Sometimes you can’t please some people no matter what you do.
Sometimes you can’t please some people no matter what you do.
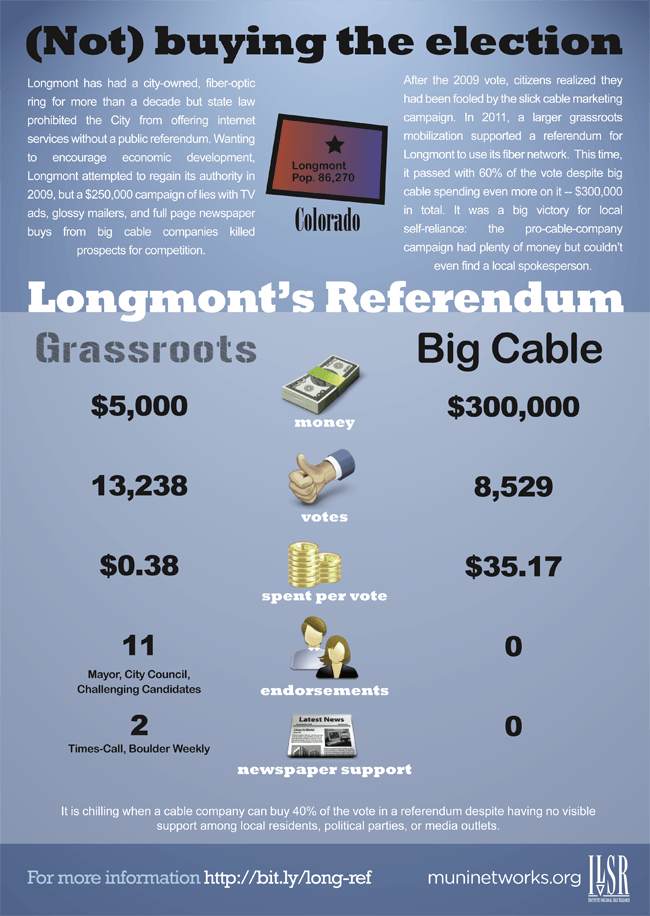
Kit Carson Electric Cooperative’s $64 million fiber-to-the-home expansion project will finally bring 21st century broadband speeds to northern New Mexico. The electric co-op intends to deliver broadband speeds up to 100Mbps to 20,000 largely rural residents and businesses in Taos, Colfax, and Rio Arriba counties who have had limited access to cable broadband or live with speeds often less than 1Mbps from CenturyLink-delivered DSL.
“It’s a whole new ballgame for rural New Mexico,” shares Stop the Cap! reader Raul. “But the pinheads at the local weekly newspaper are ringing their hands over the project, suggesting only businesses deserve 100Mbps while the rest of us should be satisfied with speeds under a megabit per second.”
Indeed, editors at the Sangre de Christo Chronicle are wringing their hands over the project:
But many of us in the Kit Carson service area already have Internet service — and we’re completely happy with it. Kit Carson CEO Luis Reyes, Jr. said a large portion of the organization’s electric customers are currently under-served by other providers with Internet speeds of less than one megabit (1,000 kilobits) per second.
We have no reason to doubt that, but many of these customers probably don’t need the higher speeds. For the Internet customers who use the Internet for email, Facebook, news and other basic functions, Kit Carson’s prices will be most important. Most of us will not pay more for faster Internet speed we don’t need, but we will consider switching to a local provider if it offers identical or better service and prices.
“CenturyLink barely delivers DSL today, and has shown no interest in investing substantially in northern New Mexico, and outside of concentrated built-up areas there is no cable competition,” Raul says. “Kit Carson is the only local concern that has shown any real interest in making our community better, and the local newspaper is complaining about it.”
