 In the race to acquire spectrum and market share, AT&T and Verizon Wireless have already won most of the awards worth taking and have little to fear from smaller competitors. The U.S. government has seen to that.
In the race to acquire spectrum and market share, AT&T and Verizon Wireless have already won most of the awards worth taking and have little to fear from smaller competitors. The U.S. government has seen to that.
The two wireless giants have benefited enormously from government spectrum auctions that award the most favorable wireless spectrum to the highest bidder, a policy that retards competition and guarantees deep-pocketed companies will continue to dominate in the coverage wars.
Winner-take-all spectrum auctions have already proven that AT&T and Verizon are best equipped to bid and win coveted 700MHz spectrum which provides the best indoor and fringe-area reception. This is why AT&T and Verizon customers often find “more bars in more places” than customers relying on Sprint or T-Mobile. Smaller carriers typically have to offer service over much-higher frequencies that don’t penetrate buildings very well. With a reduced level of service, these competitors are at an immediate competitive disadvantage. They also must spend more for a larger number of cell towers to provide uniform service.
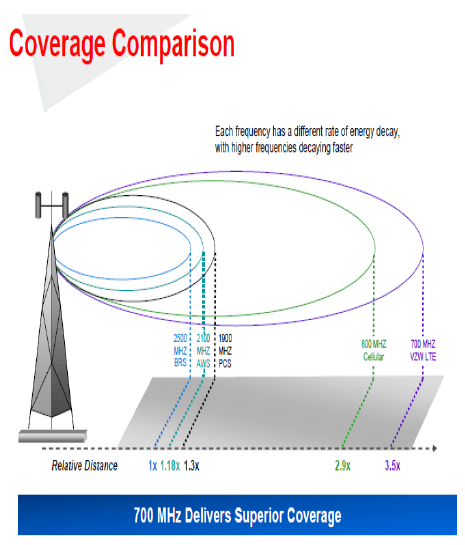
Verizon’s own presentation materials tout the benefits of controlling 700MHz spectrum, which is less costly to deploy and offers more robust coverage.
Sprint and T-Mobile have two strikes against them at the outset — less favorable spectrum and much smaller coverage areas. Customers who want the best reception under all circumstances usually get it from the biggest two players. Those focused primarily on price are willing to sacrifice that reception for a lower bill.
The same story is developing in the wireless data marketplace. AT&T and Verizon Wireless have the strongest networks as Sprint and T-Mobile fight to catch up.
Where America Went Wrong: The Repeal of Spectrum Caps

Tom Wheeler: America’s #1 advocate for repeal of Spectrum Caps is now the chairman of the FCC.
Originally, the United States prevented excessive market domination with a “Spectrum Cap,” — a maximum amount of wireless spectrum providers could hold in any local market. The rule was part of the sweeping changes in telecommunications law introduced in the mid-1990s. Wireless spectrum auctions replaced lotteries or strict frequency assignments based on merit. The U.S. government promoted the auction system as a win for the U.S. Treasury, which has been promised $60 billion in proceeds from the wireless industry (not the amount actually collected) since auctions began in 1994.
The cost to U.S. consumers from increasing cell phone bills in barely competitive markets is still adding up.
After the auction system was introduced, the largest carriers acquired some of the most favorable, lower-frequency spectrum, easily outbidding smaller rivals. Most of the smaller regional carriers that ultimately won coveted 700MHz spectrum emerged victorious only when AT&T and Verizon felt the smaller markets were not worth the investment. In larger markets, spectrum caps were a gatekeeper against acquiring excess spectrum and, more importantly, rampant industry consolidation.
Under the pre-2001 rules, wireless companies couldn’t own more than 45MHz of spectrum in a single urban area or more than 55MHz in a rural area. That was when Verizon and AT&T competed with carriers that no longer exist — old familiar names like Nextel, Cingular, VoiceStream, Alltel, Centennial Communications, Qwest, and many others considered safe from poaching because the most likely buyers would find themselves over their spectrum limits.
As the largest carriers realized the caps were an effective merger/buyout firewall, the wireless industry began a fierce lobbying campaign against them. Leading the charge was Tom Wheeler, then-president of the CTIA Wireless Association, the nation’s top cellular industry lobbying group. Today he is chairman of the Federal Communications Commission.
