little or no broadband service, the state’s electric cooperatives are jumping to deliver internet access over fiber optic cables after the governor eased restrictions written into state law on rural co-ops offering public broadband service. The conservative and industry-backed groups that coordinated with the telecom industry to push Tennessee to pass restrictive laws effectively banning municipal or public broadband competition are grudgingly tolerating co-ops entering the broadband marketplace, as long as they only service areas where they won’t compete with an established phone or cable company. They also must remain within their electric service area.
The conservative and industry-backed groups that coordinated with the telecom industry to push Tennessee to pass restrictive laws effectively banning municipal or public broadband competition are grudgingly tolerating co-ops entering the broadband marketplace, as long as they only service areas where they won’t compete with an established phone or cable company. They also must remain within their electric service area.