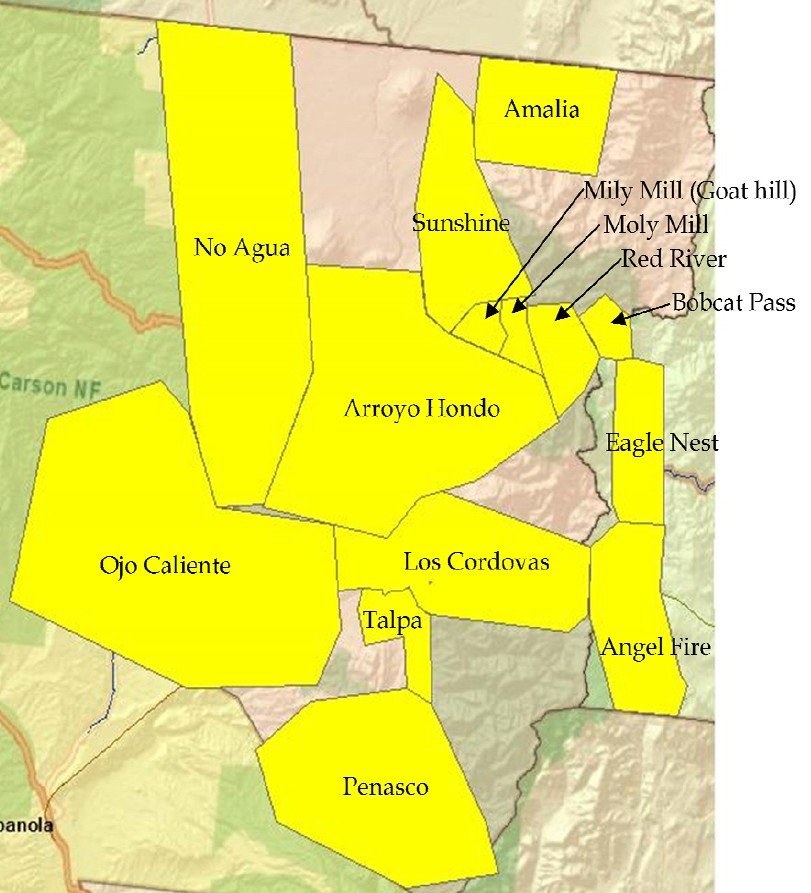
Proposed service area for Kit Carson Electric's new fiber to the home network serving northern New Mexico.
Kit Carson Electric’s project will provide a true fiber-to-the-home service bundling television, telephone, and broadband service — a substantial upgrade over what the telephone company has on offer. With speeds far beyond what cable and phone providers in New Mexico are accustomed to providing, the region stands to benefit from entrepreneurs building digital economy businesses over a broadband network that can actually help, not hinder online development.
Currently, area residents pay CenturyLink up to $55 a month for 1.5/1Mbps DSL service. Residents are so excited by the prospects of much faster speeds at significantly lower prices, Kit Carson Electric has developed an innovative stop-gap service for residents still waiting for direct fiber connections — fiber-to-wireless service. New and existing customers can sign up for the service for a $100 installation fee and choose from three service tiers:
- 3Mbps — $29.95/month
- 7Mbps — $39.95/month
- 10Mbps — $49.95/month
 A three year contract is required (early termination fee is $200). But customers who eventually obtain Kit Carson Electric’s fiber service will automatically satisfy their contract requirement.
A three year contract is required (early termination fee is $200). But customers who eventually obtain Kit Carson Electric’s fiber service will automatically satisfy their contract requirement.
“Kit Carson’s wireless project already blows away CenturyLink’s speeds and pricing, and that is for inferior wireless,” Raul argues. “The Chronicle doesn’t have a clue.”
We can’t understand the newspaper’s concerns either. Kit Carson Electric has already demonstrated their prices (and interest) in northern New Mexico is superior to that of CenturyLink, owner of former Baby Bell Qwest, which serves New Mexico.
Republican Sen. Jeff Bingaman is thrilled with Kit Carson’s broadband initiative.
“This major investment in broadband technology is exactly the kind of project I had envisioned when I voted for the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act,” U.S. Senator Jeff Bingaman said. “This grant is not only creating jobs now in northern New Mexico, it is laying the groundwork to attract new businesses, improve healthcare services and create new education opportunities in the future.”
The electric co-op has been successful operating non-profit businesses selling propane, telecommunications, and economic development space. The fiber project will also allow the electric utility to deploy “smart grid” technology to increase the efficiency of their electric service.
A groundbreaking ceremony at the broadband project’s command center held this past summer also coincided with a public emergency communications network upgrade which will increase the efficiency and reliability of first responders and other emergency and public safety agencies.


 Subscribe
Subscribe