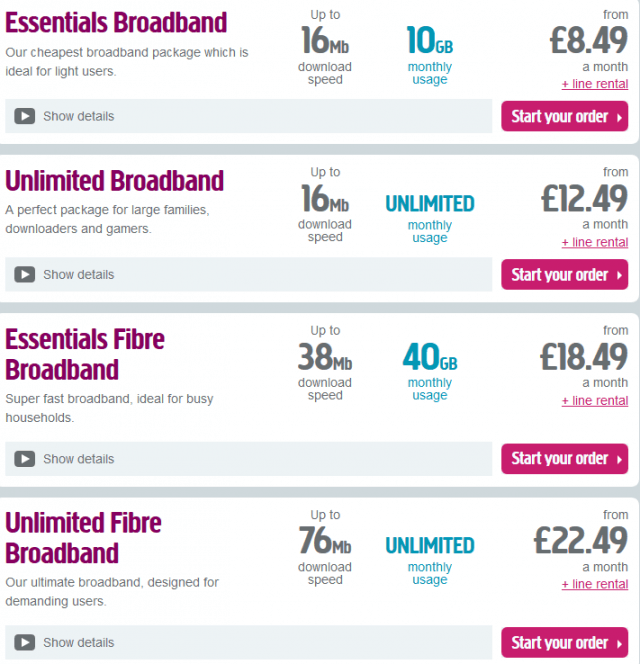
Plusnet offers DSL and fiber broadband plans (in some areas) that offer budget-priced capped or unlimited use plans.
While North American cable and phone broadband providers are among the most-hated companies on the continent, in the United Kingdom, customers gave generally high scores to their Internet providers.
PC Advisor partnered with Broadband Genie, an impartial, independent, and consumer-focused commercial broadband comparison service. Together they engaged an independent survey company (OnPoll) to survey 3,000 broadband users, chosen at random, in late 2013 and early 2014. They asked those users how happy they were with their ISP, tested the speed and reliability of their connections, and found out other valuable tidbits, such as how much they were paying, and for what exactly. Altogether, more than 10,000 U.K. broadband users contributed to the data that made an in-depth assessment of British broadband possible.
The results might stun those on the other side of the Atlantic. Unlike in Canada and the U.S., British broadband users are satisfied overall with their providers, and are enthusiastic about recommending many of them to others. Even the worst-performing provider – BE – still had a 46% recommendation rating, and the company was sold to BSkyB well over a year ago and is in the process of being merged with Sky’s broadband service.
Around 68 percent of British broadband users responding still rely primarily on various flavors of DSL for Internet service. But BT, the national telephone company, is in the process of upgrading facilities and dramatically increasing the amount of fiber optics in its network. The result is what the Brits call “Super Fast Broadband.” Back here, we call it fiber to the neighborhood service similar to AT&T’s U-verse or Bell’s Fibe. In many cases, improved service is providing speeds much closer to 25Mbps vs. the 1-6Mbps many customers used to receive. The upgrade is an important development, especially in rural Britain, often left without Internet access.
Cable broadband is much more common in North American than in the United Kingdom. While cable television became dominant here, the British favored small satellite dishes like those used by DirecTV or Dish customers. With BT dominating wired infrastructure, the government required the company to open its landline network to third-party providers. Some cable companies do exist in England, but they hold only a 12% broadband market share, even lower than fiber to the home service now at nearly 20%.
Great Britain treats broadband as a national priority, and although the current government has controversially settled for a hybrid fiber-copper network instead of delivering fiber straight to every British home, it’s a considerable improvement over what came before, especially in rural areas. Usage caps that used to dominate British broadband plans are now an option for the budget-minded. Unlimited use plans are becoming more mainstream.
With all the upgrade activity and improved service, the Brits have gotten optimistic about their broadband future. Only 12% of those surveyed loathe their broadband supplier. Another 20% were neutral about recommending their ISP, but 51% considered themselves satisfied and another 17% considered their provider top rate. Many in Britain even expect their Internet bill will decrease in 2014, and compared with North American prices, it’s often very low already.
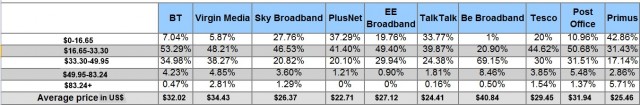
The average price paid by customers of various British ISPs (excluding line rental)
Average speed received by customers varies depending on the technology. Virgin operates cable broadband, Plusnet uses a mix of DSL and fiber, while the slower performers are primarily ADSL.
Average speed test results per ISP (kbps)
- Virgin: 27,266

Was top-rated for broadband reliability.
- Plusnet: 24,529
- BT: 13,164
- TalkTalk: 6,910
- EE: 6,818
- Demon: 6,586
- Sky: 5,942
- Eclipse: 5,786
- O2: 5,642
- Be: 5,458
- AOL: 3,809
- Post Office: 3,255
Overall ratings and reviews from PC Advisor found Virgin Media (cable) and Plusnet (DSL/Fiber) near tied for top ratings.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/PC Advisor Best cheapest fastest broadband UK ISPs rated 2-19-14.mp4[/flv]
PC Advisor talks about this year’s British ISP review, which reveals Brits are generally satisfied with their broadband speeds and pricing. (3:51)
 A Utah federal district court judge has found Aereo in violation of federal copyright law and must end online streaming of over the air television stations to customers within his jurisdiction, which includes Utah, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Wyoming and Oklahoma.
A Utah federal district court judge has found Aereo in violation of federal copyright law and must end online streaming of over the air television stations to customers within his jurisdiction, which includes Utah, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Wyoming and Oklahoma.

 Subscribe
Subscribe


 China’s top economic planning agency is assessing a monopoly case involving two large telecom companies and will make a ruling soon as the Beijing government declares uncompetitive broadband against the interests of the people.
China’s top economic planning agency is assessing a monopoly case involving two large telecom companies and will make a ruling soon as the Beijing government declares uncompetitive broadband against the interests of the people.
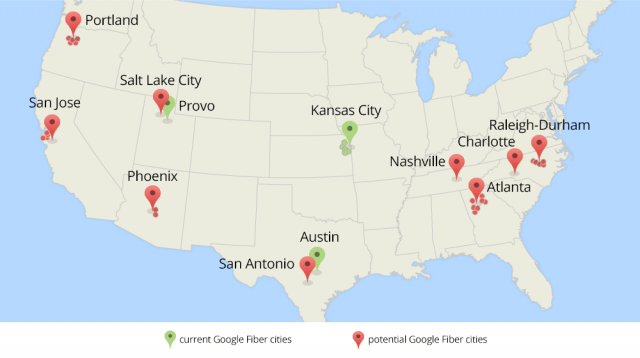
 Now that we’ve learned a lot from our Google Fiber projects in
Now that we’ve learned a lot from our Google Fiber projects in 