
Critics of the broadband stimulus project question why the state spent money on unnecessary equipment and failed to identify anchor institutions that already had adequate service.
Another round of miscalculations by project managers overseeing a $126.3 million federal broadband stimulus grant nearing expiration will cost nearly half of West Virginia’s anchor institutions their promised fiber broadband connections.
As a consolation prize, state officials are promising those left out will receive new routers paid for by federal taxpayers whether the institutions want them or not.
As the deadline nears for West Virginia to finish spending their 2010 federal broadband grant, the state has been on a spending spree. Just last week, officials designated 175 new sites as “community anchor institutions” qualified for upgraded Internet service. But the Charleston Gazette found just seven of them will receive fiber broadband upgrades. The rest are getting expensive routers that the state has been trying to unload for nearly two years or new routers the state will spend additional grant funds to purchase.
Among the top vendors paid with grant funds: Frontier Communications, which provides connectivity, and Verizon Communications, the company that supplied the overpowered routers.
“Due to the amount of time required for environmental assessments and fiber builds, we determined that we would limit most of the additional sites to ‘router-only’ so that we could complete the build on time,” Diane Holley-Brown, a spokeswoman for the state Office of Technology told the newspaper.
The state defended its decision to scale back on fiber upgrades pointing out many of the institutions targeted already had the service. That left the state scurrying to find new projects for unspent grant funds.
The state’s latest award of Internet routers is separate from the earlier revelation West Virginia had over-purchased equipment that either proved unnecessary or duplicated equipment already installed.

Eric Eyre’s watchdog reporting in the Charleston Gazette over how the state’s $100+ million broadband grant has been spent has triggered a federal and state investigation.
In 2011, then Gov. Joe Manchin promised that federal broadband stimulus funding would provide fiber connectivity to 1,064 schools, libraries, public safety and health care institutions. When the project funding expires at the end of January, only 639 institutions will be slated to receive fiber upgrades.
Schools are among the hardest hit institutions. At least 60 percent of those promised upgraded Internet service will only receive a new router instead.
The project has remained under scrutiny since the Gazette revealed $24 million of the grant was spent on 1,064 Cisco routers that were never intended for use at many of the institutions targeted to receive them. Hundreds of the $20,000+ routers were stored, unused, in state buildings for at least two years waiting for a new home.
The U.S. Department of Commerce’s Inspector General and West Virginia Legislative Auditor are reviewing the router purchase.
When the grant expires West Virginia officials have made it clear those institutions left without fiber upgrades should not hold their breath waiting for the state to pick up where the federal government left off. The reason? The grant money is nearly gone and the state is not interested in financing additional upgrades.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Time Warner Cable is expanding its footprint in the capital region of New York with the acquisition of independent Princetown Cable Company, which serves around 600 subscribers in Princetown, Duanesburg and Rotterdam in Schenectady County.
Time Warner Cable is expanding its footprint in the capital region of New York with the acquisition of independent Princetown Cable Company, which serves around 600 subscribers in Princetown, Duanesburg and Rotterdam in Schenectady County. While a lot of people would love to get Verizon to wire their communities for the company’s fiber optic network, at least three New York City multi-dwelling unit property owners have told Verizon to get lost, in some cases telling the company none of their tenants were interested in the top-rated fiber to the home network, even as they remain without phone service three months after Hurricane Sandy damaged Verizon’s facilities in the city.
While a lot of people would love to get Verizon to wire their communities for the company’s fiber optic network, at least three New York City multi-dwelling unit property owners have told Verizon to get lost, in some cases telling the company none of their tenants were interested in the top-rated fiber to the home network, even as they remain without phone service three months after Hurricane Sandy damaged Verizon’s facilities in the city. boneheads that own my building that nobody was interested,” says Brad, a Stop the Cap! reader in Manhattan. “The morons at the property management company don’t have a clue or they want money from Verizon in return for the keys. Meanwhile, there is no dial tone and Verizon says they are at an impasse until the property owners, who obviously don’t care, let them in to do repairs.”
boneheads that own my building that nobody was interested,” says Brad, a Stop the Cap! reader in Manhattan. “The morons at the property management company don’t have a clue or they want money from Verizon in return for the keys. Meanwhile, there is no dial tone and Verizon says they are at an impasse until the property owners, who obviously don’t care, let them in to do repairs.”
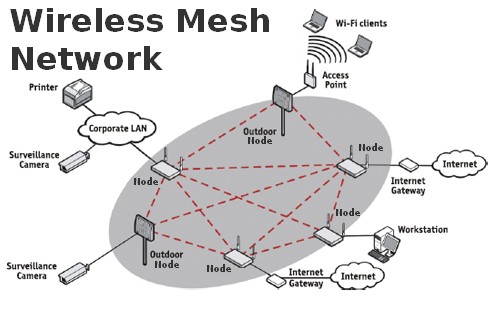 The business community of Poulsbo, Wash., a Seattle suburb of 9,000 in Kitsap County, is fed up waiting around for CenturyLink and Comcast to increase broadband speeds in the area so several have joined forces to share the city’s underused, existing fiber-optic cables to offer free Internet access for area businesses and residential users.
The business community of Poulsbo, Wash., a Seattle suburb of 9,000 in Kitsap County, is fed up waiting around for CenturyLink and Comcast to increase broadband speeds in the area so several have joined forces to share the city’s underused, existing fiber-optic cables to offer free Internet access for area businesses and residential users. Stephen Perry, the PUD’s superintendent of telecommunications, says the new network is a pilot program to test if an economic model can be created to sustain the service and eventually expand it.
Stephen Perry, the PUD’s superintendent of telecommunications, says the new network is a pilot program to test if an economic model can be created to sustain the service and eventually expand it.