
Phillip Dampier
It is no secret that there is an urban-rural broadband divide.
The market-driven, private enterprise broadband landscape delivers the best speeds and service to urban-suburban areas, particularly those in and around large cities, short-changing rural communities.
This is true regardless of the technology: the fastest fiber optic services are delivered in large population centers, and wireless speeds are fastest there as well. But as the National Telecommunications and Information Administration has discovered, the further away you get from these urban sectors, the poorer the service you are likely to get.
The NTIA’s findings present a significant challenge to phone company claims that rural customers would be better served with wireless broadband instead of spending money to support and upgrade landline infrastructure, which supports DSL and is upgradable to fiber optics.
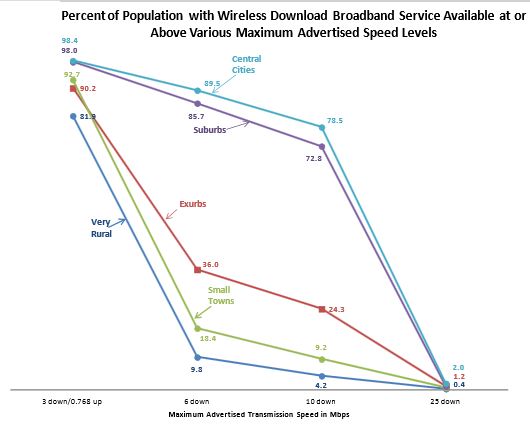
The NTIA finds these rural wireless networks to be severely lacking:
Not only are far fewer rural residents than urban residents able to access 4G wireless services (i.e., at least 6Mbps downstream), but a further divide also exists within rural communities. For wireless download services greater than 6Mbps, Very Rural communities have approximately half the availability rate of Small Towns, and Small Towns have about half the availability rate of Exurbs (10, 18, and 36 percent, respectively).
This represents nothing new. AT&T and Verizon have shortchanged their rural customers with catastrophically slow DSL service (or none at all) for years:
For wireline download service, Very Rural communities also have the least availability of all five areas. Though a rural/urban split continues to be useful in providing generalized information about availability, a five-way classification uncovers a more refined picture of the divide in broadband availability across the nation. For example, at wireline download speeds of 50Mbps, broadband availability varies from 14 percent (Very Rural), 32 percent (Exurban), 35 percent (Small Town), 62 percent (Central City), to 67 percent (Suburban), even though the overall broadband availability was 63 percent in urban areas compared to 23 percent in rural areas. In addition, wireline and wireless broadband availability, particularly at faster speeds, tends to be higher within Central Cities and the Suburbs compared to everywhere else.
Why the disparity? It is a simple case of economics. Wealthy suburbs can afford the ultimate triple play packages, so providers prioritize the best service for these areas, even above less costly to serve urban centers. Rural residents either get no service at all or only basic slow speed DSL. The Return on Investment to improve broadband is inadequate for these companies in rural areas.
Source: NTIA
The same is true with wireless 4G service. Rural areas struggle for access or endure poor reception because fewer towers provide service away from major highways or town centers.
The NTIA observed wireless download speeds of 6Mbps or more were available to 90% of urban residents, but only 18% of small town residents. Wireless upload speeds of 3Mbps or greater were found in only 14% of small towns.
Dee Davis, president, Center for Rural Strategies, based in Whitesburg, Va. said the implications were clear.
“The market’s always going to go to the well-heeled communities,” Davis observed. “It’s going to go to the densest population.”
Folks in rural communities end up paying more for a lower level of service, Davis said.
“That also means that they don’t get the same chance to participate in the economy,” Davis added. “They don’t get to bring their goods and services to market in the same way. They don’t always get to participate.”
The economics of cutting off rural landlines delivers most of the benefits to providers, and assures decades of inferior service to consumers.
Economic market tests, including Return on Investment, that impact rural broadband availability will not disappear if AT&T and Verizon abandon their rural landline networks. While cost savings will be realized once rural wired infrastructure is decommissioned, there is no free market formula that would encourage either provider to pour investment funds into rural service areas. For the same reasons rural customers are broadband-challenged today, their comparatively smaller numbers and economic abilities will continue to fail investment metrics for innovative new services tomorrow.
The primary reason broadband speeds are lower in rural areas is inferior network infrastructure. Providers argue it does not make economic sense to invest in network upgrades to boost speeds for such a small number of customers. While wireless technology can be cheaper to deploy than the upkeep of a deteriorating landline network, it is not cheap or robust enough to deliver comparable broadband speeds now available in urban areas, especially as broadband usage continues to grow.
