 While Windstream continues to heavily lobby the Georgia legislature for a bill that would ban competition from publicly owned broadband providers, the company is doing little to address the growing concerns of its own broadband customers getting poor service.
While Windstream continues to heavily lobby the Georgia legislature for a bill that would ban competition from publicly owned broadband providers, the company is doing little to address the growing concerns of its own broadband customers getting poor service.
Mark Wyatt, a Windstream customer fed up with not getting the broadband speeds he pays for, launched a Facebook group in January to collect evidence and attempt to leverage the company to fix its problems. Wyatt, like many other customers in rural Georgia, has only one option for broadband service — Windstream.
Now the growing Facebook group has gotten attention from an Atlanta reporter who wants customers to record videos detailing their broadband problems with Windstream for an upcoming news report.
Jeff Chirico at WGCL-TV, the Atlanta CBS affiliate, has a call out for videos due by March 6:
I’m a reporter for CBS Atlanta News. I want to hear from Windstream customers in Georgia about their experiences with the company’s Internet service. Please shoot a video (30 seconds or less) explaining the speed of Windstream’s service and how it impacts you, your family or your business. Please include your name and city and download it to our dropbox account. http://dropbox.yousendit.com/
JamesEstes539379 Also, feel free to follow me on Twitter @CBSATLChirico or find me on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/
JeffChiricoCbsAtlanta
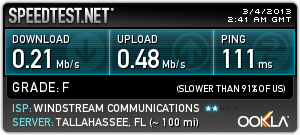 The horror stories are already clear all over Windstream’s service areas:
The horror stories are already clear all over Windstream’s service areas:
Don Jackson, who lives outside Milledgeville pays Windstream for 6/1Mbps service. On a good day, he gets 750kbps after 4pm every day, and speeds do not improve until the early morning hours.
“I talked with a local manager and he said that there is no solution anytime soon,” Jackson reported. “I have screen shots of speed tests from different sites for months to demonstrate that this is not a fluke but a fact. I have complaints on file with the FCC and BBB of Arkansas, [which handles complaints regarding Windstream].”
Adam Ridley qualified and pays for 3Mbps broadband service from Windstream, but that is not the speed he actually receives.
“It’s 9:40pm and I’m rocking my 210kbps connection — 7% of the speed I pay for,” he reported last night.
Rodney Gray pays Windstream a premium for 12Mbps service, but the phone company does not come close to delivering those speeds. His service actually ranges from 580kbps-1.4Mbps.
“My upload speed is faster than my download,” Gray complains.
A representative answering Windstream’s Complaint Line threatens a customer in Odum,. Ga. with legal action for “harassment” in June, 2012 after he complaints about Windstream’s mailers advertising DSL Internet service that is actually “not available to him this year.” (2 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Kimberly Brown’s broadband problems with Windstream are so pervasive, even the company admits there is a problem, and they have given her service credits.
“Our primary problem is dropped connections — constantly,” Brown says. “They sent a technician out because surely it must be in our lines. He told us that there is something going on in one of the main hubs or whatever, and that it should be months (if ever) that it’s fixed. Then, customer service was suddenly able to look into our account and see that we had hundreds of dropped connections in just a few days. Hundreds. To their credit, they did give us a smallish break on our monthly bill because of the aggravation.”
 A typical day for the Brown family is to wake up, reset the modem, send an e-mail or two, reset the modem, try to go to a web page, reset the modem.
A typical day for the Brown family is to wake up, reset the modem, send an e-mail or two, reset the modem, try to go to a web page, reset the modem.
“It’s crazy and extremely frustrating,” says Brown. “I work from home and rely heavily on the Internet to get my job done, so this problem affects us in many ways, not just casual web surfing.”
Things are worse for Mark B. Watson, who lost his service entirely for two days.
“The bad thing is that mine and my wife’s business is located in our house,” says Watson. “Being without Internet means we are not making an income for two days. It is getting old.”
While Windstream’s broadband service is suffering, company executives are celebrating a planned major reduction in extra investment in its broadband service, telling Wall Street its broadband expansion and fiber-for-cell-tower projects are nearing completion. That could leave rural Georgia broadband customers without improved service indefinitely.
At the same time, Windstream is reportedly the primary proponent of legislation that would make sure rural Georgians have no alternatives to choose from. The company’s support for HB 282, now working through the Georgia legislature, would prohibit communities from launching their own broadband services to improve connectivity and speeds.


