
AT&T U-verse cabinets attract unsightly trash and graffiti in San Francisco.
After a unanimous vote by San Francisco’s Board of Supervisors further restricting AT&T’s U-verse above-ground cabinets and extending the public a larger say about their placement, AT&T filed suit in San Francisco Superior Court claiming the company’s rights have been violated.
In 2011, supervisors voted 6-5 in a controversial decision to let AT&T install up to 726 metal cabinets in the city, connecting AT&T’s fiber network to existing copper telephone wiring. Since that vote, AT&T has installed almost 200 boxes that are supposed to avoid blocking pedestrian travel, curbs or fire hydrants and are kept away from street corners. But after the city received hundreds of complaints — mostly about pervasive graffiti — AT&T suspects the city intentionally slowed approval of more boxes.
AT&T’s lawsuit specifies the city has denied permits for 26 of the boxes since November without offering alternate locations. AT&T also accuses San Francisco of taking more than 60 days to approve or reject another 67 permit requests.
The last straw seems to have been the unanimous passage of a bill introduced by Supervisor Scott Wiener giving more weight to public comments about the cabinets. The new policy also requires AT&T to propose multiple locations on permit applications, preferably not on main thoroughfares, as well as requiring AT&T to install graffiti-resistant boxes.
San Francisco’s 311 hotline has processed hundreds of complaints showing repeated graffiti attacks on AT&T’s boxes. In many cases, AT&T has not directly responded to the city regarding the complaints, although most have been addressed eventually.

AT&T says any further restrictions on its U-verse expansion, including public input, violate state law.
In most states, so long as AT&T confines its box installations to the public utility easement, it can choose locations for its boxes without consultation.
In some states, particularly North Carolina, this has resulted in large 4-foot tall, unsightly lawn cabinets appearing in the front yards of residential homes. In several instances, multiple cabinets are installed side-by-side and are protected from traffic by nearby bollards that further extend the equipment’s footprint.
“The U-verse boxes are always placed adjacent to or across the street from an existing interconnect box,” notes San Francisco resident Bryce Nesbitt. “AT&T has chosen not to invest in a combined box that would reduce impact on the public realm. One slightly larger interconnect box could take the functions of the dual interconnect/VRAD solution AT&T is pushing everyone to accept.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe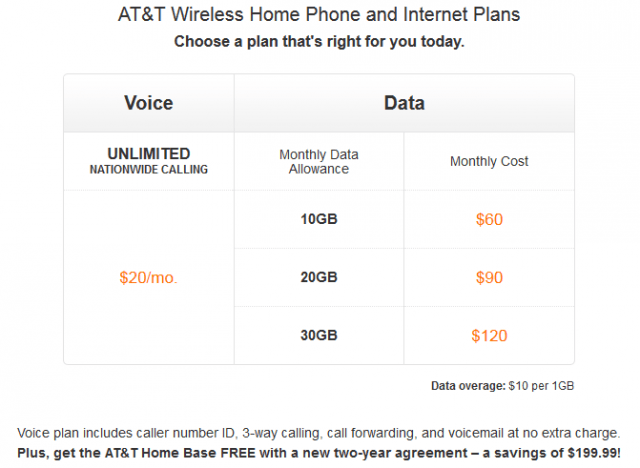

 The New York Times
The New York Times 
 Lobbyists like Gray used astroturf tactics to mobilize various unaffiliated non-profit groups to write glowing letters in support of consolidating Sirius and XM Radio, usually in return for generous contributions. It is likely to be more of the same with this merger.
Lobbyists like Gray used astroturf tactics to mobilize various unaffiliated non-profit groups to write glowing letters in support of consolidating Sirius and XM Radio, usually in return for generous contributions. It is likely to be more of the same with this merger.
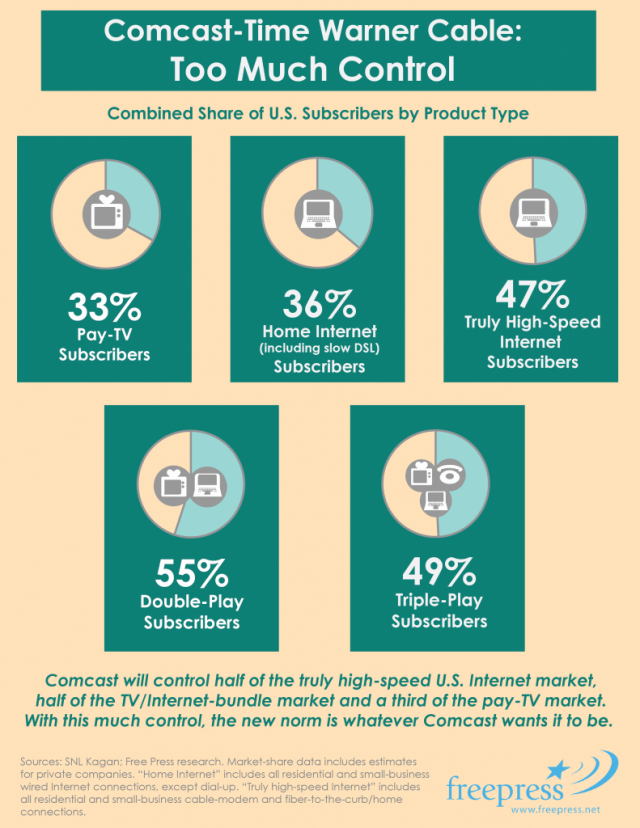
 Stop the Cap! has talked with more than a dozen customers in Comcast’s test markets about their experiences with Comcast’s “data usage policy.” Although the company claims it is seeking customer reactions, it never asks whether those customers want usage limits or not, only what kind.
Stop the Cap! has talked with more than a dozen customers in Comcast’s test markets about their experiences with Comcast’s “data usage policy.” Although the company claims it is seeking customer reactions, it never asks whether those customers want usage limits or not, only what kind.