Verizon’s chief financial officer Fran Shammo admitted as much during remarks at the at JPMorgan Global Technology, Media and Telecom Conference in May:
If you recall, way back I guess about two years ago we did a trial with DirecTV in Erie, Pa., where we did broadband on the side of a house and offered a triple-play, if you will, which consisted of broadband, voice, and linear TV provided by DirecTV.
What we found was people were adoptive to the broadband; but because of the consumption of broadband through that LTE network, it was really detrimental to the spectrum and to the network performance. Because they used so much data, it soaked up so much of the spectrum.
So what we felt was LTE for broadband works in certain rural areas, but you can’t compete LTE broadband in those dense populated areas because you can’t — first of all, you can’t match the speed with a 50-megabit or a 100-megabit delivery between cable and FiOS and U-verse. And you literally don’t have enough spectrum to be able to use that much consumption.
So what we felt was by partnering with the cable companies, and delivering our LTE network with voice and data, and having that hardwired connection into the home was a better financial way to do it than trying to go LTE broadband. Because we just didn’t see where the spectrum could hold up to the volume that would be demanded.
Without rural cable companies to partner with, Verizon’s decision to move rural broadband to wireless guarantees rural Americans will not benefit from ongoing speed and capacity upgrades that are necessary to support the evolving Internet.
 West Virginia has spent nearly three times more than it anticipated for each mile of fiber optics being laid by Frontier Communications as part of the state’s taxpayer-funded broadband expansion project, according to a new report.
West Virginia has spent nearly three times more than it anticipated for each mile of fiber optics being laid by Frontier Communications as part of the state’s taxpayer-funded broadband expansion project, according to a new report.

 Subscribe
Subscribe A law establishing a voluntary, national emergency alert system to give localized text warning messages to cell phone users about severe weather, terrorist attacks, natural disasters and missing children has generated conspiracy theories and complaints from some on the political right who suspect the system is designed to help President Obama promote his political agenda.
A law establishing a voluntary, national emergency alert system to give localized text warning messages to cell phone users about severe weather, terrorist attacks, natural disasters and missing children has generated conspiracy theories and complaints from some on the political right who suspect the system is designed to help President Obama promote his political agenda. The people of Malta will soon have a choice between a cable broadband provider offering 250/20Mbps service or a fiber to the home network now under construction that will be capable of delivering gigabit broadband across the island — all without usage limits or speed throttles.
The people of Malta will soon have a choice between a cable broadband provider offering 250/20Mbps service or a fiber to the home network now under construction that will be capable of delivering gigabit broadband across the island — all without usage limits or speed throttles. The Maltese government made broadband expansion a national priority and set regulatory policies that would increase competition. But the government also insisted that telecom market improvements also benefit customers, and the country laid the foundation of its broadband policy on encouraging the development of a nationwide fiber to the home network.
The Maltese government made broadband expansion a national priority and set regulatory policies that would increase competition. But the government also insisted that telecom market improvements also benefit customers, and the country laid the foundation of its broadband policy on encouraging the development of a nationwide fiber to the home network. As a result, Melita has aggressively invested in cable broadband upgrades that have delivered broadband speeds faster than what most Americans and Canadians can buy from their cable providers. The cable operator plans to be among the earliest adopters of DOCSIS 3.1 which will support up to 10/1Gbps broadband speeds.
As a result, Melita has aggressively invested in cable broadband upgrades that have delivered broadband speeds faster than what most Americans and Canadians can buy from their cable providers. The cable operator plans to be among the earliest adopters of DOCSIS 3.1 which will support up to 10/1Gbps broadband speeds. Israel has decided its broadband future can no longer lie in the hands of one phone and one cable company, so the country is commissioning a nationwide fiber to the home broadband network that will be run as a public-private partnership, eventually reaching every home and business in the country.
Israel has decided its broadband future can no longer lie in the hands of one phone and one cable company, so the country is commissioning a nationwide fiber to the home broadband network that will be run as a public-private partnership, eventually reaching every home and business in the country. Current consumer broadband speeds in Israel top out at around 100Mbps, but at a price. Broadband is still costly in Israel and most customers choose packages comparable to what Americans receive — 10-15Mbps service.
Current consumer broadband speeds in Israel top out at around 100Mbps, but at a price. Broadband is still costly in Israel and most customers choose packages comparable to what Americans receive — 10-15Mbps service.

