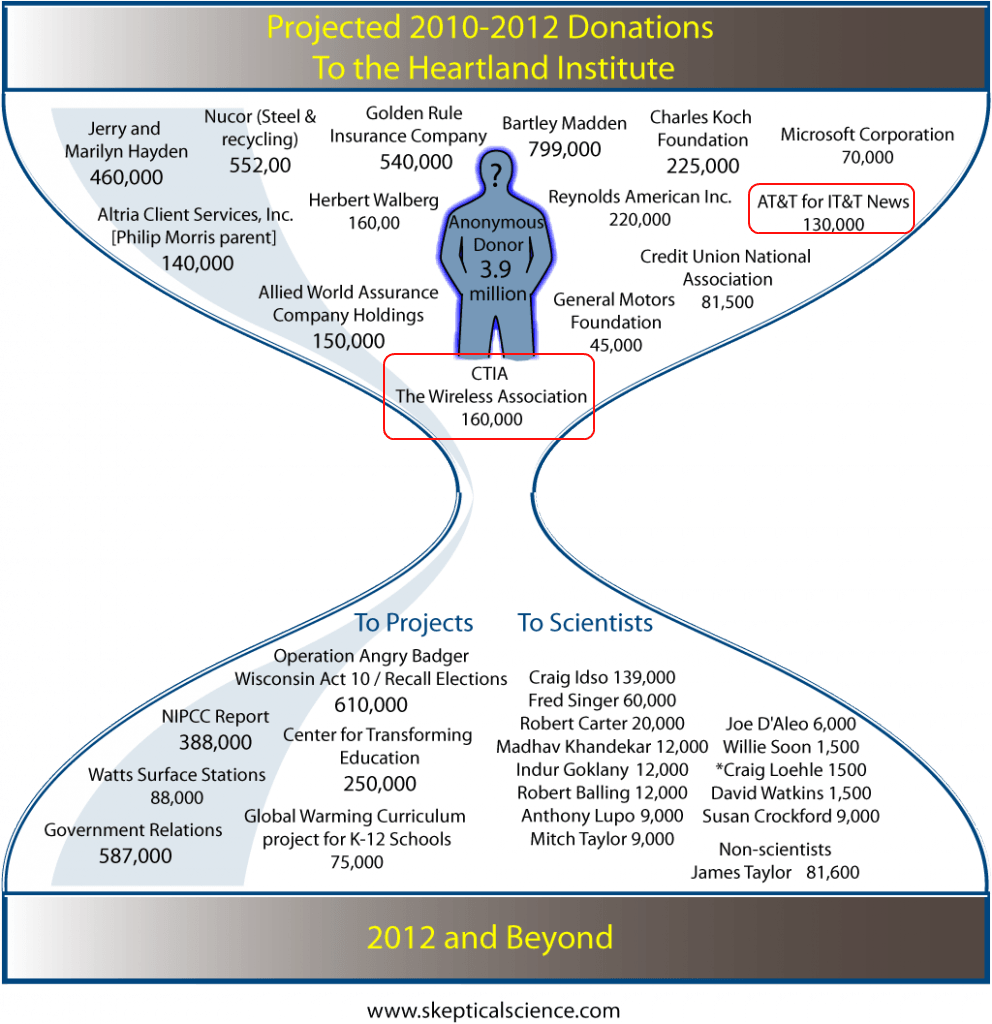
Both sides agree Time Warner Cable needs to add a new music channel, one owned by MSG parent Cablevision Industries, to your cable lineup.
Some suspicious Buffalo hockey fans suspect the real reason for the sudden focus towards a weekend resolution of a nearly two month dispute that kept MSG off Time Warner Cable customers’ screens since Jan. 1 is the fact the New York (City) Knicks are winning some basketball games and player Jeremy Lin is enjoying his “15 minutes of fame” in the national media spotlight. Both companies announced the latest round of negotiations, held in New York City, have brought an end to the dispute.
Now that MSG is back on Time Warner Cable, neither company is getting a round of applause for finally reaching a deal. In fact, a key provision of the settlement requires that the cable company add a new network — Fuse — to the cable lineup. That means Time Warner Cable customers will eventually pay for a music channel they never asked to receive.
The New York Daily News is just the latest newspaper to put fans’ frustrations into print:
[MSG and Time Warner Cable] don’t give a damn about you.
[…] Fans once apathetic over the blackout and the lethargic Knicks are now fired up and vocal. They are calling TWC and MSG. They are making their feelings known inside the Valley of the Stupid, too.
At this point they are having little impact. The two sides said they recently met. How long? Five minutes? The response from the suits at both companies is the same. Their propaganda never changes. They are more interested in gift-wrapping their problem.
Instead of locking itself in a room for around-the-clock negotiating, TWC is taking fans to a Knicks game in Charlotte. Or MSG, catering to the Asian market it suddenly discovered, is throwing a Knicks viewing party at a Chinatown restaurant. This is known as manipulation. These are nothing more than visuals. They don’t change a damn thing.
The song remains the same: TWC says MSG is looking for a 53% increase in subscriber fees, which now, according to industry analysts, average just over $2.63 per customer. MSG responds by saying TWC is lying. TWC says in September MSG agreed to a 6.5% increase. MSG says that’s a lie, too.
Someone is lying. Everyone is lying. That’s part of the spin. Instead of taking it out on both sides for shafting you, they want you to choose sides, identify a bad guy. Don’t. When two lying swines are fighting in the slop, only a sucker would try to intervene.
After nearly two months of cable subscribers complaining they were paying for a sports channel they were not getting, everyone –and– the governor got involved. But perhaps nothing motivated a resolution more than the sudden media spotlight on Knicks’ player Jeremy Lin, dubbed Linsanity.
“Linsanity helped,” Chris Marangi, a portfolio manager at Gamco Investors told Bloomberg News. The investment firm owns about 5 million MSG shares and 500,000 Time Warner Cable shares. “Time Warner Cable realistically couldn’t have dropped MSG — it’s too important to too many fans in New York to not be carried. Both sides probably gave a little.”
While state politicians thanked each other for a “job well done,” Time Warner Cable subscribers won’t be getting a refund for a channel missing from their lineup for eight weeks. But they will likely face a higher rate increase in 2013, in part to pay for a music channel few knew existed and even fewer wanted.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WIVB Buffalo Fans React to MSG Deal 2-19-12.mp4[/flv]
WIVB in Buffalo explores the fallout of Time Warner Cable and MSG’s near-two-month dispute. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe