Cities left out of Verizon Communications’ fiber to the home upgrade FiOS are telling the Federal Communications Commission to reject any wireless spectrum swap between the phone company and the nation’s largest cable operators unless Verizon commits to getting the fiber upgrade done in their cities.
Cities left out of Verizon Communications’ fiber to the home upgrade FiOS are telling the Federal Communications Commission to reject any wireless spectrum swap between the phone company and the nation’s largest cable operators unless Verizon commits to getting the fiber upgrade done in their cities.
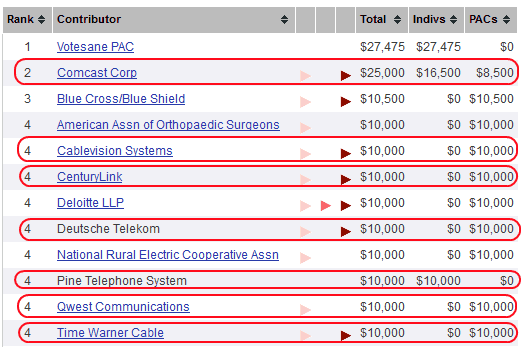
Coordinated by the Communications Workers of America, which represents many Verizon workers, elected officials and community groups in Boston, Baltimore, and the upstate New York cities of Albany, Syracuse, and Buffalo collectively blasted the proposed swap as bad news for consumers. On a city-by-city basis, they each filed comments with the FCC opposing the deal unless the Commission mandates Verizon complete fiber upgrades as a condition for the approval of the spectrum swap.
For the past few years, we have watched as Verizon Communications has built its all fiber FiOS network in 10 suburban communities that ring our city. In those communities, we have seen what happens when Time Warner Cable, our local cable monopoly, competes head-on with Verizon’s FiOS to provide video and broadband services. Consumers benefit from competitive choice; small businesses benefit from truly high-speed connections to suppliers and customers; schools and hospitals benefit from education and health-related applications; communications workers benefit from the jobs building, maintaining, and servicing networks; and families and communities benefit from the 21st century jobs and expanded tax base.
But the residents and small business owners in Buffalo have not been able to reap these benefits. To date, Verizon has chosen not to deploy its all-fiber FiOS network to the more densely-populated city of Buffalo. The proposed Verizon Wireless/cable company partnership would cement this digital divide and foreclose the possibility of effective high-speed broadband and video competition in our city. Verizon Wireless is a subsidiary of Verizon Communications. We are deeply concerned that as a result of the new joint marketing agreement, Verizon will no longer have the incentive to invest in an all-fiber network that competes with Verizon Wireless’ new partner, the cable company. Therefore, to promote high-speed broadband investment and video competition, especially in heavily minority and lower-income areas like the city of Buffalo, the FCC should include as a condition for approval of this Transaction a requirement that Verizon continue to invest in and build-out its FiOS network to currently unserved areas that are inside its traditional telephone service area footprint, including the city of Buffalo and the surrounding areas.
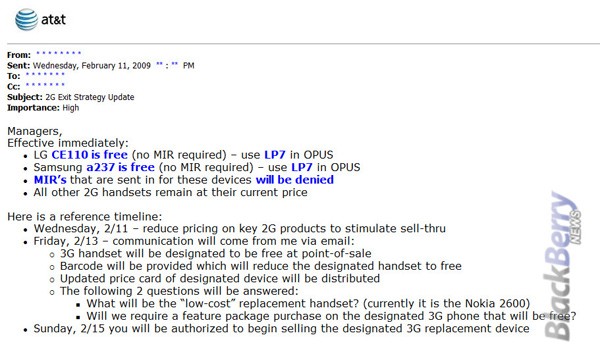
In response, Verizon confirmed it never had any intention of wiring any of those cities for fiber service. Multichannel News reports:
But a Verizon exec points out that those cities are all areas that were not scheduled to get FiOS, whether or not the cable spectrum deal goes through. As Verizon has pointed out, the company decided back in 2010 that it was going to build out the franchises it had already secured and target those 18 million customers in and around New York City, Washington, D.C., and Philadelphia, rather than spend any more of its shareholders money in a wider buildout. The above cities were not in those franchise areas.
Baltimore City Council member William H. Cole accused Verizon of leaving the city of Baltimore behind in a letter he addressed to the Commission this week:
High-speed, fiber-optic networks are vital for economic competitiveness. Currently, Verizon’s FiOS is the only all fiber-optic commercially-available network for businesses and households. Other advanced industrialized nations have already deployed fiber-optic networks on a large-scale; they recognize that high-speed fiber is the competitive infrastructure of the 21 st century. Much of the suburban areas outside of Baltimore already have FiOS. The City of Baltimore will never get a fiber-optic network if this deal is approved, which concerns me greatly. I am not willing to see Baltimore permanently relegated to the wrong side of the digital divide.


 Subscribe
Subscribe