“Today, America faces a severe spectrum shortage for wireless services,” Wheeler said in 2001. “The spectrum cap is a legacy of spectrum abundance, not shortages; the inefficiencies it perpetuates cannot be allowed to continue. While the U.S. government is looking for ways to catch up to the rest of the world on spectrum allocations, removal of the cap can at least increase the efficiency of existing spectrum.”

Former FCC Commissioner Michael Copps opposed retiring Spectrum Caps: “Let’s not kid ourselves: This is, for some, more about corporate mergers than it is about anything else.”
Wheeler was backed by an intensive lobbying effort funded by the largest wireless companies itching to merge and acquire.
By the end of 2001, the new Bush Administration’s FCC was ready to deal, gradually repealing the spectrum caps and fueling major wireless industry consolidation in the process. Providers everywhere could now own or control 55MHz of spectrum in any market, with the promise the caps would be repealed altogether by March 2003.
The result was already foreseen by former FCC Commissioner Michael Copps in November 2001, when he strongly dissented to the Republican majority gung ho for dissolving spectrum caps.
“Let’s not kid ourselves: This is, for some, more about corporate mergers than it is about anything else,” Copps wrote in his strong dissent. “Just look at what the analysts are talking about as the specter of spectrum cap renewal approaches – their almost exclusive focus is on evaluating the candidates for corporate takeovers and handicapping the winners and losers in the spectrum bazaar we are about to open.”
Just in case Copps might be making headway in his campaign to protect competition, Wheeler began complaining even louder about spectrum caps during the spring of 2003, just before their dissolution.
“The wireless industry fought long and hard to secure this spectrum for America’s wireless consumers,” said Wheeler. “Now we must tread carefully — in this era of rapid technological change, writing rules that are too restrictive would be irresponsible. In order to use this spectrum both efficiently and effectively, those who purchase this spectrum at auction must be allowed the freedom to grow and evolve with the demands of the market.”
Europe: Protecting Consumers from Giant Multinational Competition Consolidators (Some of the same ones AT&T reportedly wants to buy)
There is a reason Europeans are shocked by the costs of wireless service in the United States and Canada. North Americans pay higher prices for less service than our European counterparts. Most of the New World also has fewer choices in near-equivalent service providers.
Much of this difference can be attributed to European regulators maintaining focus on driving competition forward and disallowing rampant industry consolidation. But as Wall Street turns its attentions increasingly towards Europe to push for the next big wave of wireless mergers, the European system of “competition first” could be undermined if providers follow the North American model of high profits and reduced competition through consolidation.
Across much of Europe, at least four national carriers serve each EU member state, almost all controlling a share of the most valued, low-frequency wireless spectrum. European regulators do not allow a small handful of providers to maintain a stranglehold on the most valuable radio spectrum. Competitors have traditionally been offered a spectrum foundation to build networks that can stand up to their larger counterparts — the large multinationals or ex-state monopoly providers who had a head start providing service.
A report released by Finland market research firm Rewheel in May found clear evidence that the European model was benefiting consumers at the expense of rampant provider profits. Europeans in “progressive” markets that welcomed new competitive entrants pay lower prices for far more service. In some cases, the price differences between the five giant multinational providers that dominate Europe — Vodafone, KPN, France Telecom, Telefonica and Deutsche Telekom — were staggering. Competitors like Tele2, TeliaSonera, and “3” charge up to ten times less than the larger companies for equal levels of service.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg ATT Takeover List of European Wireless Carriers 7-15-13.flv[/flv]
“Europe is ripe for competition,” reports Bloomberg News. Providers like AT&T may be preparing to embark on a European wireless acquisition frenzy, but Wall Street warns profits are much lower because of robust price competition in Europe that benefits consumers. (4 minutes)
The study also found a number of the largest European providers were following in the footsteps of Verizon Wireless, AT&T, Rogers, Bell, and Telus here in North America:
- Prices were enormously higher in markets that lack effective competition from an upstart competitor able to deliver a comparable level of service. Smaller cell companies with very limited infrastructure or with non-favored spectrum could not provoke dominant players to cut prices because reception quality was starkly lower and consumers would have to cope with a reduced level of service. In Europe, when new competitors were able to fully build-out their networks using favorable spectrum, incumbents in these progressive markets slashed prices and boosted services to compete. In North America, upstart competitors cannot access favorable spectrum for financial reasons and the investor community has dismissed many of these players as afterthoughts, starving them of much-needed investment.
