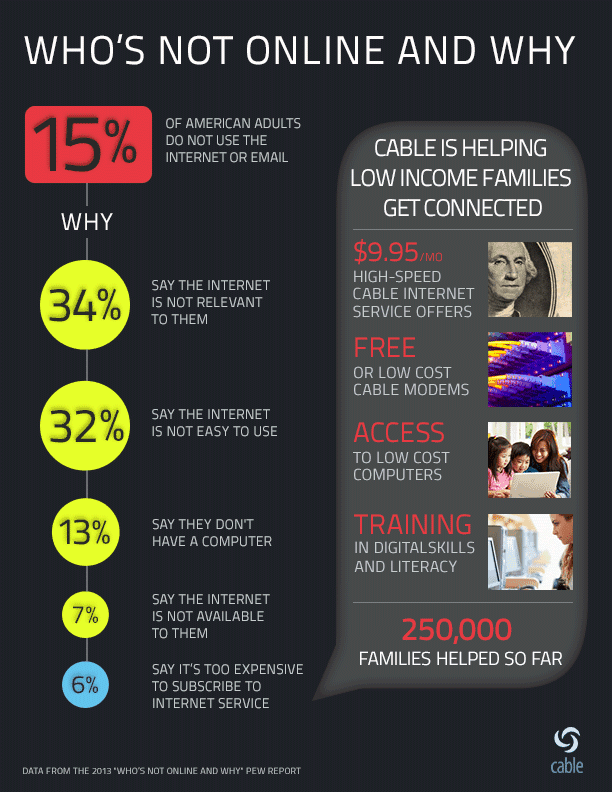
The cable industry believes the majority of America not using the Internet remain offline by choice.
The National Cable Telecommunications Association (NCTA) says the digital divide is not their fault. Price have very little to do with it, according to an NCTA infographic showing just 6% cite “cost” as the main reason they are not signed up for Internet service.
“Cable has made extensive efforts to connect all Americans to the Internet. And while high-speed Internet adoption has rapidly increased in the United States, still too many low-income families remain unconnected and are at risk of falling behind in the global information economy,” writes NCTA blogger John Solit. “Connecting all Americans in order to bridge the digital divide and expand the availability of broadband service remains a national goal embraced by cable companies. In a recent blog post, David L. Cohen, Comcast Executive VP & Chief Diversity Officer said, “[I]n just over two years through our Internet Essentials program, Comcast has connected an estimated 1 million low-income Americans, or more than 250,000 families, to the Internet at home.”
The “digital divide” — broadband have’s and have-nots — has been a regular topic among regulators and legislators for more than a decade. A suspicion that cost is a major factor keeping people from signing up could result in legislation compelling providers to offer low-cost Lifeline broadband service to the income-disadvantaged. In the last three years, the cable industry has tried to fight off that type of approach with voluntary programs that selectively target non-customers.

Comcast’s Internet Essentials provides 5/1Mbps service for $9.95 a month, but signing up isn’t easy.
The discounted service is available only to families with school-age children that qualify for the school lunch aid program. Comcast often promotes its discount program to legislators and others in the industry as an example of the voluntary effort the cable industry is making to solve the digital divide. Target customers who most likely qualify for the service are not going to learn about it through television ads or cable company mailers targeting low-income zip codes. Most of Comcast’s marketing effort is in cooperation with area schools.
Ironically, Comcast’s Internet Essentials actually forces some people to temporarily give up Internet access if they want to participate.
Customers must be current on their Comcast bills and must not have a subscription to any Comcast Internet service for the last 90 days to receive consideration. If you already have Comcast broadband service, you must disconnect it for at least three months before you can apply for Internet Essentials.
This requirement is designed to protect Comcast’s bottom line. Why offer a discount to customers already willing to sacrifice for home Internet service at Comcast’s regular price?
“How is this helping me and my family out,” asks one Tennessee customer who tried to sign up for Internet Essentials but couldn’t because they were already paying for Comcast Internet service. “The Comcast representative said that if I wanted to be enrolled in the program I would have to discontinue my Internet service for 90 days and then reapply. We have the Economy Internet Promotion and pay $19.95 per month. After the promotion ends our fee will increase to $26.95 a month. In our current economy and financial situation saving $17 per month would greatly help our family to keep our service. I will not rest until I find a solution to this problem. My children at least deserve that.”
Comcast also makes it its business to check your household to make sure at least one child still qualifies for the National School Lunch Program. The company reserves the right to immediately cancel service if you miss a payment or move. Participants also must not upgrade, alter or change Comcast service for any reason or risk being removed from the program.
Comcast’s Wi-Fi Ban

Shapiro
One of the most annoying conditions of the Internet Essentials program is that it does not allow Wi-Fi access.
Phil Shapiro, who refurbishes donated computers and distributes them to needy families regularly runs into Comcast’s Wi-Fi ban — a significant issue for larger families that need to be online concurrently.
“I’ve taken three donated computers to [one] family and I was expecting to get them all online with this cable modem service,” Shapiro tells The Hechinger Report. “But not so fast. Comcast’s telephone tech support tells me that Internet Essentials users cannot use Wi-Fi with their cable modems. Nowhere in Comcast’s printed literature or on the website is this limitation mentioned. Naturally, families who sign up for Internet Essentials get confused about this, but they are not well positioned to advocate for their needs.”
Charlie Douglas, a Comcast spokesperson, confirms that Internet Essentials does not offer Wi-Fi service, although he noted a customer could theoretically buy a wireless router themselves and use that to provide wireless connectivity. But that isn’t what Comcast’s technical support team recommends. Any deviation from the terms of the service offered to Internet Essentials customers could lead to an immediate disqualification. Comcast defines Internet Essentials as a wired service, including one outlet and a basic (not wireless) modem.
“The family that I was helping patiently waited for me while I talked on the phone,” said Shapiro. “They could see that I spoke very politely with the tech support person. They also saw that I had reached the end of my patience.”
A representative told Stop the Cap! Internet Essentials accounts have insufficient bandwidth and speed for Wi-Fi service, so it is not offered.
Shapiro dismisses Comcast’s explanation. Many public Wi-Fi networks offer even slower service than Comcast.
Douglas defended Comcast’s policy noting families served by the program don’t miss Wi-Fi and don’t need it.
But those using tablets might disagree, and with an increasing number of students using them as school textbooks are gradually phased out, Wi-Fi will only grow in importance.
Many large school districts, including Los Angeles, are introducing Wi-Fi only tablets for student use because they are cheaper and easier to support. When Internet Essentials participants ask about Wi-Fi access with the discounted broadband service, Comcast representatives are trained to up sell customers out of the program and sign them to a more costly plan than includes built-in Wi-Fi support.
Customers can successfully, if covertly, connect a router with Wi-Fi capability to the basic cable modem supplied by Comcast and configure wireless Internet Essentials service. But there are no guarantees Comcast will not give customers grief about it, if they wish.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Comcast Internet Essentials Key Milestones 11-13.mp4[/flv]
Comcast produced this video marking the start of the second year of its Internet Essentials program. Chicago Mayor Rahm Emanuel gushed Internet Essentials was “top of the line” Internet access. He was joined by other recognizable political leaders and the former chairman of the Federal Communications Commission Julius Genachowski. (2:47)


 Subscribe
Subscribe





 After nine months of foot dragging-negotiations between Overland Park officials and Google Fiber, a last-minute protest by a city council member over an indemnification clause that turned out to be insignificant was the last straw.
After nine months of foot dragging-negotiations between Overland Park officials and Google Fiber, a last-minute protest by a city council member over an indemnification clause that turned out to be insignificant was the last straw.
 Industry observers agree with Walch.
Industry observers agree with Walch. But now Overland Park will have to wait even as neighborhoods around the community get the fiber optic service first.
But now Overland Park will have to wait even as neighborhoods around the community get the fiber optic service first.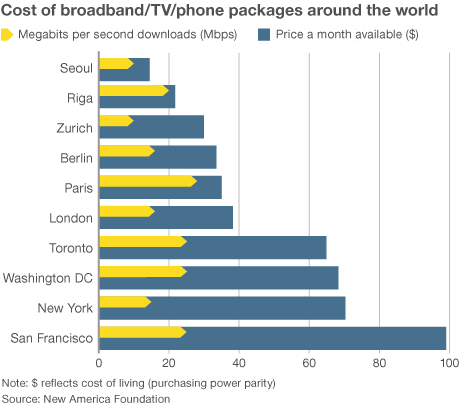 Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries —
Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries — 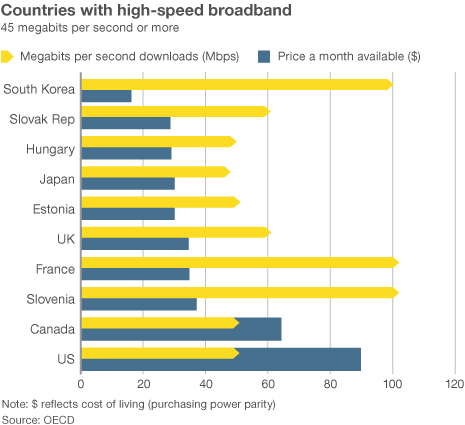 “Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
“Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