 Subscribe
Subscribe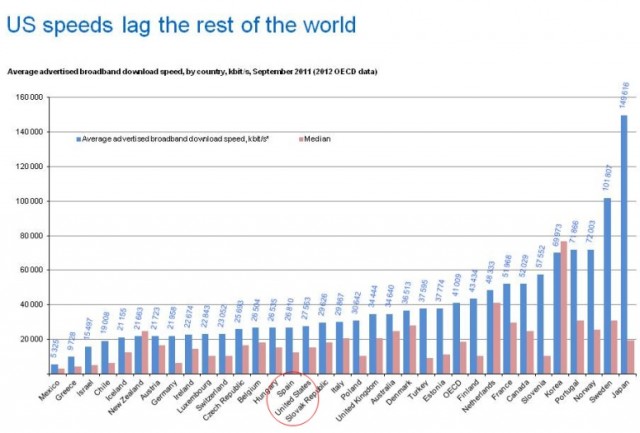
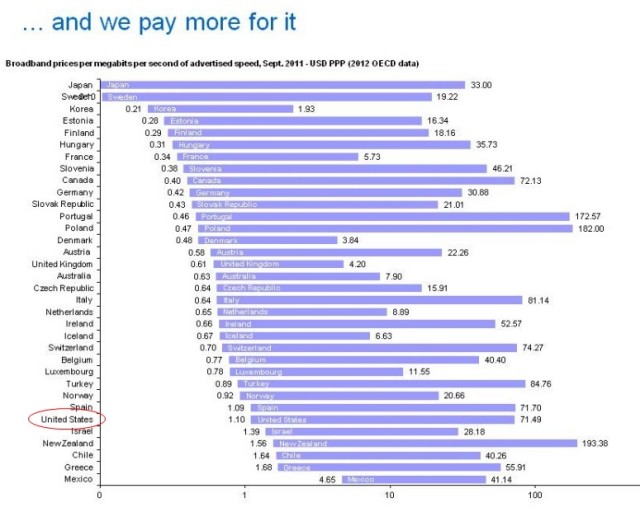
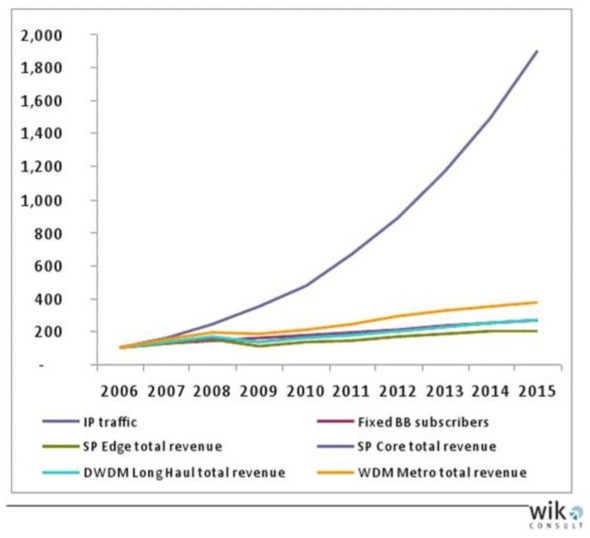
 Data caps protect incumbent big studio and network content creators at the expense of independent producers and others challenging conventional entertainment business models.
Data caps protect incumbent big studio and network content creators at the expense of independent producers and others challenging conventional entertainment business models.
 Windstream has announced the increased broadband investments that expanded DSL service to about 75,000 more homes and businesses and brought fiber connections to cell towers are nearly complete and the company intends to dramatically cut spending on further enhancements by the end of 2013.
Windstream has announced the increased broadband investments that expanded DSL service to about 75,000 more homes and businesses and brought fiber connections to cell towers are nearly complete and the company intends to dramatically cut spending on further enhancements by the end of 2013. “We expect to substantially complete our capital investments related to fiber to the tower projects, reaching 4,500 towers by the end of 2013,” said Gardner. “In addition, we will finish most of our broadband stimulus initiatives […] to roughly 75,000 new households. As we exit 2013, we will see capital spending related to these projects decrease substantially.”
“We expect to substantially complete our capital investments related to fiber to the tower projects, reaching 4,500 towers by the end of 2013,” said Gardner. “In addition, we will finish most of our broadband stimulus initiatives […] to roughly 75,000 new households. As we exit 2013, we will see capital spending related to these projects decrease substantially.”
