“The city needs to know if you’re going to block traffic or create a hazard to sidewalk users,” Frasher said. Maybe there’s a way to streamline those regulations, “… but with only 10 percent city government representation, how helpful will the end product be?”
The FCC also didn’t choose David Guttenberg, member of the Alaska state legislature. He said service providers writing local rules for internet deployment makes him fear for Alaskan residents, many of whom have such poor wireless service that they have trouble downloading emails.
“They [telecommunications companies] are only going to look after their own self interests,” Guttenberg said. “Find me the guy that works for telecommunications on this committee that’s going to sign onto a plan telling their business to do something they don’t want to do. Find me that guy.”
What Pai has done by packing the panel with industry representatives is, in the end, “pretty standard in Washington,” said Sarah Treul, a political science professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “The FCC expects certain outcomes from this advisory committee.”

Pai
That point was not lost by San Jose Mayor Liccardo, who finally had enough after witnessing several cases of BDAC’s industry members wielding veto power and unilaterally rewriting collaborative proposals to fit the agenda of large cable and phone companies.
“One working group, which did not have a single municipal representative among its 30+ participants, created a draft model state code that included provisions to eliminate all municipal control over when, how, and whether to accept industry applications for infrastructure deployment,” Liccardo complained. “Another working group had an industry representative dramatically re-write its draft municipal code in the 11th hour, pushing aside the product of months of the working group’s deliberations. The result, in each case, were provisions that plainly prioritized industry interests.”
Also dovetailing with Pai’s narrative, many telecom companies griped about the cost of complying with local rules and regulations. In April, Larry Thompson, CEO of the National Exchange Carrier Association, with 1,300+ local telephone company members, complained one member had to pay $700,000 in costs to comply with environmental laws, historical preservation rules, zoning, and construction-related paperwork.
 A representative from Comcast worried that the BDAC’s work has been so polarized towards the telecom industry, excluded state and local officials will have every reason to resist the BDAC’s findings and recommendations and refuse to adopt them.
A representative from Comcast worried that the BDAC’s work has been so polarized towards the telecom industry, excluded state and local officials will have every reason to resist the BDAC’s findings and recommendations and refuse to adopt them.
“If they don’t feel included, not only are they outside throwing [darts] at this process, but then in the end it’s those groups that we want to adopt these model codes,” said David Don, vice president of regulatory affairs at Comcast.
But Liccardo warns Pai and his Republican allies are laying the foundation to “steamroll” over local officials by bulldozing local control of zoning and code rulemaking. For that reason, he quit the committee.
“The apparent goal is to create a set of rules that will provide industry with easy access to publicly funded infrastructure at taxpayer subsidized rates, without any obligation to provide broadband access to underserved residents.”
If Pai does manage to enact new federal rules that are as industry-friendly as Liccardo and other city officials fear, the FCC could overrule local zoning and permitting rules on a scale never seen before.
“It’s obvious that this body is going to deliver to the industry what the industry wants,” Liccardo said.
That appears to be Mr. Pai’s agenda as well.


 Subscribe
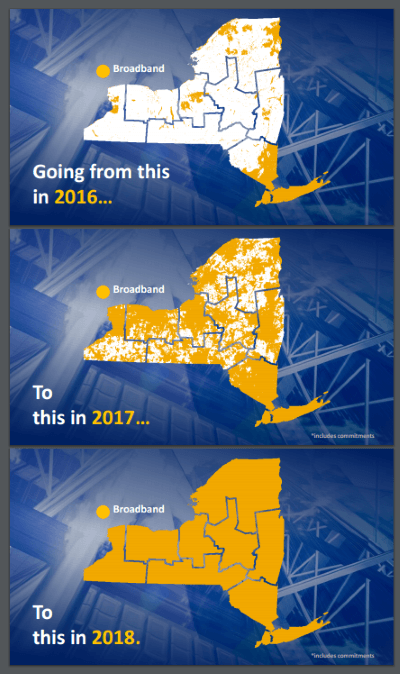
Subscribe New York’s Broadband for All Program yesterday
New York’s Broadband for All Program yesterday  Central New York Region
Central New York Region

 “This is a huge disappointment for us,” Pat added. “We were counting on this happening. Told numerous times it would. Now we have to debate moving, we can’t continue not having internet. My oldest son just graduated high school never having internet at home.”
“This is a huge disappointment for us,” Pat added. “We were counting on this happening. Told numerous times it would. Now we have to debate moving, we can’t continue not having internet. My oldest son just graduated high school never having internet at home.” Washington’s Attorney General on Monday issued a
Washington’s Attorney General on Monday issued a 





 “When I called [the FCC] to check on the status of the BDAC selection process [earlier this year] and identified myself as an employee from the City of Santa Monica, the gentleman on the phone laughed hysterically,” Carter said. “At first I didn’t get the joke. When I saw the appointees for the municipal working group—only three out of 24 positions were from local government—I got the joke.”
“When I called [the FCC] to check on the status of the BDAC selection process [earlier this year] and identified myself as an employee from the City of Santa Monica, the gentleman on the phone laughed hysterically,” Carter said. “At first I didn’t get the joke. When I saw the appointees for the municipal working group—only three out of 24 positions were from local government—I got the joke.” CPI spoke with many local officials who asked to participate as a member of BDAC, but were turned down:
CPI spoke with many local officials who asked to participate as a member of BDAC, but were turned down: