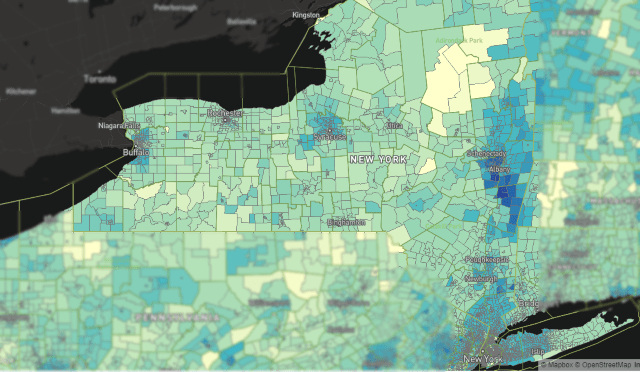
 Customer satisfaction with fiber to the home internet service is so high, one industry leader says the only time customers cancel service is if they move or die.
Customer satisfaction with fiber to the home internet service is so high, one industry leader says the only time customers cancel service is if they move or die.
Carl Russo, CEO of internet equipment vendor Calix, says phone companies are relying on fiber optic networks to turn their struggling businesses around except in the most rural areas of the country.
“Fixed wireless will sometimes be the right choice and Calix’s software supports it. But our telco customers with fiber will lose very few customers. If they provide strong, customer-focused service, no one will have a reason to switch,” Russo told Dave Burstein’s Fast Net News. “It’s only a slight exaggeration to say customers only churn if they move or die. This is provided the service provider chooses to ‘own’ the subscriber experience. A service provider that invests in fiber but doesn’t further invest in an excellent subscriber experience is still vulnerable.”
Russo argues that fiber to the home service has been the right choice for most of the developed world for several years now, at least where there is hearty competition between providers.
Where competition is lacking, phone companies often still rely on archaic DSL service, which is increasingly incapable of competing with even smaller cable operators. Phone companies are now up against the wall, forced to recognize that existing, decades-old copper wire infrastructure cannot sustain their future in the broadband business. Companies that drag their feet on fiber upgrades are bleeding customers, and some companies are even in bankruptcy reorganization.

Russo
Fiber networks are future-proof, with most offering up to gigabit speed to consumers and businesses. But upgrading to 10 Gbps will “add little to the cost” once demand for such faster speed appears, Russo said.
Fast Net News notes that France Telecom, Telefonica Spain, Bell Canada, and Telus have all proven successful using fiber to the home service to compete with cable companies to market internet access. Companies that approved less costly fiber to the neighborhood projects that relied on keeping a portion of a company’s legacy copper network, including AT&T, BT in the United Kingdom, and Deutsche Telekom in Germany, have had to bring back construction equipment to further extend fiber optic cables to individual customer homes — a costly expense.
Even public broadband projects like Australia’s National Broadband Network (NBN) paid dearly for a political decision to downsize the NBN’s original fiber optic design to save money. The NBN was hobbled by a more conservative government that came to power just as the network was being built. Many NBN customers ended up with a more advanced form of DSL supplied from oversubscribed remote terminals, which delivered just 50 Mbps to some subscribers. For-profit companies have also been pressured to keep costs down and limit fiber rollouts by Wall Street and investors. Verizon FiOS is the best known American example, with further network expansion of the fiber optic service essentially shelved in 2010 at the behest of investors that claimed the upgrades cost too much.
![]() Underfunded upgrades often bring customer dissatisfaction as speeds cannot achieve expectations, and many hybrid fiber-copper networks are less robust and more subject to breakdowns. In the United Kingdom, BT’s “super fast” broadband initiative has been a political problem for years, and communities frequently compete to argue who has the worst service in the country. BT’s fiber-to-the-village approach supplies fiber internet service to street cabinets in smaller communities that link to existing BT copper phone lines that are often in poor shape. Customers often get less than 50 Mbps service from BT’s “super fast” service while a few UK cable companies are constructing all-fiber networks in larger cities capable of supplying gigabit internet speed to every customer.
Underfunded upgrades often bring customer dissatisfaction as speeds cannot achieve expectations, and many hybrid fiber-copper networks are less robust and more subject to breakdowns. In the United Kingdom, BT’s “super fast” broadband initiative has been a political problem for years, and communities frequently compete to argue who has the worst service in the country. BT’s fiber-to-the-village approach supplies fiber internet service to street cabinets in smaller communities that link to existing BT copper phone lines that are often in poor shape. Customers often get less than 50 Mbps service from BT’s “super fast” service while a few UK cable companies are constructing all-fiber networks in larger cities capable of supplying gigabit internet speed to every customer.
Calix is positioned to earn heavily by selling the equipment and infrastructure that will power future fiber network upgrades that are inevitable if companies want to attract and keep customers. A new round of federal rural broadband funding will help phone companies pay for the upgrades, which means many rural Americans will find fiber to the home service in their future.


 Subscribe
Subscribe If you’ve ever lived in small-town America, you know how bad the internet can sometimes be. So one town in North Carolina decided: If we can’t make fast internet come to us, we’ll build it ourselves. And they did, despite laughter and disbelief from Time Warner Cable (today known as Spectrum).
If you’ve ever lived in small-town America, you know how bad the internet can sometimes be. So one town in North Carolina decided: If we can’t make fast internet come to us, we’ll build it ourselves. And they did, despite laughter and disbelief from Time Warner Cable (today known as Spectrum). One of America’s internet service providers managed to achieve a customer satisfaction score of 94%, an unprecedented vote of approval from consumers that typically loathe their cable or phone company.
One of America’s internet service providers managed to achieve a customer satisfaction score of 94%, an unprecedented vote of approval from consumers that typically loathe their cable or phone company. FairlawnGig offers two plans to residents: 300/300 Mbps service for $55 a month or 1,000/1,000 Mbps service for $75. Landline phone service is an extra $25 a month, and the municipal provider has pointed its customers to online cable TV alternatives like Hulu and YouTube TV for television service. Incumbent cable and phone companies usually respond to this kind of competition with cut-rate promotions to keep the customers they have and lure others back. Spectrum has countered with promotions offering 400 Mbps internet for as little as $30/mo for two years. Despite the potential savings, most people in Fairlawn won’t go back to Spectrum regardless of the price. FairlawnGig’s loyalty score is 80, with 85% of those not only sticking with FairlawnGig but also actively recommending it to others.
FairlawnGig offers two plans to residents: 300/300 Mbps service for $55 a month or 1,000/1,000 Mbps service for $75. Landline phone service is an extra $25 a month, and the municipal provider has pointed its customers to online cable TV alternatives like Hulu and YouTube TV for television service. Incumbent cable and phone companies usually respond to this kind of competition with cut-rate promotions to keep the customers they have and lure others back. Spectrum has countered with promotions offering 400 Mbps internet for as little as $30/mo for two years. Despite the potential savings, most people in Fairlawn won’t go back to Spectrum regardless of the price. FairlawnGig’s loyalty score is 80, with 85% of those not only sticking with FairlawnGig but also actively recommending it to others.
 Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.
Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.
 “Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,”
“Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,”