- Large dominant European providers are now heavily lobbying for deregulation of merger and acquisition rules and want the right to acquire the competition entering their markets.
- In almost half of the EU27 member state markets spectrum is utilized very inefficiently by the largest incumbent telco groups who are keen to protect their legacy fixed assets and cement their European dominance with more consolidation at the price of competition. In the United States and Canada, many of the largest providers crying the loudest for more wireless spectrum have still not used the spectrum already acquired.
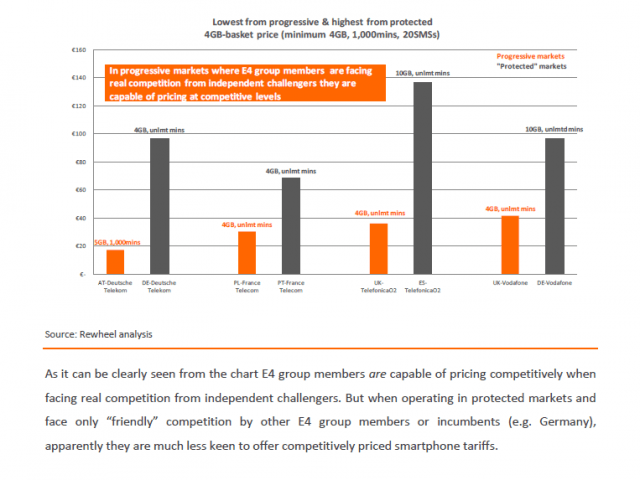
From the Finnish report:
The obvious question that needs to be asked is how is it technologically possible and economically viable for Tele2, 3 and TeliaSonera to offer four times more gigabytes of data usage at a fraction of the price charged by larger companies.
- Do independent challengers have privileged access to more efficient technologies (i.e. LTE) than the E4 group members?
- Do they hold relatively more spectrum capacity than the E4 group members?
- Do independent challengers have access to more radio sites and their spectrum reuse factor is higher than the E4 group members?
- Or are independent challengers (i.e. Tele2, DNA) unprofitable?
None of the above are true.
The answer is actually very simple. Independent challengers and incumbents such as TeliaSonera present mainly in progressive markets are utilizing the spectrum resources assigned to them. In contrast, incumbent telco groups […] rather than utilizing their spectrum resources instead appear to be more concerned about keeping the unit price of mobile data very high […] by restricting supply, the same way the lawful “cartel” of OPEC controls the price of oil by turning the tap off.
In progressive markets (where at least one independent challenger is present, triggering spectrum utilization competition) such as Finland, Sweden, Austria and the UK, mobile data consumption per capita is up to ten times higher than in protected markets.
In some European countries dominated by the biggest players, consumers are being gouged for service. Where robust competition exists, prices are dramatically lower.
The European nation where market conditions are most similar to the United States is Germany. Two large carriers dominate the market: Deutsche Telekom, the former state-owned telephone company and Vodafone, part owner of Verizon Wireless.
In Germany, consumers spending €20 ($26) end up with a data plan offering as little as 200MB of usage per month. In progressive markets in adjacent countries, spending the same amount will buy an unlimited use data plan or at least one offering tens of gigabytes of usage. In short, German smartphone service is up to 100 times more restrictive than that found in nearby Scandinavia or in the United Kingdom. These same two companies charge Germans double what English customers pay and a Berliner will end up with 22 times less data service after the bill is settled.
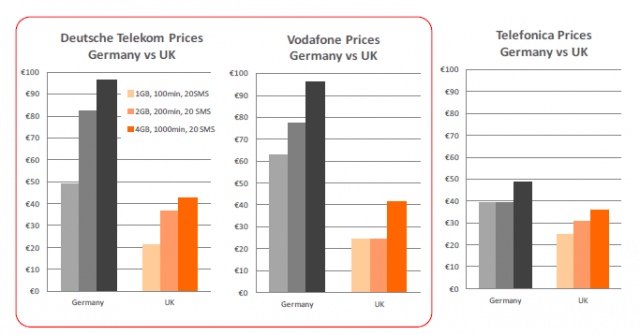
So what is going on in Germany that allows the marketplace to stay so price-distorted? The fact all four significant competitors have close ties to or are owned by the large multinational telecom operators mentioned above. Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, Telefonica and E-Plus, the latter one belonging to the Dutch KPN Group are all members of a lobbying organization attempting to persuade the EU to invest public funds into improving Europe’s wired broadband networks. Playing against that proposition is a growing number of Europeans moving to wireless. By charging dramatically higher wireless prices in Germany, all four companies have successfully argued that wireless adoption is not a significant reason to stall public financing of private broadband projects. In fact, Germany’s wireless growth is well below other EU nations.
The Finnish researchers point out the evidence of informal provider collusion is pretty stark in Germany:
“One would expect these ‘European Champions,’ especially the ones with lower market shares (Telefonica and E-Plus), to look at the smartphone centric market transformation as an opportunity to secure or improve their market share, especially in light of the fact they should have plenty of unused radio spectrum capacities to make their offers more consumer-appealing,” the report finds. But in fact these new entrants have priced their services very closely in alignment with the larger two.
“Undoubtedly, multinational incumbent telco groups and their investors have good reasons to lobby EU decision makers to enact friendly policies that will protect their inherited oligopolistic high profit margins,” the report states. “But will the German model serve the best interest of consumers and business in other EU member states? In Rewheel’s opinion, clearly not. Enforcing an overly ‘convergent player friendly’ German model would severely limit competition in the mobile markets, leading to high prices for consumers and the Internet of mobile things and sever under-utilization of the member states’ scarce national radio spectrum resources.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg ATT Entry in Europe Not Seen as Competitive Threat 7-15-13.flv[/flv]
Competition is brutal in Europe’s wireless marketplace — a factor Bloomberg News says could temper AT&T’s planned “European Wireless Takeover.” What makes the difference between enormous profits in North America and heavy price discounting in Europe? Spectrum policy, which gives European competitors a more level playing field. Bloomberg analysts speculate AT&T will bankroll its rumored European buyouts and mergers with the enormous profits it earns from U.S. subscribers. (4 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Malone also thinks it is time to discard reliance on cable television to bring home the revenue and profits Wall Street expects. The industry should instead turn its earning attention to broadband, a product few Americans can live without. Malone believes the cable industry is not only positioned to control content distributed on its TV Everywhere online video platform for authenticated cable subscribers, but also have a say in competing content from Netflix, among others, which are totally reliant on the broadband pipes provided by ISPs.
Malone also thinks it is time to discard reliance on cable television to bring home the revenue and profits Wall Street expects. The industry should instead turn its earning attention to broadband, a product few Americans can live without. Malone believes the cable industry is not only positioned to control content distributed on its TV Everywhere online video platform for authenticated cable subscribers, but also have a say in competing content from Netflix, among others, which are totally reliant on the broadband pipes provided by ISPs. Among the top recipients: Comcast, which collects $25-30 million a year and Time Warner Cable, which nets “tens of millions of dollars” from Google, Microsoft, and Facebook.
Among the top recipients: Comcast, which collects $25-30 million a year and Time Warner Cable, which nets “tens of millions of dollars” from Google, Microsoft, and Facebook.

 Malone sees the future sustainability of the cable industry dependent on the high revenue broadband business.
Malone sees the future sustainability of the cable industry dependent on the high revenue broadband business.

 Under Malone’s leadership, TCI Cable raised rates 60 percent in 1992 alone, helping drive the enactment of the 1992 Cable Act which began to slow the pace of rate hikes. The bill was vetoed by then President George H.W. Bush but overridden in Congress after tens of thousands of constituent complaints poured into Washington. It was sweet justice for many elected officials who were on the receiving end of Malone’s hardball tactics for nearly 20 years. Malone was well known for retaliating against local officials who opposed his unfettered rate increases by suddenly cutting off service to customers and putting up on-screen messages in the place of favorite channels with the names and phone numbers of elected officials Malone claimed were responsible.
Under Malone’s leadership, TCI Cable raised rates 60 percent in 1992 alone, helping drive the enactment of the 1992 Cable Act which began to slow the pace of rate hikes. The bill was vetoed by then President George H.W. Bush but overridden in Congress after tens of thousands of constituent complaints poured into Washington. It was sweet justice for many elected officials who were on the receiving end of Malone’s hardball tactics for nearly 20 years. Malone was well known for retaliating against local officials who opposed his unfettered rate increases by suddenly cutting off service to customers and putting up on-screen messages in the place of favorite channels with the names and phone numbers of elected officials Malone claimed were responsible.
 Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”
Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”

